Health
Discrimination Affects Health

Introduction to Discrimination and Health
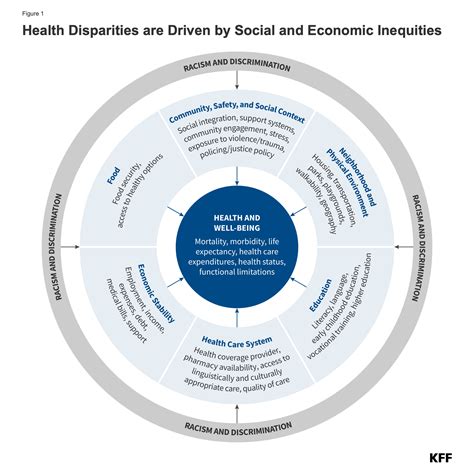
Discrimination is a pervasive issue that affects individuals from all walks of life, and its impact extends beyond the social and economic spheres to have a profound effect on physical and mental health. The experience of being discriminated against, whether based on race, gender, sexual orientation, age, or any other characteristic, can lead to a range of health problems. This blog post aims to explore the complex relationship between discrimination and health, highlighting the key pathways through which discrimination affects health outcomes and discussing potential strategies for mitigating these effects.
Understanding Discrimination
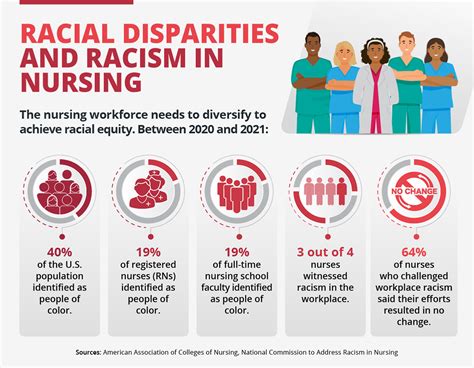
Before diving into the health impacts of discrimination, it’s essential to understand what discrimination entails. Discrimination refers to the unjust or prejudicial treatment of different categories of people, especially on the grounds of race, age, sex, or disability. It can be institutional, interpersonal, or internalized, affecting individuals in various aspects of their lives, from employment and education to healthcare and social interactions. The perception of being discriminated against can evoke strong emotional responses, including feelings of anger, sadness, fear, and hopelessness, which can have lasting effects on an individual’s well-being.
Pathways Through Which Discrimination Affects Health

Discrimination affects health through several pathways: - Social and Economic Disadvantage: Discrimination can limit access to resources such as education, employment, and healthcare, leading to social and economic disadvantage. Individuals who experience discrimination may have lower incomes, less access to healthcare, and higher levels of stress, all of which can negatively impact health. - Psychological Stress: The experience of discrimination is a significant source of psychological stress. Chronic stress can lead to a range of health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. - Health Behaviors: Discrimination can influence health behaviors, with individuals who experience discrimination possibly engaging in unhealthy coping mechanisms such as substance abuse or avoiding healthcare services due to mistrust or past negative experiences. - Access to Healthcare: Discrimination can affect the quality of care received. Healthcare providers may hold biases that influence the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases, leading to disparities in health outcomes.
Health Outcomes Associated with Discrimination
The health outcomes associated with discrimination are varied and can be severe. Some of the most notable include: - Mental Health Disorders: Discrimination is linked to higher rates of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. - Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic stress resulting from discrimination can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. - Immune System Suppression: Prolonged exposure to stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. - Poor Health Behaviors: Discrimination can lead to poor health behaviors, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and substance abuse, which can further exacerbate health problems.
Strategies for Mitigating the Health Effects of Discrimination

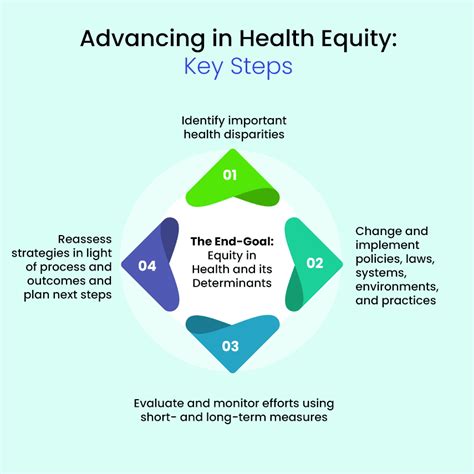
Mitigating the health effects of discrimination requires a multi-faceted approach that involves individuals, communities, and societies as a whole. Some strategies include: - Promoting Awareness and Education: Educating individuals about the effects of discrimination and promoting empathy and understanding can help reduce discriminatory behaviors. - Implementing Anti-Discriminatory Policies: Policies that prohibit discrimination in all forms can help create environments where individuals feel safe and supported. - Improving Access to Healthcare: Ensuring that all individuals have access to high-quality, non-discriminatory healthcare is crucial for mitigating the health effects of discrimination. - Supporting Mental Health: Providing resources and support for mental health, including counseling and therapy, can help individuals cope with the psychological impacts of discrimination.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, discrimination has a profound impact on health, affecting individuals in multiple dimensions. Understanding the pathways through which discrimination affects health and implementing strategies to mitigate these effects are crucial for promoting health equity. Future directions should focus on continued research into the health impacts of discrimination, the development of effective interventions, and the implementation of policies that promote equality and justice for all.
What are the primary ways through which discrimination affects health?

+
Discrimination affects health primarily through social and economic disadvantage, psychological stress, influencing health behaviors, and affecting access to healthcare.
How can we mitigate the health effects of discrimination?

+
Mitigating the health effects of discrimination involves promoting awareness and education, implementing anti-discriminatory policies, improving access to healthcare, and supporting mental health.
What role does psychological stress play in the health impacts of discrimination?
+
Psychological stress resulting from discrimination can lead to a range of health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Related Terms:
- health inequality discrimination
- role of discrimination in healthcare
- social determinants of health inequality
- impact of discrimination on health
- why is discrimination important
- discrimination definition healthcare



