Army Officer Rank Chart Guide
Introduction to Army Officer Ranks

The army officer rank structure is a complex system that defines the roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority within the military. Understanding the different ranks and their corresponding insignia, duties, and requirements is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career as an army officer. In this guide, we will delve into the world of army officer ranks, exploring the various levels, from the lowest to the highest, and discussing the key aspects of each.
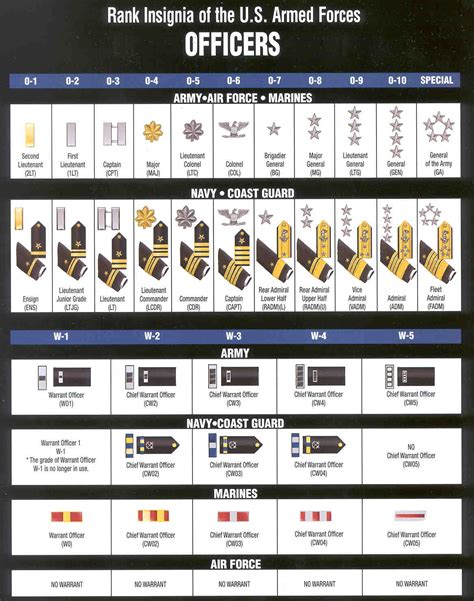
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officers are the leaders of the army, responsible for making strategic decisions, leading troops, and overseeing operations. The commissioned officer ranks are divided into several categories, including company grade, field grade, and general officers.
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The entry-level commissioned officer rank, typically held by new officers upon graduation from officer training.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A junior officer rank, often serving as a platoon leader or executive officer.
- Captain (CPT): A company-grade officer rank, responsible for commanding a company or serving as a staff officer.
- Major (MAJ): A field-grade officer rank, often serving as an executive officer or battalion staff officer.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A senior field-grade officer rank, responsible for commanding a battalion or serving as a brigade staff officer.
- Colonel (COL): A senior officer rank, often serving as a brigade commander or division staff officer.
General Officer Ranks
General officers are the highest-ranking officers in the army, responsible for making strategic decisions and leading large formations. The general officer ranks include:
- Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer rank, often serving as a brigade commander or division staff officer.
- Major General (MG): A two-star general officer rank, responsible for commanding a division or serving as a corps staff officer.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer rank, often serving as a corps commander or army staff officer.
- General (GEN): A four-star general officer rank, the highest rank in the army, responsible for leading the entire army or serving as a joint chiefs of staff member.
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts who serve in specialized roles, providing critical support to the army. The warrant officer ranks include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The entry-level warrant officer rank, typically held by new warrant officers upon completion of training.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A junior warrant officer rank, often serving as a technical expert or advisor.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer rank, responsible for leading teams or serving as a senior technical expert.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A master warrant officer rank, often serving as a senior leader or technical expert.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest warrant officer rank, responsible for leading warrant officer teams or serving as a senior technical advisor.
Officer Rank Insignia

Each officer rank has a unique insignia, worn on the uniform to indicate the officer’s rank and branch. The insignia typically consists of a combination of bars, oak leaves, and stars, which are used to distinguish between the different ranks.
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Second Lieutenant | Single gold bar |
| First Lieutenant | Single silver bar |
| Captain | Two silver bars |
| Major | Gold oak leaf |
| Lieutenant Colonel | Silver oak leaf |
| Colonel | Eagle |
| Brigadier General | One star |
| Major General | Two stars |
| Lieutenant General | Three stars |
| General | Four stars |
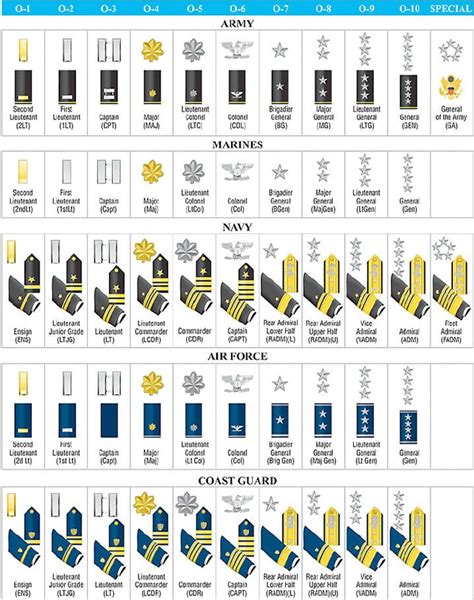
📝 Note: The insignia may vary depending on the branch and uniform.
Key Takeaways
In summary, the army officer rank structure is a complex system that defines the roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority within the military. Understanding the different ranks, their corresponding insignia, duties, and requirements is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career as an army officer. Whether you’re a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, knowing the ranks and their significance is crucial for success in the army.
As we reflect on the various ranks and their responsibilities, it’s clear that each role plays a vital part in the army’s overall mission. From the junior officers to the senior leaders, every rank requires a unique set of skills, knowledge, and experience. By understanding the army officer rank structure, individuals can better navigate their careers, make informed decisions, and strive for excellence in their chosen profession.
In the end, the army officer rank structure is a testament to the army’s commitment to excellence, leadership, and service. By recognizing the importance of each rank and the contributions of every officer, we can appreciate the dedication, sacrifice, and bravery that define the army’s finest leaders.
What is the highest rank in the army?

+
The highest rank in the army is General (GEN), a four-star general officer rank.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?

+
Commissioned officers are leaders who hold a commission from the President, while warrant officers are technical experts who serve in specialized roles.
How do officers progress through the ranks?
+
Officers progress through the ranks based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance, education, and training.
Related Terms:
- military ranks cheat sheet
- army rank cheat sheet
- navy ranks chart printable
- air force rank cheat sheet
- is supervisor higher than lieutenant
- printable army rank chart



