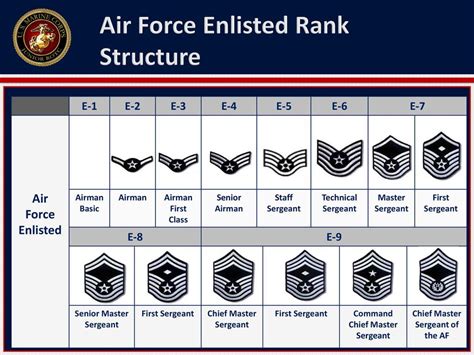
5 Air Force Ranks
Introduction to Air Force Ranks
The Air Force, a vital branch of the military, is structured with a hierarchy of ranks that define the roles, responsibilities, and chain of command. Understanding these ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the Air Force or simply wanting to learn more about its organizational structure. In this article, we will delve into the details of five key Air Force ranks, exploring their duties, requirements, and the significance of each within the Air Force’s operational framework.
1. Airman Basic (AB)

The Airman Basic (AB) is the most junior rank in the Air Force. It is the rank at which all new recruits begin their career. Individuals holding this rank are typically in the initial stages of their training, learning the basics of the Air Force way of life, including its values, traditions, and job-specific skills. The primary focus for an Airman Basic is to learn and adapt to the military environment, preparing themselves for the responsibilities that come with higher ranks.
2. Airman (AMN)
After completing basic training and technical school, an Airman Basic is usually promoted to Airman (AMN). This rank signifies that the individual has begun their job-specific training and is applying the skills learned in their technical school to real-world situations. Airmen are still considered to be in the early stages of their careers but are taking on more responsibilities within their units. They are expected to continue learning, growing, and developing their skills to prepare for future leadership roles.
3. Airman First Class (A1C)
The rank of Airman First Class (A1C) is the first rank where airmen are considered to be fully trained and qualified in their job specialty. A1Cs have gained experience and are taking on more significant roles within their units, including leadership positions. They are expected to mentor junior airmen, contributing to the development of their colleagues. This rank is a milestone, marking the transition from initial training to becoming a skilled and integral part of the Air Force team.
4. Senior Airman (SrA)
Senior Airman (SrA) is a rank that signifies a higher level of expertise and leadership. Senior Airmen have typically been in the Air Force for several years and have honed their skills to become specialists in their field. They are often tasked with supervisory roles, overseeing the work of junior airmen and ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and effectively. Senior Airmen are also expected to continue their education and training, preparing themselves for the challenges of higher ranks.
5. Staff Sergeant (SSgt)
The rank of Staff Sergeant (SSgt) marks a significant step into non-commissioned officer (NCO) leadership. Staff Sergeants are seasoned professionals with extensive experience and a deep understanding of their job and the Air Force as a whole. They are responsible for leading teams, making critical decisions, and mentoring junior NCOs. This rank requires strong leadership skills, the ability to manage complex situations, and a commitment to the development of their team members. Staff Sergeants play a crucial role in the day-to-day operations of the Air Force, serving as a link between junior personnel and senior leadership.
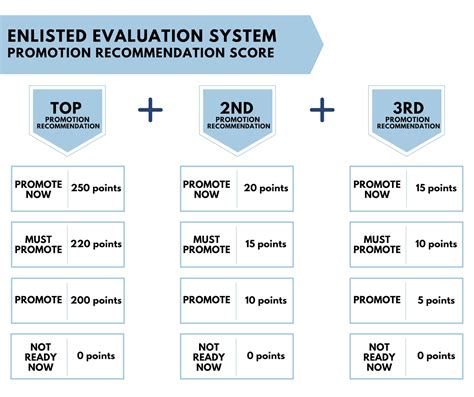
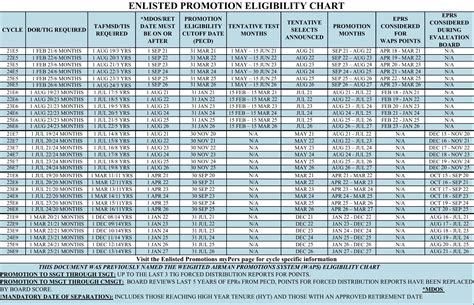
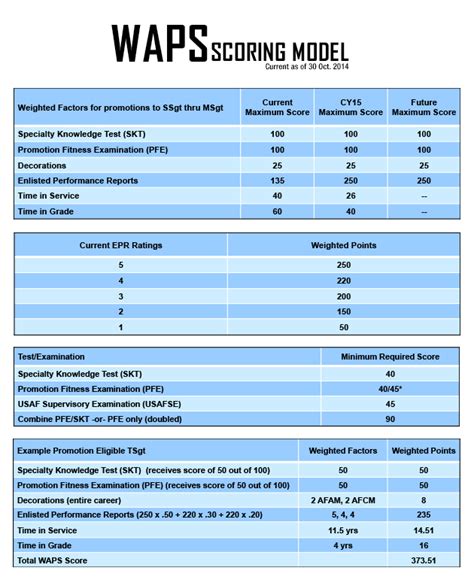
🚀 Note: Advancement through these ranks is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and completion of professional military education. Each rank brings new challenges and opportunities for growth and development.
In summary, the structure of Air Force ranks is designed to promote a culture of learning, leadership, and service. From the initial rank of Airman Basic to the more senior rank of Staff Sergeant, each step in the hierarchy represents a progression in responsibility, skill, and leadership ability. Understanding these ranks and their roles within the Air Force provides insight into the organization’s operational efficiency and its commitment to developing its personnel.
What is the starting rank in the Air Force?
+
The starting rank in the Air Force is Airman Basic (AB), which is the most junior rank and the entry point for all new recruits.
How long does it typically take to advance through the ranks?

+
Advancement through the ranks in the Air Force is based on performance, time in service, and completion of certain educational and training requirements. The time it takes to advance can vary significantly from one individual to another.
What are the responsibilities of a Staff Sergeant?
+
A Staff Sergeant is a non-commissioned officer who leads teams, makes critical decisions, and mentors junior personnel. They are responsible for the development and supervision of their team members and play a key role in the operational success of their unit.
Related Terms:
- waps calculator 2024
- air force rank calculator promotion
- btz calculator 6 year
- below the zone calculator
- air force enlisted promotion calculator
- btz eligibility chart



