5 Ways Proxy War Works

Introduction to Proxy Wars

Proxy wars have been a significant aspect of international relations and conflicts for decades. These are wars where two or more opposing parties use third parties as substitutes for fighting each other directly. The reasons behind proxy wars can vary, including avoiding direct confrontation, preserving diplomatic relations, or adhering to international norms and laws. The complexity and the clandestine nature of proxy wars make them intriguing yet challenging to understand. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of proxy wars, exploring how they are initiated, maintained, and the roles various actors play within them.
Understanding Proxy Wars

A proxy war involves a conflict where two powers use intermediaries to fight on their behalf. These intermediaries can be other countries, rebel groups, insurgents, or even mercenaries. The use of proxies allows the primary powers to influence the outcome of a conflict without directly engaging their military forces. This can be particularly useful in situations where direct military intervention might lead to severe repercussions, such as escalating tensions, international condemnation, or even nuclear war.
Initiation of Proxy Wars

The initiation of a proxy war often involves strategic planning and diplomatic efforts. Here are some steps typically involved: - Identification of Interests: The first step involves identifying the strategic interests that a nation wants to protect or advance. This could range from geopolitical influence, access to resources, to spreading ideology. - Selection of Proxies: After identifying interests, the next step is to select suitable proxies. This selection is based on various factors including the proxy’s military capabilities, political influence, and alignment with the sponsoring nation’s objectives. - Support and Funding: Once proxies are selected, they are provided with necessary support, which can include financial aid, military equipment, training, and strategic guidance. The level of support can vary depending on the goals of the sponsoring nation and the capabilities of the proxy. - Execution and Management: The execution phase involves the proxy engaging in military or political actions against the target. The sponsoring nation typically maintains a level of control through the provision of support and strategic guidance, ensuring that the proxy’s actions align with their objectives.
Mechanisms of Proxy Wars

Proxy wars can manifest in various forms, depending on the objectives of the sponsoring nations and the capabilities of the proxies. Some common mechanisms include: - Armed Insurgency: This involves supporting rebel or insurgent groups within a country to destabilize the government or achieve specific political objectives. - Political Manipulation: Sponsoring nations may also engage in political manipulation, supporting certain political parties or candidates that align with their interests. - Economic Influence: Economic tools such as sanctions, trade agreements, or foreign aid can be used to influence the political and economic landscape of a target country.
Examples of Proxy Wars

Throughout history, there have been numerous examples of proxy wars. Some notable examples include: - The Soviet-Afghan War: The Soviet Union’s invasion of Afghanistan led to a proxy war, with the United States supporting anti-Soviet mujahideen fighters. - The Syrian Civil War: The conflict in Syria has involved multiple proxy wars, with the United States, Russia, Iran, and Turkey supporting different factions within the country. - The Cold War: During the Cold War, the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in numerous proxy wars around the world, including in Korea, Vietnam, and Angola.
Challenges and Implications
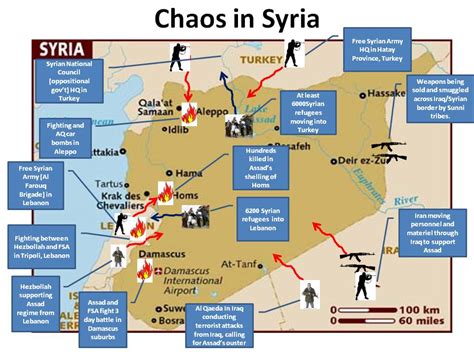
Proxy wars present several challenges and implications, both for the sponsoring nations and the international community. These include: - Escalation Risk: Proxy wars can escalate into larger conflicts, especially if the sponsoring nations are drawn into direct military engagement. - Humanitarian Concerns: Proxy wars often result in significant humanitarian crises, including civilian casualties, displacement, and human rights abuses. - International Law: The use of proxy forces can complicate issues of international law, particularly regarding the legality of interventions and the responsibility for actions taken by proxies.
📝 Note: Understanding the dynamics of proxy wars is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of international relations and conflict resolution.
Proxy wars, with their clandestine nature and indirect involvement, pose significant challenges for international relations, conflict resolution, and humanitarian efforts. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the mechanisms and implications of proxy wars will continue to evolve, necessitating a deeper understanding and more nuanced approaches to conflict management and resolution.
In reflecting on the key points discussed, it becomes clear that proxy wars are multifaceted and can have far-reaching consequences. The initiation, mechanisms, and examples of proxy wars highlight the complexity of international conflicts and the need for careful consideration and strategic planning in geopolitical maneuvers. Ultimately, the future of international relations will likely involve continued instances of proxy wars, making it essential to develop effective strategies for managing and resolving these conflicts in a manner that minimizes harm and promotes stability.
What is a proxy war?

+
A proxy war is a conflict where two or more opposing parties use third parties as substitutes for fighting each other directly.
Why do nations engage in proxy wars?

+
Nations engage in proxy wars to avoid direct confrontation, preserve diplomatic relations, or adhere to international norms and laws, among other reasons.
What are the implications of proxy wars?

+
The implications of proxy wars include the risk of escalation, humanitarian crises, and challenges to international law, among others.
Related Terms:
- proxy war definition world history
- example of a proxy war
- proxy war meaning simple
- what does proxy war mean
- define the term proxy war
- why were there proxy war