5 Dimethoate Health Hazards
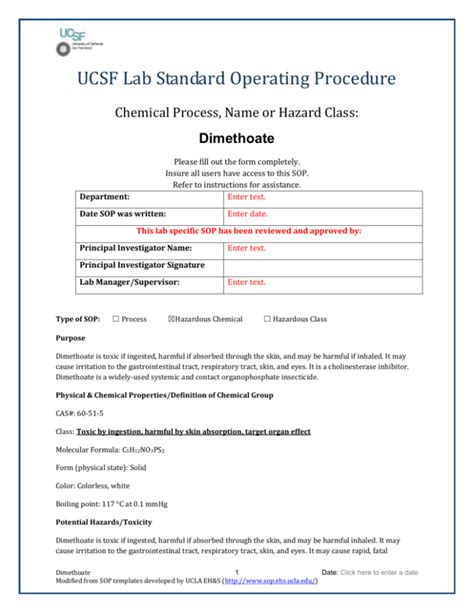
Introduction to Dimethoate and Its Health Hazards

Dimethoate is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide used to control a wide range of pests. It is commonly applied in agricultural settings to protect crops such as fruits, vegetables, and grains. Despite its effectiveness as a pesticide, dimethoate poses significant health hazards to humans, wildlife, and the environment. This blog post aims to explore the health hazards associated with dimethoate, its uses, and the measures that can be taken to mitigate its adverse effects.
What is Dimethoate?
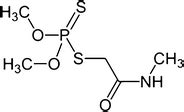
Dimethoate is a systemic insecticide, meaning it is absorbed by plants and distributed throughout their tissues. It works by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system in insects. This inhibition leads to an accumulation of acetylcholine, causing overstimulation of the insect’s nervous system, ultimately resulting in its death.
Health Hazards of Dimethoate
The health hazards of dimethoate are primarily associated with its neurotoxic properties. Exposure to dimethoate can occur through various routes, including ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact. The severity of the health effects depends on the level and duration of exposure. Some of the potential health hazards of dimethoate include: - Neurological effects: Dimethoate can cause a range of neurological symptoms, including headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, it can lead to confusion, seizures, and even respiratory failure. - Reproductive and developmental effects: There is evidence suggesting that dimethoate may have reproductive and developmental effects, particularly in cases of prolonged exposure. - Cancer concerns: Although the evidence is not conclusive, some studies have suggested a potential link between dimethoate exposure and an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
Uses of Dimethoate
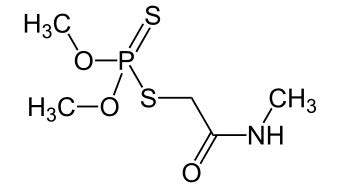
Dimethoate is used in various agricultural and non-agricultural settings. Its primary use is as an insecticide to control pests in crops, gardens, and homes. It is also used in public health programs to control vectors of diseases such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Measures to Mitigate Health Hazards

To minimize the health hazards associated with dimethoate, several measures can be taken: - Proper handling and use: It is essential to follow the instructions provided on the label and use personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling dimethoate. - Avoidance of exposure: Individuals should avoid exposure to dimethoate by staying away from treated areas and avoiding consumption of contaminated food and water. - Environmental protection: Measures should be taken to prevent dimethoate from contaminating soil, water, and air. This includes proper disposal of waste and the use of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
Alternatives to Dimethoate

Given the health hazards associated with dimethoate, there is a growing interest in finding alternatives that are safer for humans and the environment. Some of these alternatives include: - Biological control methods: These involve the use of natural predators or parasites to control pest populations. - Organic farming practices: These practices focus on the use of natural substances and techniques to control pests and diseases. - Integrated pest management (IPM): IPM involves the use of a combination of techniques, including cultural, biological, and chemical controls, to manage pest populations in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
🚨 Note: When handling pesticides like dimethoate, it is crucial to follow all safety precautions to minimize exposure and risk of adverse health effects.
Regulations and Safety Standards
Regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have established safety standards and guidelines for the use of dimethoate. These regulations include limits on the amount of dimethoate that can be used, requirements for personal protective equipment, and guidelines for the safe disposal of waste.
| Agency | Safety Standard |
|---|---|
| EPA | Establishes tolerance levels for dimethoate residues on crops |
| WHO | Provides guidelines for the safe use of dimethoate in public health programs |
In summary, dimethoate is a widely used insecticide that poses significant health hazards to humans, wildlife, and the environment. While it is effective in controlling pests, its use must be carefully managed to minimize exposure and risk of adverse health effects. By understanding the health hazards of dimethoate, taking measures to mitigate its effects, and exploring safer alternatives, we can work towards creating a healthier and more sustainable environment.
What is dimethoate used for?
+
Dimethoate is used as an insecticide and acaricide to control a wide range of pests in agricultural and non-agricultural settings.
What are the health hazards of dimethoate?

+
The health hazards of dimethoate include neurological effects, reproductive and developmental effects, and potential cancer concerns.
How can I minimize exposure to dimethoate?

+
To minimize exposure to dimethoate, follow the instructions provided on the label, use personal protective equipment, and avoid consumption of contaminated food and water.
Related Terms:
- dimethoate uses in agriculture
- dimethoate chemicals
- is dimethoate soluble
- dimethoate fact sheet
- dimethoate hsg 20 pdf
- dimethoate pesticide uses



