5 Ways To Join Army

Introduction to Joining the Army

Joining the army can be a rewarding and challenging career path for those who are interested in serving their country. There are several ways to join the army, and the process can vary depending on the country and the individual’s qualifications. In this article, we will explore five ways to join the army and provide information on the requirements and benefits of each path.
Method 1: Enlisting as a Recruit

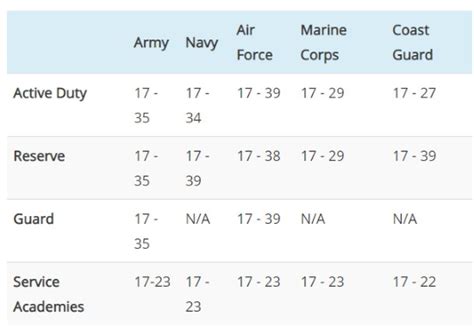
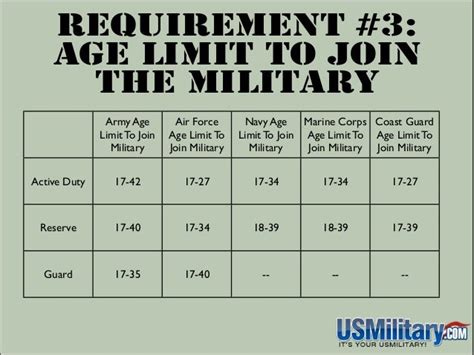
The most common way to join the army is by enlisting as a recruit. This involves meeting the basic requirements, such as being a citizen of the country, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. Recruits will undergo basic training, which includes physical fitness, combat skills, and military protocol. After completing basic training, recruits will attend advanced individual training (AIT) to learn a specific job skill. Enlisting as a recruit is a great way to start a career in the army and can lead to advancement opportunities and specialized training.
Method 2: Joining as an Officer
Another way to join the army is by becoming an officer. Officers are leaders in the army and are responsible for making decisions and giving orders. To become an officer, individuals must meet certain requirements, such as having a bachelor’s degree, being a citizen of the country, and passing a physical fitness test. Officers will attend officer candidate school (OCS) or a similar program to learn leadership skills and military protocol. Joining as an officer can provide a higher level of responsibility and pay, but also requires a greater level of commitment and education.
Method 3: Joining the Army Reserve or National Guard

The army reserve and national guard are part-time military organizations that allow individuals to serve their country while also pursuing a civilian career. To join the army reserve or national guard, individuals must meet the basic requirements, such as being a citizen of the country and having a high school diploma or equivalent. Members of the army reserve and national guard will attend basic training and AIT, but will only serve part-time. Joining the army reserve or national guard can provide a flexible way to serve the country and can also provide education and training benefits.
Method 4: Joining through a Military Academy

For individuals who are interested in pursuing a higher education while also serving their country, joining a military academy can be a great option. Military academies, such as West Point, provide a free education in exchange for a commitment to serve in the army after graduation. To join a military academy, individuals must meet certain requirements, such as being a citizen of the country, having a high school diploma or equivalent, and passing a physical fitness test. Joining a military academy can provide a unique and challenging educational experience, but also requires a greater level of commitment and discipline.
Method 5: Joining through a Direct Commission

Finally, individuals with specialized skills or experience can join the army through a direct commission. This involves being commissioned as an officer without having to attend officer candidate school. To join through a direct commission, individuals must meet certain requirements, such as having a bachelor’s degree, being a citizen of the country, and having relevant work experience. Joining through a direct commission can provide a way for individuals with specialized skills to serve their country and can also provide a higher level of pay and responsibility.
💡 Note: The requirements and benefits of each method may vary depending on the country and the individual's qualifications. It's essential to research and understand the specific requirements and benefits of each path before making a decision.
In terms of the benefits of joining the army, some of the most significant advantages include: * Education and training benefits: The army provides a wide range of education and training opportunities, including tuition assistance, vocational training, and leadership development. * Career advancement opportunities: The army provides a clear path for career advancement, with opportunities for promotion and specialized training. * Health and wellness benefits: The army provides comprehensive health and wellness benefits, including medical, dental, and vision coverage. * Travel opportunities: The army provides opportunities for travel and exploration, both within the country and abroad. * Camaraderie and esprit de corps: The army provides a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, with a strong emphasis on teamwork and unity.
The following table summarizes the five ways to join the army:
| Method | Requirements | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Enlisting as a Recruit | Basic requirements, such as citizenship and high school diploma | Education and training benefits, career advancement opportunities |
| Joining as an Officer | Bachelor’s degree, citizenship, physical fitness test | Higher level of responsibility and pay, leadership development |
| Joining the Army Reserve or National Guard | Basic requirements, such as citizenship and high school diploma | Flexible way to serve the country, education and training benefits |
| Joining through a Military Academy | Citizenship, high school diploma, physical fitness test | Free education, unique and challenging educational experience |
| Joining through a Direct Commission | Bachelor’s degree, citizenship, relevant work experience | Higher level of pay and responsibility, opportunity to serve the country |

In summary, joining the army can be a rewarding and challenging career path, with a range of benefits and opportunities for advancement. Whether you’re interested in enlisting as a recruit, joining as an officer, or pursuing a different path, there are many ways to serve your country and achieve your goals. By understanding the requirements and benefits of each method, you can make an informed decision and start your journey towards a successful and fulfilling career in the army.
What are the basic requirements for joining the army?

+
The basic requirements for joining the army include being a citizen of the country, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent.
What is the difference between enlisting as a recruit and joining as an officer?

+
Enlisting as a recruit involves meeting the basic requirements and attending basic training, while joining as an officer requires a bachelor’s degree and attendance at officer candidate school.
Can I join the army if I have a criminal record?

+
It may be possible to join the army with a criminal record, but it depends on the nature of the offense and the individual’s circumstances. It’s best to consult with a recruiter or military official to determine eligibility.
What are the benefits of joining the army?
+
The benefits of joining the army include education and training benefits, career advancement opportunities, health and wellness benefits, travel opportunities, and camaraderie and esprit de corps.
Can I join the army if I’m not a citizen of the country?
+
It may be possible to join the army as a non-citizen, but it depends on the country’s policies and the individual’s circumstances. It’s best to consult with a recruiter or military official to determine eligibility.
Related Terms:
- U S Army recruitment
- join u s army
- Army Roles
- u s army foreign recruitment
- U S Marine recruitment
- U S military



