Adverse Health Effects Explained
Introduction to Adverse Health Effects

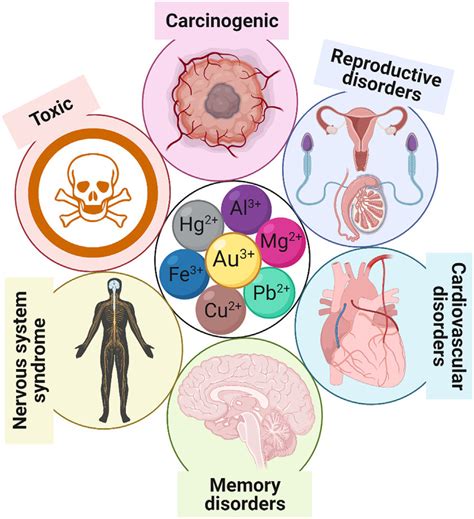
Adverse health effects refer to the unwanted and harmful consequences that certain substances, environments, or actions can have on human health. These effects can range from mild symptoms such as headaches or nausea to severe conditions like cancer or neurological damage. Understanding the causes and consequences of adverse health effects is crucial for preventing and mitigating their impact on individuals and communities.
Types of Adverse Health Effects

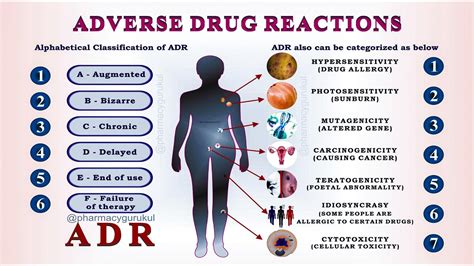
There are various types of adverse health effects, including: * Acute effects: These occur immediately or shortly after exposure to a harmful substance or environment. Examples include chemical burns or respiratory distress from inhaling toxic fumes. * Chronic effects: These develop over a longer period, sometimes years or decades after initial exposure. Examples include cancer from asbestos exposure or neurological damage from prolonged exposure to pesticides. * Genotoxic effects: These involve damage to an individual’s DNA, which can lead to genetic mutations and increased risk of cancer or other diseases. * Epigenetic effects: These involve changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself, which can also have long-term health consequences.
Causes of Adverse Health Effects
Adverse health effects can be caused by a wide range of factors, including: * Environmental pollutants: Such as air pollution, water contamination, or exposure to toxic chemicals. * Occupational hazards: Such as inhalation of dust or fumes in the workplace, or exposure to loud noises. * Lifestyle choices: Such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or poor diet. * Medical treatments: Such as adverse reactions to medications or complications from surgical procedures.
Examples of Adverse Health Effects
Some notable examples of adverse health effects include: * Asbestos-related diseases: Such as mesothelioma, lung cancer, or asbestosis, which can result from inhalation of asbestos fibers. * Lead poisoning: Which can cause developmental delays, neurological damage, or organ damage, particularly in children. * Smoking-related illnesses: Such as lung cancer, heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). * Adverse reactions to medications: Such as allergic reactions, overdoses, or interactions with other medications.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
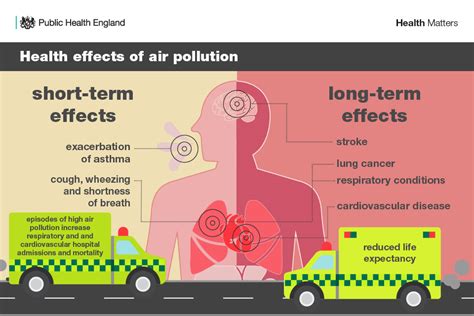
To prevent or mitigate adverse health effects, individuals and communities can take several steps: * Avoid exposure to harmful substances: Such as quitting smoking, using protective equipment in the workplace, or reducing exposure to environmental pollutants. * Follow safety guidelines: Such as wearing seatbelts, using sunscreen, or following proper food handling procedures. * Get regular health check-ups: To monitor health status and detect potential problems early. * Support policies and initiatives: That promote public health and safety, such as clean air and water regulations, or occupational safety standards.
🚨 Note: It is essential to be aware of the potential risks and take proactive steps to prevent or minimize adverse health effects.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are crucial for understanding and addressing adverse health effects. This includes: * Identifying new risk factors: Such as emerging environmental pollutants or previously unknown health hazards. * Developing new treatments and interventions: Such as medications, therapies, or technologies that can help prevent or mitigate adverse health effects. * Improving public health policies and regulations: To better protect individuals and communities from adverse health effects.
| Substance/Environment | Adverse Health Effect | Prevention/Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Asbestos | Lung cancer, mesothelioma | Avoid exposure, use protective equipment |
| Lead | Developmental delays, neurological damage | Reduce exposure, use lead-free products |
| Tobacco smoke | Lung cancer, heart disease | Quit smoking, avoid secondhand smoke |

In summary, adverse health effects are a significant concern for individuals and communities worldwide. By understanding the causes and consequences of these effects, and taking proactive steps to prevent or mitigate them, we can work towards creating a healthier and safer environment for everyone. The key takeaways from this discussion include the importance of avoiding exposure to harmful substances, following safety guidelines, and supporting policies and initiatives that promote public health and safety. By working together, we can reduce the burden of adverse health effects and promote a healthier future for all.
What are adverse health effects?
+
Adverse health effects refer to the unwanted and harmful consequences that certain substances, environments, or actions can have on human health.
How can I prevent adverse health effects?

+
To prevent adverse health effects, individuals can take several steps, including avoiding exposure to harmful substances, following safety guidelines, and getting regular health check-ups.
What are some common examples of adverse health effects?
+
Some notable examples of adverse health effects include asbestos-related diseases, lead poisoning, smoking-related illnesses, and adverse reactions to medications.
Related Terms:
- Adverse health effects synonym
- Health effects examples
- Health effects meaning
- Effect health or affect health
- Effects of health issues
- Adverse effect examples



