5 Ways Transfer Military Branches

Introduction to Inter-Service Transfers

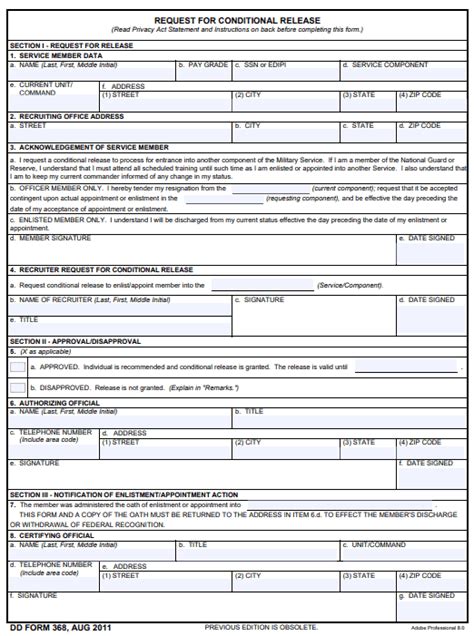
For various reasons, some military personnel may wish to transfer from one branch of the military to another. This process, known as an inter-service transfer, can be complex and involves several steps. Each branch of the military has its own requirements and procedures for accepting transfers from other branches. In this article, we will explore the ways to transfer between military branches, highlighting the key considerations and steps involved in each process.
Understanding the Basics of Inter-Service Transfers

Before diving into the specifics of transferring between branches, it’s essential to understand the basics. An inter-service transfer allows a service member to move from one branch of the military to another, retaining their rank and, in some cases, their Military Occupational Specialty (MOS). This can be an attractive option for those looking for new challenges, different work environments, or to align their career with their personal goals more closely.
5 Ways to Transfer Military Branches

There are several ways to transfer between military branches, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and application processes. Here are five common methods:
- 1. Direct Commission: This method involves commissioning directly into a new branch as an officer. It’s typically available for those with specific skills or professions that are in high demand, such as medical professionals or lawyers. The process usually requires meeting the basic eligibility requirements for officer commissioning in the desired branch and applying through specific programs designed for direct commissions.
- 2. Lateral Transfer: A lateral transfer refers to the process of moving from one branch to another without a change in rank or job specialty. This can be a straightforward process but often requires approval from both the losing and gaining branches. Service members must meet the eligibility criteria set by the gaining branch and apply through the appropriate channels.
- 3. Enlisted to Officer Transfer: For enlisted personnel wishing to become officers in a different branch, there are several programs available, such as Officer Candidate School (OCS) or the Warrant Officer Program. These programs require meeting specific eligibility criteria, including education requirements, service time, and performance evaluations.
- 4. Inter-Service Transfer Program (ISTP): The ISTP allows enlisted members to transfer from one branch to another. This program is designed to facilitate the movement of personnel between branches to fill critical specialties or to meet the personal goals of service members. Eligibility and application procedures vary, but generally, members must have a certain amount of service time, meet specific job qualifications, and apply through their chain of command.
- 5. Reenlistment or Extension for Transfer: In some cases, service members may be able to reenlist or extend their service contract in exchange for the opportunity to transfer to a different branch. This can be a viable option for those nearing the end of their service obligation or looking to commit to additional service time in a new branch.
Steps to Transfer Between Military Branches

The process of transferring between military branches involves several key steps:
- Meet Eligibility Criteria: Each transfer method has its own set of eligibility requirements. These can include age limits, time in service, education levels, performance evaluations, and security clearance levels.
- Research and Choose a Transfer Method: Service members should carefully consider their goals, current situation, and the options available to them. Choosing the right transfer method is crucial for a successful transition.
- Prepare and Submit an Application: Applications for transfer will typically require documentation, such as transcripts, evaluations, and medical records. Ensuring all paperwork is in order and submitted correctly is vital.
- Interviews and Assessments: Depending on the transfer method, applicants may be required to participate in interviews, assessments, or other evaluation processes.
- Approval and Processing: After application submission, the process involves approval from the losing branch, the gaining branch, and sometimes other authorities. This can take several months, and patience is advised.
📝 Note: The transfer process can be lengthy and involves careful planning. It's essential to start the process early and to seek guidance from career counselors or transfer specialists within the military.
Benefits and Challenges of Transferring Between Military Branches
Transferring between military branches can offer numerous benefits, including new career opportunities, changes in work environment, and personal fulfillment. However, it also presents challenges, such as adjusting to new cultures, learning new systems and procedures, and potentially facing uncertainty about one’s career trajectory.
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| New career opportunities | Adjusting to a new branch culture |
| Change in work environment | Learning new systems and procedures |
| Personal fulfillment | Uncertainty about career trajectory |

Preparing for a Successful Transfer

To ensure a successful transfer between military branches, service members should be well-prepared. This involves:
- Research: Understand the requirements, procedures, and what to expect in the new branch.
- Planning: Start the process early and plan carefully, considering all aspects of the transfer.
- Professional Development: Continuously work on personal and professional development to make oneself a more competitive candidate.
- Networking: Building relationships within the desired branch can provide valuable insights and support.
In summary, transferring between military branches is a significant decision that requires careful consideration and planning. Understanding the different methods of transfer, the steps involved, and the benefits and challenges can help service members make informed decisions about their military careers.
What are the main reasons service members transfer between military branches?

+
The main reasons include seeking new challenges, aligning their career with personal goals, and changing their work environment. Additionally, some may transfer to fill critical specialties or due to personal circumstances.
How long does the transfer process typically take?
+
The length of the transfer process can vary significantly depending on the method of transfer, the complexity of the application, and the efficiency of the approval process. It can take anywhere from a few months to over a year.
Do service members retain their rank when transferring between branches?

+
Generally, service members can retain their rank when transferring through certain programs designed for lateral moves or direct commissions. However, rank retention is not guaranteed in all cases and depends on the specific transfer method and the policies of the gaining branch.
Ultimately, the decision to transfer between military branches should be based on careful consideration of personal and professional goals. By understanding the process, the benefits, and the challenges, service members can make informed decisions that align with their aspirations and contribute to a fulfilling military career.
Related Terms:
- switching branches in the military
- transferring from usmc to usaf
- lateral transfer to space force
- switching from army to navy
- navy to army transfer enlisted
- switching from marines to army



