5 Air Force Ranks
Introduction to Air Force Ranks
The Air Force is one of the most prestigious and respected branches of the military, with a rich history and a wide range of career opportunities. One of the key aspects of the Air Force is its ranking system, which is used to denote an individual’s level of experience, responsibility, and authority. In this article, we will explore five key Air Force ranks, including their responsibilities, requirements, and benefits.
Airman Basic (AB)
The first rank we will discuss is Airman Basic (AB), which is the most junior rank in the Air Force. Airman Basic is the entry-level rank for new recruits, and it is typically held by individuals who are in the process of completing their basic training. The primary responsibility of an Airman Basic is to learn and follow orders, as well as to complete their training and education requirements. To become an Airman Basic, an individual must meet the Air Force’s basic eligibility requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 39, and meeting certain physical and mental standards.
Airman (AMN)
The next rank is Airman (AMN), which is the first rank that an individual can attain after completing their basic training. Airmen are typically assigned to a specific job or career field, and they are responsible for performing their duties to the best of their ability. To become an Airman, an individual must complete their basic training and meet certain performance and evaluation requirements. Airmen are also eligible for certain benefits, including education assistance and housing allowances.
Airman First Class (A1C)
The third rank we will discuss is Airman First Class (A1C), which is a junior enlisted rank that is typically held by individuals who have completed their initial training and have gained some experience in their career field. Airmen First Class are responsible for performing their duties with a high level of proficiency, as well as for mentoring and training junior airmen. To become an Airman First Class, an individual must meet certain time-in-service and performance requirements, and they must also complete a series of evaluations and assessments.
Senior Airman (SrA)
The fourth rank is Senior Airman (SrA), which is a mid-level enlisted rank that is typically held by individuals who have gained significant experience and expertise in their career field. Senior Airmen are responsible for leading and mentoring teams of airmen, as well as for performing complex and critical tasks. To become a Senior Airman, an individual must meet certain time-in-service and performance requirements, and they must also complete a series of evaluations and assessments.
Staff Sergeant (SSgt)
The final rank we will discuss is Staff Sergeant (SSgt), which is a senior enlisted rank that is typically held by individuals who have gained significant experience and expertise in their career field. Staff Sergeants are responsible for leading and managing teams of airmen, as well as for performing critical and complex tasks. To become a Staff Sergeant, an individual must meet certain time-in-service and performance requirements, and they must also complete a series of evaluations and assessments.
🚀 Note: The requirements and benefits for each rank may vary depending on the individual's career field and other factors.
In terms of benefits, the Air Force offers a wide range of perks and incentives to its airmen, including: * Competitive pay and allowances * Comprehensive health and dental insurance * Education assistance and tuition reimbursement * Housing allowances and on-base housing * Access to on-base facilities and amenities * Opportunities for advancement and career development
Here is a summary of the five Air Force ranks we discussed:
| Rank | Responsibilities | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Airman Basic (AB) | Learn and follow orders, complete basic training | Meet basic eligibility requirements |
| Airman (AMN) | Perform duties to the best of their ability, complete job training | Complete basic training, meet performance requirements |
| Airman First Class (A1C) | Perform duties with a high level of proficiency, mentor junior airmen | Meet time-in-service and performance requirements |
| Senior Airman (SrA) | Lead and mentor teams, perform complex tasks | Meet time-in-service and performance requirements |
| Staff Sergeant (SSgt) | Lead and manage teams, perform critical tasks | Meet time-in-service and performance requirements |
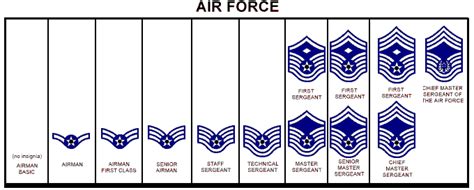
To summarize, the Air Force offers a wide range of career opportunities and benefits to its airmen, and its ranking system is designed to recognize and reward individual achievement and expertise. Whether you are just starting out as an Airman Basic or are a seasoned Staff Sergeant, the Air Force has something to offer everyone.
What are the benefits of joining the Air Force?
+
The Air Force offers a wide range of benefits, including competitive pay and allowances, comprehensive health and dental insurance, education assistance, and access to on-base facilities and amenities.
How do I become an Airman Basic?
+
To become an Airman Basic, you must meet the Air Force’s basic eligibility requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 39, and meeting certain physical and mental standards.
What is the difference between an Airman and an Airman First Class?
+
An Airman is typically assigned to a specific job or career field, while an Airman First Class has gained some experience and expertise in their career field and is responsible for mentoring and training junior airmen.
Related Terms:
- saf ia org chart
- air force secretariat org chart
- a2 6 org chart
- headquarters air force organizational chart
- air force squadron organization chart
- air force organization chart 2024



