5 Health Survey Tips

Introduction to Health Surveys
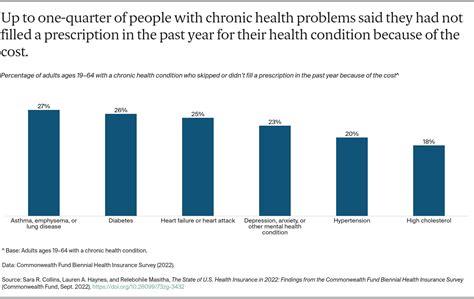
Conducting health surveys is a crucial aspect of understanding the health needs and trends within a community or population. These surveys can provide valuable insights into the prevalence of certain health conditions, the effectiveness of healthcare services, and the impact of health policies. However, designing and implementing an effective health survey requires careful planning and consideration of several key factors. In this article, we will discuss five essential tips for conducting successful health surveys, focusing on aspects such as survey design, participant selection, data collection methods, data analysis, and ethical considerations.
Tip 1: Clear Survey Design

A well-designed survey is fundamental to collecting meaningful and relevant data. This involves clearly defining the survey objectives, identifying the target population, and developing questions that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The survey questions should be concise, easy to understand, and free from bias to ensure that participants can provide accurate and reliable responses. Additionally, pilot-testing the survey with a small group of participants can help identify any issues or ambiguities in the questions, allowing for necessary adjustments before the full-scale implementation.
Tip 2: Appropriate Participant Selection
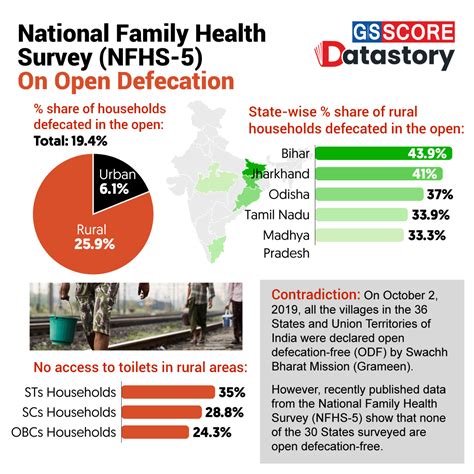
Selecting the right participants for the health survey is critical for ensuring that the data collected is representative of the population of interest. This involves identifying the inclusion and exclusion criteria for participants, such as age, gender, health status, or geographical location. The sampling method used should also be carefully considered, with options including random sampling, stratified sampling, or convenience sampling, each with its own advantages and limitations. Ensuring participant diversity can help in generalizing the survey findings to the broader population.
Tip 3: Effective Data Collection Methods

The method of data collection can significantly impact the response rate and the quality of the data collected. Common methods include online surveys, paper-based surveys, telephone interviews, and face-to-face interviews. The choice of method depends on the target population, the complexity of the survey questions, and the resources available. For instance, online surveys can be cost-effective and reach a wide audience, but may not be suitable for populations with limited access to technology. Mixed-mode surveys, which combine multiple data collection methods, can offer flexibility and increase response rates.
Tip 4: Robust Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the next crucial step is analyzing it to draw meaningful conclusions. This involves using appropriate statistical methods to describe the sample characteristics, identify trends, and test hypotheses. Data analysis should also consider the potential biases and limitations of the survey, such as non-response bias or social desirability bias. Furthermore, presenting the findings in a clear and understandable manner, using tables, figures, and graphs, can facilitate the interpretation of the results for both technical and non-technical audiences.
Tip 5: Ethical Considerations

Lastly, ethical considerations are paramount in health surveys to protect the rights and welfare of the participants. This includes obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring the confidentiality and anonymity of the data, and avoiding any potential harm or distress. Survey designers must also be mindful of cultural sensitivities and ensure that the survey questions and methods are respectful and appropriate for the target population. Compliance with relevant regulatory requirements, such as those related to data protection, is also essential.
📝 Note: Ensuring the ethical integrity of health surveys not only complies with legal and regulatory standards but also fosters trust among participants and contributes to the overall validity of the survey findings.
In essence, conducting a successful health survey requires a meticulous approach that considers all aspects from design to ethical considerations. By following these five tips, researchers and healthcare professionals can gather high-quality data that informs healthcare decisions, policy developments, and future research directions. Ultimately, the goal of health surveys is to improve health outcomes and the quality of life for individuals and communities, and achieving this goal depends on the rigor and thoughtfulness with which these surveys are designed and implemented.
What is the primary purpose of conducting health surveys?

+
The primary purpose of conducting health surveys is to understand the health needs, trends, and outcomes within a population, which can inform healthcare decisions, policy developments, and future research directions.
How can the quality of data collected in health surveys be ensured?

+
The quality of data can be ensured by using clear and unbiased survey questions, selecting an appropriate sample of participants, using effective data collection methods, and conducting robust data analysis while considering potential biases and limitations.
What are some common data collection methods used in health surveys?
+
Common data collection methods include online surveys, paper-based surveys, telephone interviews, and face-to-face interviews. The choice of method depends on the target population and the resources available.
Related Terms:
- Annual Health Survey 2022
- AHS survey
- national family health survey latest
- annual health survey report
- nfhs fact sheet
- te whatu ora tier 1



