Clinical Mental Health Counselor Guide

Introduction to Clinical Mental Health Counseling
Clinical mental health counseling is a vital profession that involves helping individuals, couples, families, and groups to cope with mental health issues, trauma, and other challenges that affect their well-being. Clinical mental health counselors work in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, private practices, and community organizations, to provide assessment, diagnosis, and treatment for mental health disorders. In this guide, we will explore the role of clinical mental health counselors, their responsibilities, and the skills required to succeed in this profession.
Roles and Responsibilities of Clinical Mental Health Counselors

Clinical mental health counselors play a crucial role in promoting mental health and well-being. Their primary responsibilities include: * Conducting intakes and assessments to identify clients’ needs and develop treatment plans * Providing individual, group, and family therapy to address mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and trauma * Developing and implementing treatment plans that incorporate evidence-based practices and clinical interventions * Collaborating with other mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists and social workers, to provide comprehensive care * Maintaining confidentiality and adhering to ethical standards in all aspects of practice
Education and Training Requirements

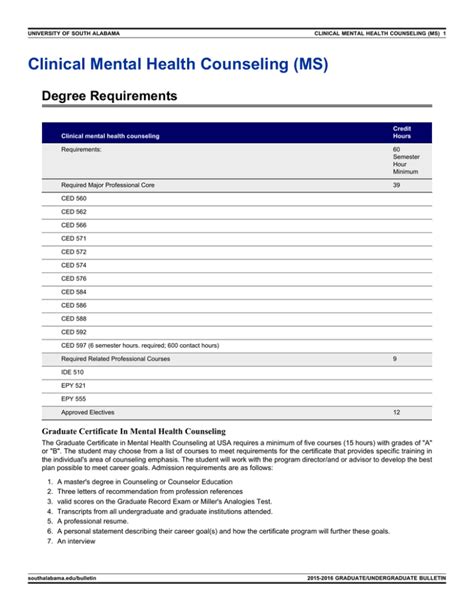
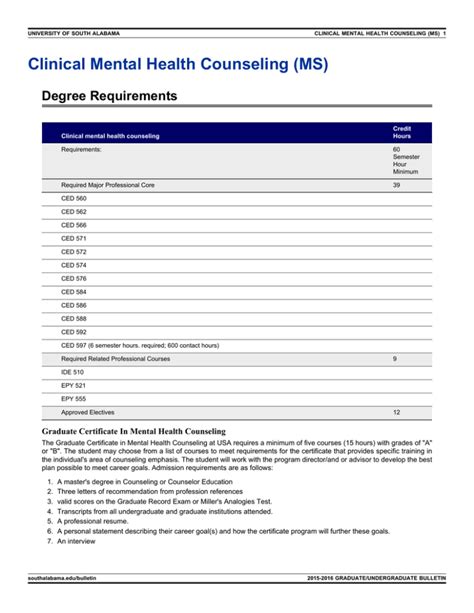
To become a clinical mental health counselor, one must complete a master’s degree in clinical mental health counseling or a related field, such as counseling psychology or social work. The program should be accredited by the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP). In addition to formal education, clinical mental health counselors must also complete clinical training and internships to gain practical experience.
Skills and Qualities Required

To succeed as a clinical mental health counselor, one must possess certain skills and qualities, including: * Excellent communication skills to establish rapport with clients and communicate effectively with other professionals * Empathy and compassion to understand and support clients’ experiences and emotions * Cultural competence to work effectively with diverse populations and address issues related to social justice and advocacy * Strong assessment and diagnostic skills to identify clients’ needs and develop effective treatment plans * Ability to work in a fast-paced environment and manage multiple responsibilities and priorities
Specializations and Areas of Focus

Clinical mental health counselors may specialize in various areas, such as: * Child and adolescent counseling * Adult counseling * Geriatric counseling * Substance abuse counseling * Trauma-informed care Each specialization requires unique knowledge, skills, and training to address the specific needs of the population being served.
Benefits and Challenges of the Profession

Clinical mental health counseling is a rewarding profession that offers many benefits, including: * Personal fulfillment from helping others and making a positive impact on their lives * Opportunities for specialization and professional growth * Collaboration with other professionals to provide comprehensive care However, the profession also presents challenges, such as: * High stress levels and emotional demands * Complexity and uncertainty in working with diverse populations and issues * Continuous education and training to stay current with best practices and research
💡 Note: Clinical mental health counselors must be aware of their own self-care needs and take steps to maintain their physical, emotional, and mental well-being to avoid burnout and compassion fatigue.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, clinical mental health counseling is a vital profession that requires specialized education, training, and skills to address the complex mental health needs of individuals, couples, families, and groups. As the demand for mental health services continues to grow, clinical mental health counselors must be prepared to adapt to changing healthcare landscapes, technological advancements, and shifting societal needs. By prioritizing self-care, professional development, and collaboration, clinical mental health counselors can provide high-quality care and make a positive impact on the lives of their clients.
What is the difference between a clinical mental health counselor and a psychologist?
+
Clinical mental health counselors and psychologists are both mental health professionals, but they have different educational backgrounds, training, and scopes of practice. Clinical mental health counselors typically have a master’s degree in counseling or a related field, while psychologists have a doctoral degree in psychology.
What kind of training and education do clinical mental health counselors need?

+
Clinical mental health counselors need a master’s degree in clinical mental health counseling or a related field, such as counseling psychology or social work. The program should be accredited by the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP). In addition to formal education, clinical mental health counselors must also complete clinical training and internships to gain practical experience.
What are some common specializations for clinical mental health counselors?

+
Clinical mental health counselors may specialize in various areas, such as child and adolescent counseling, adult counseling, geriatric counseling, substance abuse counseling, and trauma-informed care. Each specialization requires unique knowledge, skills, and training to address the specific needs of the population being served.
Related Terms:
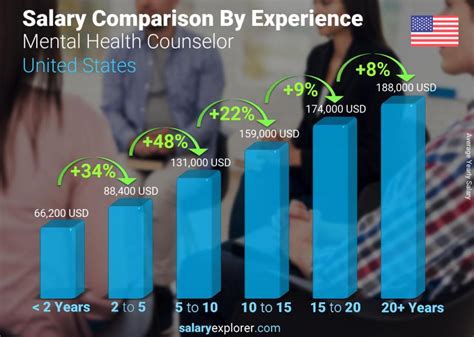
- Clinical Mental Health Counselor salary
- Clinical mental health counselor degree
- Clinical Mental Health Counselor jobs
- Clinical mental health counselor license
- Licensed Clinical Mental Health Counselor
- clinical mental health counselor abbreviation



