5 Combat Medic Tips

Introduction to Combat Medicine
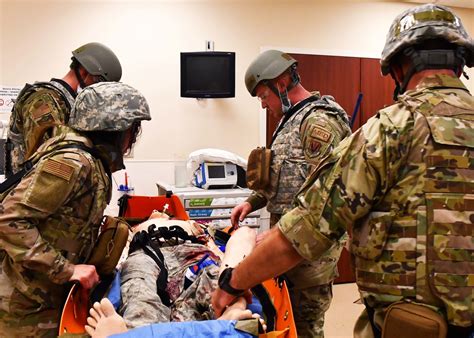
Combat medicine is a critical aspect of military and emergency response operations, focusing on providing immediate medical care in high-stress, dynamic environments. The role of a combat medic is multifaceted, requiring not only a deep understanding of medical procedures but also the ability to remain calm under fire and make quick, lifesaving decisions. For those interested in this field or looking to improve their skills, here are several key tips and considerations.
Understanding the Fundamentals

To be an effective combat medic, one must first have a solid foundation in basic life support skills, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), bleeding control, and airway management. These skills are crucial in stabilizing patients until they can receive more definitive care. Moreover, a combat medic must be knowledgeable about the tactical combat casualty care (TCCC) guidelines, which provide evidence-based recommendations for caring for wounded personnel in a tactical environment.
Tactical Considerations
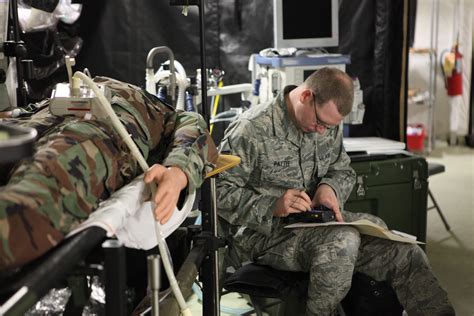
Combat medics must always consider the tactical situation when providing care. This includes: - Scene safety: Ensuring the area is secure before beginning medical treatment. - Personal protective equipment (PPE): Wearing appropriate gear to minimize personal risk. - Triage: Quickly assessing the severity of injuries to prioritize care for those most in need. - Communication: Clearly and effectively communicating with team members about the situation and the care being provided.
Advanced Skills and Training

Beyond the basics, combat medics should pursue advanced training in areas such as: - IV fluid administration - Pain management - Advanced airway management - Tactical evacuation techniques Staying updated with the latest medical advancements and guidelines is also crucial, as combat medicine is a field that continuously evolves based on new research and lessons learned from the field.
Staying Prepared

Preparation is key for combat medics. This includes: - Physical conditioning: Maintaining a high level of physical fitness to perform duties effectively in challenging environments. - Mental toughness: Developing the resilience to cope with the psychological stresses of combat and making sound decisions under pressure. - Equipment familiarity: Being proficient with all medical and tactical gear to ensure seamless operation in high-stress situations. - Ongoing training: Participating in regular drills and scenarios to hone skills and adapt to new procedures and technologies.
📝 Note: The role of a combat medic is incredibly demanding, both physically and mentally. Continuous training, self-study, and a commitment to excellence are essential for success in this field.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In summary, being a combat medic requires a unique blend of medical knowledge, tactical awareness, and personal attributes such as courage and resilience. By focusing on developing a strong foundation in medical skills, staying updated with the latest advancements, and maintaining a high level of physical and mental readiness, individuals can excel in this critical role. Whether in military operations, emergency medical services, or other high-risk environments, the contributions of combat medics are invaluable, saving countless lives and making a significant difference in the outcomes of critical situations.
What is the primary role of a combat medic?

+
The primary role of a combat medic is to provide immediate medical care in high-stress, dynamic environments, with the goal of stabilizing patients until they can receive more definitive care.
What are some key skills for a combat medic to have?

+
Key skills include basic life support skills such as CPR, bleeding control, and airway management, as well as knowledge of tactical combat casualty care (TCCC) guidelines, advanced medical procedures, and tactical considerations like scene safety and triage.
How can someone become a skilled combat medic?

+
Becoming a skilled combat medic involves a combination of formal medical training, tactical training, continuous self-study, and practical experience. Staying updated with the latest medical guidelines and participating in regular drills and scenarios are also crucial.
Related Terms:
- basic combat medical training
- combat medic training manual pdf
- us army medical training courses
- 68w army combat medic training
- 68 whiskey combat medic training
- us army combat medic training



