MIG Welding Stainless Steel Guide

Introduction to MIG Welding Stainless Steel

MIG (GMAW) welding is a popular method for joining stainless steel due to its high efficiency, versatility, and ability to produce high-quality welds. However, welding stainless steel can be challenging due to its unique properties, such as high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and the formation of a tenacious oxide layer. In this guide, we will discuss the best practices, techniques, and equipment required for successful MIG welding of stainless steel.
Pre-Welding Preparation
Before starting the welding process, it is essential to prepare the stainless steel properly. This includes: * Cleaning the surface: Remove any dirt, oil, or grease from the surface using a wire brush or a cleaning solution. * Removing the oxide layer: Use a stainless steel brush or a chemical cleaning solution to remove the oxide layer and prevent porosity. * Checking for contamination: Ensure the surface is free from contaminants, such as moisture, dust, or other substances that can affect weld quality. * Aligning the joint: Properly align the joint to ensure a consistent gap and prevent distortion.
Choosing the Right Equipment

To weld stainless steel effectively, you will need: * A MIG welder with a suitable power source and wire feed system. * A shielding gas system, such as argon or helium, to protect the weld area from atmospheric gases. * A welding gun with a stainless steel nozzle to prevent contamination and ensure a smooth wire feed. * MIG welding wire specifically designed for stainless steel, such as ER308L or ER316L.
Welding Techniques

To achieve high-quality welds, follow these techniques: * Use the correct welding position: Weld in the flat position (PA) or horizontal position (PB) to minimize distortion and ensure a consistent weld pool. * Maintain a consistent arc length: Keep the arc length consistent to prevent overheating or underheating the weld area. * Use the correct travel speed: Adjust the travel speed to ensure a consistent weld pool and prevent lack of fusion or porosity. * Monitor the weld pool: Observe the weld pool to ensure it is consistent, smooth, and free from defects.
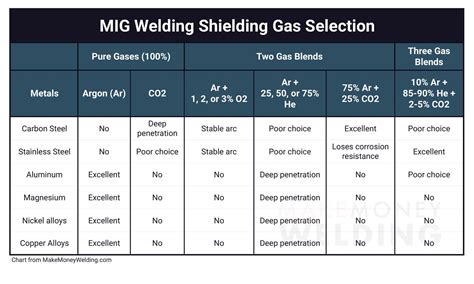
Shielding Gas Selection

The choice of shielding gas is critical when welding stainless steel. The most common shielding gases used are: * Argon: Provides a clean, inert atmosphere and is suitable for most stainless steel welding applications. * Helium: Offers better penetration and is often used for thicker stainless steel sections. * Argon-helium mixtures: Provide a balance between cleanliness and penetration.
Welding Parameters

The welding parameters will depend on the specific stainless steel alloy, thickness, and joint design. However, here are some general guidelines: * Voltage: Typically ranges from 16 to 24 volts, depending on the wire feed speed and joint thickness. * Wire feed speed: Usually ranges from 100 to 400 inches per minute (ipm), depending on the joint thickness and welding position. * Shielding gas flow rate: Typically ranges from 15 to 30 cubic feet per hour (cfh), depending on the joint thickness and welding position.
| Stainless Steel Alloy | Thickness (in) | Voltage (V) | Wire Feed Speed (ipm) | Shielding Gas Flow Rate (cfh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304L | 1/8 | 18 | 200 | 20 |
| 316L | 1/4 | 20 | 250 | 25 |
| 309L | 1/2 | 22 | 300 | 30 |

💡 Note: The welding parameters may vary depending on the specific application, joint design, and equipment used. It is essential to consult the manufacturer's recommendations and perform trial welds to determine the optimal parameters.
In summary, MIG welding stainless steel requires careful preparation, equipment selection, and technique to produce high-quality welds. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, welders can ensure a strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant weld that meets the required standards. The key takeaways from this guide include the importance of proper surface preparation, choosing the right equipment, and using the correct welding techniques and parameters. With practice and experience, welders can develop the skills and knowledge necessary to successfully weld stainless steel using the MIG process.
What is the best shielding gas for MIG welding stainless steel?

+
The best shielding gas for MIG welding stainless steel is argon, as it provides a clean, inert atmosphere and is suitable for most stainless steel welding applications.
What is the recommended wire feed speed for MIG welding 1⁄4 inch thick 316L stainless steel?

+
The recommended wire feed speed for MIG welding 1⁄4 inch thick 316L stainless steel is typically around 250 ipm, depending on the joint design and welding position.
How do I prevent porosity when MIG welding stainless steel?

+
To prevent porosity when MIG welding stainless steel, ensure the surface is clean and free from contaminants, use the correct shielding gas, and maintain a consistent arc length and travel speed.
Related Terms:
- how to mig weld stainless
- mig welding stainless what gas
- stainless wire for mig welder
- mig welding for stainless steel
- mig welding stainless steel techniques
- how to mig stainless steel



