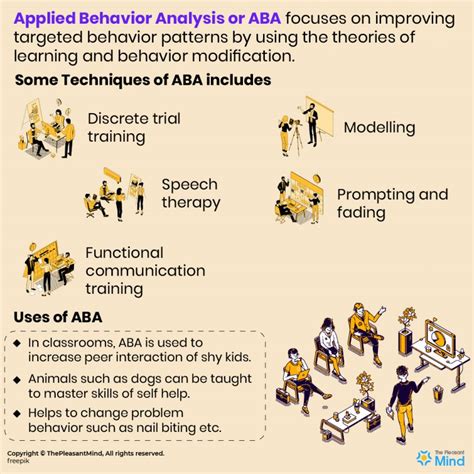
5 Tips Behavioral Analysis

Introduction to Behavioral Analysis

Behavioral analysis is a powerful tool used in various fields, including psychology, marketing, and cybersecurity, to understand and predict human behavior. By analyzing patterns and trends in behavior, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions, improve performance, and reduce risks. In this article, we will explore five tips for effective behavioral analysis, highlighting the importance of data quality, contextual understanding, pattern recognition, predictive modeling, and continuous monitoring.
Tip 1: Ensure High-Quality Data

The foundation of behavioral analysis is data. Accurate and relevant data is essential for drawing meaningful insights and making informed decisions. When collecting data, it is crucial to consider the following factors: * Data sources: Ensure that data is collected from credible and reliable sources. * Data consistency: Establish a consistent format for data collection to facilitate analysis. * Data completeness: Collect comprehensive data that covers all relevant aspects of behavior. By prioritizing data quality, analysts can build a robust foundation for their analysis, reducing the risk of biased or misleading conclusions.
Tip 2: Understand the Context

Behavioral analysis is not just about collecting data; it is also about understanding the context in which behavior occurs. Contextual factors, such as environment, culture, and social norms, can significantly influence behavior. To gain a deeper understanding of behavior, analysts should consider the following: * Environmental factors: How do physical and social environments impact behavior? * Cultural factors: How do cultural norms and values shape behavior? * Social factors: How do social relationships and networks influence behavior? By considering these contextual factors, analysts can develop a more nuanced understanding of behavior, recognizing that behavior is often shaped by complex interactions between individual and environmental factors.
Tip 3: Recognize Patterns

Behavioral analysis involves identifying patterns and trends in behavior. Pattern recognition is a critical skill for analysts, as it enables them to identify predictive indicators of future behavior. To recognize patterns, analysts should: * Look for correlations: Identify relationships between different behaviors or variables. * Identify anomalies: Recognize unusual or outlier behavior that may indicate a larger issue. * Analyze sequences: Examine the order and timing of behaviors to understand causal relationships. By recognizing patterns, analysts can develop predictive models that forecast future behavior, enabling proactive interventions and strategic decision-making.
Tip 4: Develop Predictive Models
Predictive modeling is a powerful application of behavioral analysis, enabling analysts to forecast future behavior. By developing predictive models, analysts can: * Identify high-risk individuals: Predict which individuals are most likely to engage in problematic behavior. * Anticipate behavioral trends: Forecast changes in behavioral patterns, enabling proactive interventions. * Evaluate intervention effectiveness: Assess the impact of interventions on behavior, refining strategies for improved outcomes. To develop effective predictive models, analysts should consider the following: * Use machine learning algorithms: Leverage advanced statistical techniques to identify complex patterns in data. * Incorporate domain expertise: Collaborate with subject matter experts to ensure that models are informed by practical knowledge. * Continuously refine models: Update models with new data, ensuring that they remain accurate and relevant.
Tip 5: Continuously Monitor and Refine

Behavioral analysis is an ongoing process, requiring continuous monitoring and refinement. Analysts should: * Regularly update data: Ensure that data remains current and relevant, reflecting changes in behavior and context. * Refine predictive models: Update models with new data, incorporating lessons learned from previous analyses. * Assess intervention effectiveness: Evaluate the impact of interventions on behavior, refining strategies for improved outcomes. By continuously monitoring and refining their analysis, analysts can ensure that their insights remain relevant and accurate, supporting informed decision-making and strategic interventions.
📝 Note: Behavioral analysis is a complex and multidisciplinary field, requiring collaboration between analysts, subject matter experts, and stakeholders. By following these five tips, analysts can develop a robust and effective approach to behavioral analysis, driving informed decision-making and improved outcomes.
In summary, effective behavioral analysis requires a combination of high-quality data, contextual understanding, pattern recognition, predictive modeling, and continuous monitoring. By prioritizing these factors, analysts can develop a nuanced understanding of behavior, forecasting future trends and supporting proactive interventions. As the field of behavioral analysis continues to evolve, it is essential to remain adaptable and responsive, incorporating new techniques and insights into analytical frameworks. Ultimately, the goal of behavioral analysis is to drive positive change, supporting individuals and organizations in achieving their goals and improving outcomes.
What is behavioral analysis?

+
Behavioral analysis is a process of studying and understanding human behavior, often used in fields like psychology, marketing, and cybersecurity.
Why is data quality important in behavioral analysis?
+
Data quality is crucial in behavioral analysis because it ensures that the insights and conclusions drawn are accurate and reliable.
How can predictive models be used in behavioral analysis?

+
Predictive models can be used in behavioral analysis to forecast future behavior, identify high-risk individuals, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
Related Terms:
- behavior analysis public health
- History of behavior Analysis
- Student behavior analysis
- Behavior analysis in education
- Behavior analysis in environmental sustainability
- Intro to behavior Analysis