Health
Adverse Health Effects Exposure

Introduction to Adverse Health Effects of Exposure

Exposure to harmful substances, environments, or situations can have severe and long-lasting effects on human health. The term “adverse health effects” refers to the negative consequences that occur when an individual is exposed to a harmful agent or condition. These effects can range from mild and temporary to severe and permanent, depending on the nature and duration of the exposure. Understanding the causes, mechanisms, and consequences of adverse health effects is crucial for preventing, diagnosing, and treating exposure-related illnesses.
Types of Adverse Health Effects

Adverse health effects can be categorized into several types, including: * Acute effects: These occur immediately or shortly after exposure and can include symptoms such as nausea, headaches, and respiratory problems. * Chronic effects: These develop over a longer period, often years or decades, and can include conditions such as cancer, neurological damage, and reproductive problems. * Systemic effects: These affect multiple organ systems and can include conditions such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and immune system suppression. * Local effects: These are limited to a specific area or organ and can include conditions such as skin irritation, eye damage, and respiratory problems.
Causes of Adverse Health Effects
Adverse health effects can be caused by a wide range of factors, including: * Chemical exposure: Exposure to toxic chemicals, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants, can cause a range of health problems. * Physical agents: Exposure to physical agents, such as radiation, noise, and extreme temperatures, can also cause adverse health effects. * Biological agents: Exposure to biological agents, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause infections and other health problems. * Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental factors, such as air pollution, water pollution, and poor housing conditions, can also contribute to adverse health effects.
Examples of Adverse Health Effects
Some examples of adverse health effects include: * Cancer: Exposure to carcinogenic chemicals, radiation, and other agents can increase the risk of developing cancer. * Neurological damage: Exposure to neurotoxic chemicals, such as lead and mercury, can cause neurological damage and developmental problems. * Respiratory problems: Exposure to air pollutants, such as particulate matter and ozone, can cause respiratory problems, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). * Reproductive problems: Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, can cause reproductive problems, including birth defects and infertility.
Prevention and Mitigation of Adverse Health Effects
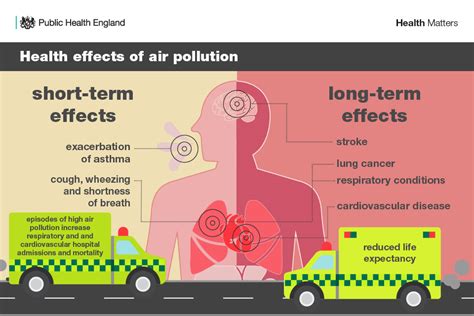
Preventing and mitigating adverse health effects requires a multi-faceted approach that includes: * Risk assessment: Identifying and assessing the risks associated with exposure to harmful agents or conditions. * Risk management: Implementing measures to reduce or eliminate exposure to harmful agents or conditions. * Personal protective equipment: Using personal protective equipment, such as masks and gloves, to reduce exposure to harmful agents. * Environmental remediation: Cleaning up contaminated environments to reduce exposure to harmful agents.
🚨 Note: Preventing adverse health effects requires a proactive approach that involves individuals, communities, and governments working together to reduce exposure to harmful agents and conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Adverse Health Effects
Diagnosing and treating adverse health effects requires a comprehensive approach that includes: * Medical evaluation: Evaluating the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and exposure history to determine the cause of the adverse health effect. * Laboratory testing: Conducting laboratory tests, such as blood and urine tests, to detect exposure to harmful agents. * Medical treatment: Providing medical treatment, such as medication and surgery, to manage the adverse health effect. * Rehabilitation: Providing rehabilitation services, such as physical and occupational therapy, to help the individual recover from the adverse health effect.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, adverse health effects of exposure are a significant public health concern that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By understanding the causes, mechanisms, and consequences of adverse health effects, we can work towards reducing the burden of exposure-related illnesses and promoting healthier environments and communities. Future directions for research and practice include developing more effective methods for preventing and mitigating adverse health effects, improving diagnosis and treatment options, and promoting policies and practices that prioritize environmental health and safety.
What are the most common causes of adverse health effects?
+
The most common causes of adverse health effects include chemical exposure, physical agents, biological agents, and environmental factors.
How can I reduce my risk of adverse health effects?
+
You can reduce your risk of adverse health effects by avoiding exposure to harmful agents, using personal protective equipment, and promoting environmental health and safety practices.
What are the long-term consequences of adverse health effects?

+
The long-term consequences of adverse health effects can include chronic diseases, neurological damage, reproductive problems, and increased risk of cancer and other illnesses.
Related Terms:
- Adverse health effects synonym
- Health effects examples
- Health effects meaning
- Effect health or affect health
- Effects of health issues
- Adverse effect examples



