Army vs Army Reserve Differences
Introduction to Army and Army Reserve
The United States Army and the Army Reserve are two distinct components of the US military, each with its own unique role, responsibilities, and requirements. While both components are part of the US Army, they differ significantly in terms of their mission, deployment, training, and lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the differences between the Army and the Army Reserve, helping you make an informed decision about which path to choose.
Mission and Deployment

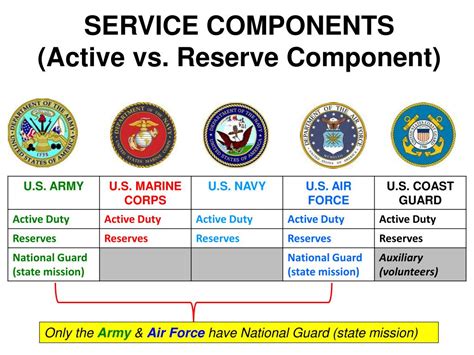
The primary mission of the US Army is to protect the country and its interests by engaging in combat operations, peacekeeping missions, and humanitarian efforts around the world. Army soldiers are full-time warriors who are deployed for extended periods, often in high-risk areas. In contrast, the Army Reserve is a part-time force that supports the US Army by providing trained units and personnel to augment active-duty forces during times of war or national emergencies. Army Reserve soldiers typically serve one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with some exceptions for deployments or training exercises.
Training and Education
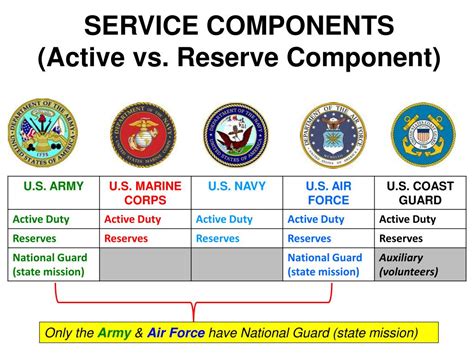
Both the Army and the Army Reserve provide comprehensive training to their soldiers, including Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT). However, Army soldiers receive more extensive training and education, including specialized courses and leadership development programs. Army Reserve soldiers, on the other hand, focus on maintaining their skills and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and tactics. The Army also offers more opportunities for education and career advancement, including tuition assistance and promotion opportunities.
Lifestyle and Benefits

The lifestyle of Army soldiers is highly demanding, with frequent deployments, long hours, and high-stress situations. Army soldiers must be willing to relocate and adapt to new environments, often with limited notice. In contrast, Army Reserve soldiers have more control over their schedules and can maintain a civilian career while serving part-time. The Army Reserve also offers competitive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance. However, Army soldiers receive more comprehensive benefits, including on-base housing, food allowances, and access to military facilities.
Enlistment and Commissioning

To join the Army, individuals must meet strict eligibility requirements, including age, education, and physical fitness standards. The enlistment process typically involves taking the ASVAB test, completing basic training, and attending advanced training courses. To join the Army Reserve, individuals must also meet eligibility requirements, but the process is less rigorous, with more flexibility in terms of training schedules and deployment commitments. Commissioned officers in both the Army and the Army Reserve must hold a bachelor’s degree and complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC).
Career Opportunities

The Army offers a wide range of career opportunities, including combat arms, support branches, and specialized fields like cybersecurity and intelligence. Army soldiers can choose from over 150 Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), with opportunities for advancement and specialized training. The Army Reserve also offers varied career paths, but with more limited opportunities for advancement and specialization. However, Army Reserve soldiers can still pursue careers in fields like medicine, engineering, and administration.
💡 Note: The Army and Army Reserve have different promotion systems, with the Army offering more opportunities for advancement and leadership development.
Summary of Key Differences

The main differences between the Army and the Army Reserve are: * Mission and deployment: The Army is a full-time force that engages in combat operations, while the Army Reserve is a part-time force that supports the US Army during times of war or national emergencies. * Training and education: The Army provides more extensive training and education, while the Army Reserve focuses on maintaining skills and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and tactics. * Lifestyle and benefits: The Army lifestyle is highly demanding, with frequent deployments and high-stress situations, while the Army Reserve offers more control over schedules and competitive benefits. * Enlistment and commissioning: The Army has stricter eligibility requirements and a more rigorous enlistment process, while the Army Reserve has more flexibility in terms of training schedules and deployment commitments. * Career opportunities: The Army offers a wide range of career opportunities, with opportunities for advancement and specialized training, while the Army Reserve has more limited opportunities for advancement and specialization.
| Component | Mission | Deployment | Training | Lifestyle | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army | Protect the country and its interests | Full-time deployments | Comprehensive training and education | Highly demanding, with frequent deployments and high-stress situations | Comprehensive benefits, including on-base housing, food allowances, and access to military facilities |
| Army Reserve | Support the US Army during times of war or national emergencies | Part-time deployments, with one weekend per month and two weeks per year | Maintenance of skills and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and tactics | More control over schedules, with competitive benefits and opportunities for education and career advancement | Competitive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance |

In the end, the choice between the Army and the Army Reserve depends on your individual goals, priorities, and circumstances. Whether you’re looking for a challenging and rewarding full-time career or a part-time opportunity to serve your country, both components offer unique benefits and opportunities for growth and development. By understanding the differences between the Army and the Army Reserve, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your values, interests, and aspirations.
What is the main difference between the Army and the Army Reserve?

+
The main difference between the Army and the Army Reserve is their mission and deployment. The Army is a full-time force that engages in combat operations, while the Army Reserve is a part-time force that supports the US Army during times of war or national emergencies.
How do the training and education programs differ between the Army and the Army Reserve?

+
The Army provides more extensive training and education, including specialized courses and leadership development programs, while the Army Reserve focuses on maintaining skills and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and tactics.
What are the benefits of joining the Army versus the Army Reserve?

+
The Army offers comprehensive benefits, including on-base housing, food allowances, and access to military facilities, while the Army Reserve offers competitive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance.
Related Terms:
- active duty vs reserve service
- active duty enlisted vs reserve
- army active duty vs reserve
- active duty vs reserve base
- active vs reserve duty
- active duty vs reserve force