Bulimia Nervosa Definition

Introduction to Bulimia Nervosa
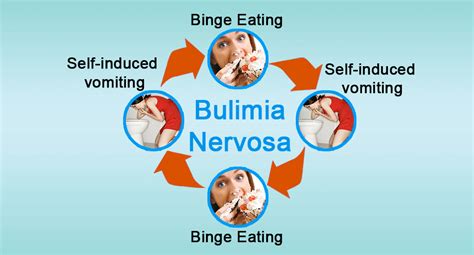
Bulimia nervosa, often simply called bulimia, is a serious eating disorder characterized by a cycle of bingeing and compensatory behaviors such as self-induced vomiting, using laxatives, or excessive exercise to prevent weight gain. This condition is marked by recurrent episodes of eating significantly more food in a short period of time than most people would eat under similar circumstances, with episodes marked by feelings of lack of control. It is a complex condition that affects not only the physical health but also the psychological well-being of the individual.
Understanding the Cycle of Bulimia Nervosa

The cycle of bulimia nervosa typically involves binge eating, which is followed by purging or compensatory behaviors. Binge eating episodes are often accompanied by feelings of guilt, shame, and self-criticism, which can lead to further emotional distress. The purging or compensatory behaviors are attempts to counteract the binge eating, but they can have severe physical and emotional consequences.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bulimia Nervosa

The exact cause of bulimia nervosa is not known, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition, brain chemistry, psychological factors such as low self-esteem, and environmental factors including cultural pressures to be thin can all play a role. Individuals with a family history of eating disorders, those who have experienced traumatic events, and those with certain personality traits or mental health conditions may be at a higher risk of developing bulimia nervosa.
Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa

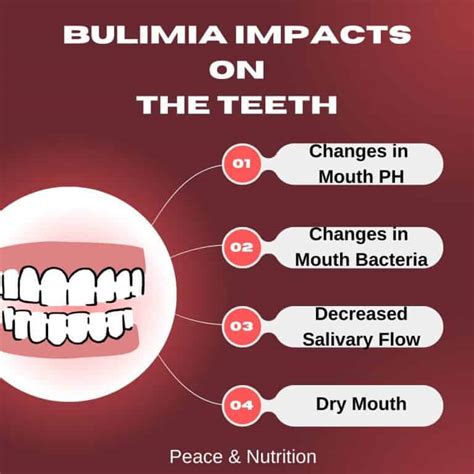
The symptoms of bulimia nervosa can be physical, emotional, and behavioral. Physical symptoms may include: - Fluctuations in weight - Tooth decay and oral health issues due to frequent vomiting - Gastrointestinal problems - Electrolyte imbalances - Menstrual irregularities
Emotional and behavioral symptoms can include: - Feelings of guilt and shame after binge eating - Secrecy about eating habits - Preoccupation with body shape and weight - Using laxatives, diuretics, or excessive exercise to prevent weight gain
Diagnosis of Bulimia Nervosa

Diagnosing bulimia nervosa involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a physical examination, psychological assessment, and a review of eating habits and behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), provides specific criteria for diagnosing bulimia nervosa, including the frequency and duration of binge eating and compensatory behaviors.
Treatment Options for Bulimia Nervosa

Treatment for bulimia nervosa usually involves a combination of psychotherapy, nutrition counseling, and medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used psychotherapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the disorder. Family-based therapy may also be recommended, especially for adolescents. Medications such as antidepressants may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety that often co-occur with bulimia nervosa.
Recovery from Bulimia Nervosa

Recovery from bulimia nervosa is possible with the right treatment and support. It involves not only the cessation of binge eating and purging behaviors but also the development of a healthier relationship with food and one’s body. Support groups can play a crucial role in the recovery process, providing a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and receive support from others who are going through similar challenges. Developing coping strategies and learning to manage stress and negative emotions in healthier ways are also important aspects of recovery.
💡 Note: Recovery is a long-term process that requires patience, understanding, and a commitment to seeking help when needed.
Prevention of Bulimia Nervosa

Preventing bulimia nervosa involves promoting a positive body image, healthy eating habits, and self-esteem. Education and awareness about eating disorders, their signs, and the importance of seeking help early are crucial. Encouraging open conversations about body image, dieting, and the dangers of unhealthy weight control behaviors can also help in preventing the development of bulimia nervosa.
| Aspect of Prevention | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Healthy Eating Habits | Encouraging balanced meals, avoiding dieting, promoting mindful eating |
| Positive Body Image | Promoting self-acceptance, challenging societal beauty standards, fostering self-esteem |
| Early Intervention | Recognizing early signs of eating disorders, seeking professional help, supporting affected individuals |
In the end, understanding and addressing bulimia nervosa requires a comprehensive approach that considers the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the disorder. By promoting awareness, encouraging healthy habits, and supporting those affected, we can work towards preventing bulimia nervosa and fostering a culture that values and supports the well-being of all individuals.
What are the most common symptoms of bulimia nervosa?

+
The most common symptoms include binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors like self-induced vomiting, using laxatives, or excessive exercise, along with feelings of guilt, shame, and preoccupation with body shape and weight.
How is bulimia nervosa diagnosed?
+
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a physical examination, psychological assessment, and a review of eating habits and behaviors, using the criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5).
What are the treatment options for bulimia nervosa?

+
Treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), nutrition counseling, and medication. Family-based therapy and support groups can also play a significant role in the recovery process.
Related Terms:
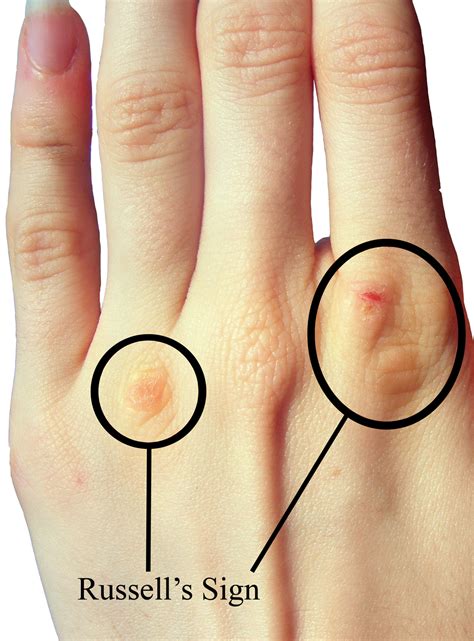
- bulimia finger
- bulimia nervosa nhs
- how to identify bulimia
- bulimia pics
- signs of bulimia face
- support for bulimia sufferers