What is Behavioral Health

Introduction to Behavioral Health

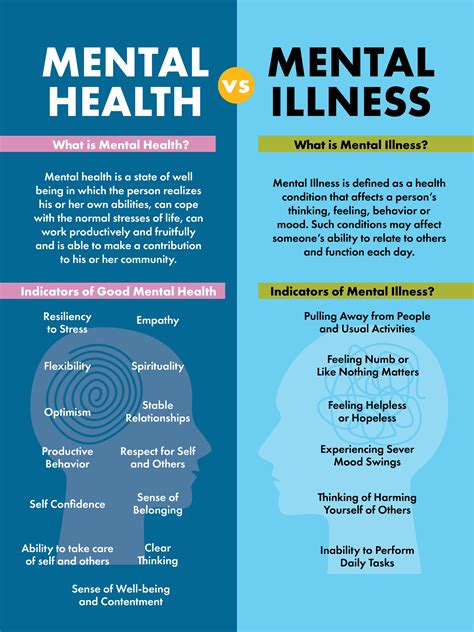
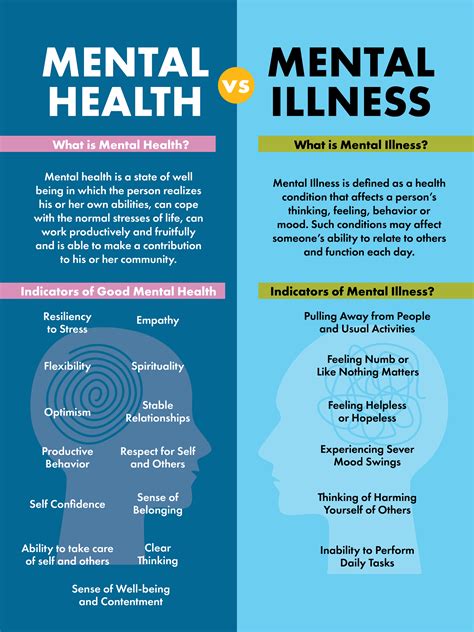
Behavioral health refers to the interconnectedness of physical health and mental well-being, encompassing a broad range of factors that influence an individual’s overall health and quality of life. It is a holistic approach that recognizes the complex relationships between physical, emotional, and psychological health, and seeks to address the underlying causes of health issues rather than just treating symptoms.
Key Components of Behavioral Health

The key components of behavioral health include: * Physical health: The absence of illness or disease, and the presence of physical functioning and well-being. * Mental health: The presence of emotional, psychological, and social well-being, and the absence of mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, or substance abuse. * Emotional health: The ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s emotions, and to develop healthy relationships with others. * Behavioral health disorders: Conditions such as substance abuse, addiction, or mental health disorders that affect an individual’s behavior and overall health.
Factors that Influence Behavioral Health
A range of factors can influence an individual’s behavioral health, including: * Genetics: Family history and genetic predisposition to certain health conditions. * Environment: Exposure to trauma, stress, or social determinants of health such as poverty, education, or housing. * Lifestyle choices: Diet, exercise, substance use, or other behaviors that can impact physical and mental health. * Social connections: The presence or absence of supportive relationships with family, friends, or community.
Behavioral Health Services
Behavioral health services aim to promote overall health and well-being by addressing the underlying causes of health issues. These services may include: * Counseling or therapy: Individual, group, or family counseling to address mental health concerns or behavioral issues. * Medication management: The use of medication to treat mental health conditions or substance abuse disorders. * Behavioral interventions: Strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or motivational interviewing to help individuals change their behavior. * Support groups: Group meetings or online forums that provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and connect with others.
Benefits of Behavioral Health

The benefits of behavioral health include: * Improved mental health: Reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions. * Increased physical health: Improved management of chronic health conditions, and reduced risk of disease. * Enhanced emotional well-being: Improved emotional regulation, resilience, and overall quality of life. * Stronger social connections: Improved relationships with family, friends, and community, and increased social support.
💡 Note: Behavioral health is a complex and multifaceted field, and this overview is just a starting point for understanding the many factors that influence an individual's overall health and well-being.
Barriers to Accessing Behavioral Health Services

Despite the importance of behavioral health, many individuals face barriers to accessing behavioral health services, including: * Lack of insurance coverage: Limited or no insurance coverage for behavioral health services. * Cost: High out-of-pocket costs for behavioral health services. * Stigma: Negative attitudes or stereotypes associated with mental health or substance abuse disorders. * Accessibility: Limited availability of behavioral health services in rural or underserved areas.
Future Directions in Behavioral Health
The future of behavioral health holds much promise, with advances in technology, research, and policy aimed at improving access to and quality of behavioral health services. Some potential future directions include: * Telehealth: The use of technology to deliver behavioral health services remotely. * Personalized medicine: The use of genetic or other data to tailor behavioral health interventions to an individual’s unique needs. * Integrated care: The coordination of physical and behavioral health services to provide comprehensive care. * Policies and laws: Changes in policy and law aimed at increasing access to and funding for behavioral health services.
Conclusion

In summary, behavioral health is a complex and multifaceted field that recognizes the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, and psychological health. By addressing the underlying causes of health issues and providing comprehensive care, behavioral health services can promote overall health and well-being, and improve quality of life. As the field continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see advances in technology, research, and policy aimed at improving access to and quality of behavioral health services.
What is the difference between mental health and behavioral health?

+
Mental health refers specifically to the presence or absence of mental health disorders, while behavioral health encompasses a broader range of factors that influence overall health and well-being, including physical health, emotional health, and behavioral health disorders.
How can I access behavioral health services?

+
There are many ways to access behavioral health services, including contacting your primary care provider, searching online for local providers, or calling a hotline or support line. You can also check with your insurance provider to see what services are covered.
What are some common behavioral health disorders?

+
Common behavioral health disorders include substance abuse or addiction, anxiety or depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and eating disorders. These conditions can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall health and well-being, and can often be treated with a combination of counseling, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Related Terms:
- What is mental health
- behavioral health vs psychiatry
- what does behavioral health do
- examples of behavioral health
- defintion of behavioral health
- behavioral health description