5 Ways Dism Restore Health
Introduction to Dism Restore Health

The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool is a command-line utility used in Windows operating systems to service and manage Windows images, including the Windows Recovery Environment, Windows Setup, and Windows PE (Windows Preinstallation Environment). One of the key features of DISM is its ability to restore health to a Windows image by checking for corruption and replacing damaged files with healthy ones from a known good source, such as Windows Update or a mounted Windows image. In this article, we will delve into 5 ways to use the Dism Restore Health feature to troubleshoot and fix common issues in Windows.
Understanding DISM and Its Importance
Before diving into the ways to use Dism Restore Health, it’s essential to understand the importance of DISM in maintaining a healthy Windows system. DISM can be used to mount a Windows image, apply updates, drivers, and packages, and even to manage Windows features. Its ability to check for corruption and repair damaged system files makes it a crucial tool for troubleshooting and resolving issues that might be caused by corrupted system files.
5 Ways to Dism Restore Health

Here are five methods to utilize the Dism Restore Health feature, each tailored to different scenarios and needs:
1. Using DISM with Windows Update

To restore health using Windows Update as the source for repairing corrupted files, you can use the following command in the Command Prompt (run as administrator):
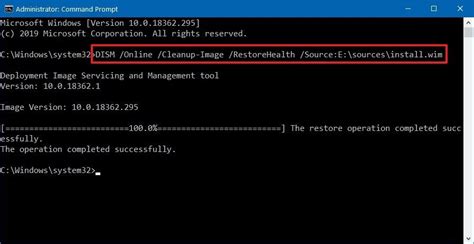
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:wim:X:\Sources\Install.wim /LimitAccess
Replace X with the drive letter where your Windows installation media is located. This method is useful when you have the original installation media available.
2. Using a Local Windows Image
If you have a local Windows image (e.g., install.wim) that you trust is healthy, you can use it as the source for repairing corrupted files. The command would look something like this:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:C:\Windows\Image /LimitAccess
Assuming the healthy Windows image is located in C:\Windows\Image.
3. Utilizing Windows Update Without Limiting Access
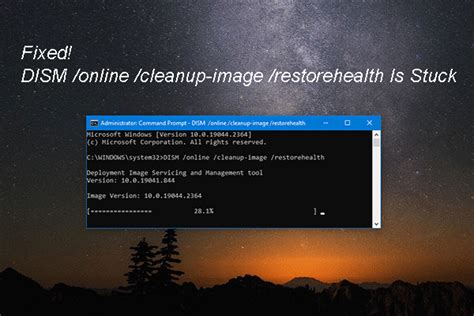
For situations where you want to use Windows Update without limiting access to other sources, you can omit the /LimitAccess option:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
This command allows DISM to use Windows Update and other sources to repair corrupted system files.
4. Using DISM with a Repair Source for a Specific Windows Version
If you are running a specific version of Windows (like Windows 10 or Windows 11) and have access to a healthy image of the same version, you can specify the source to use for repairs:
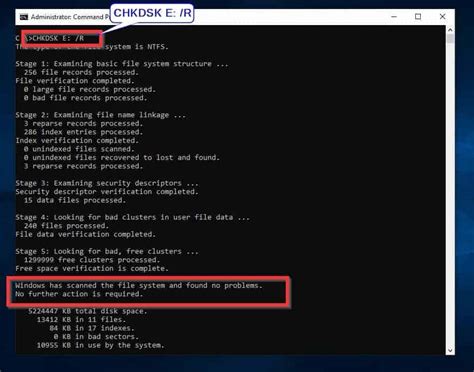
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:C:\Repair\Windows10.iso /LimitAccess
This assumes you have mounted a Windows 10 ISO file to C:\Repair\Windows10.iso and want to use it as the repair source.
5. Checking for Corruption Without Immediate Repair
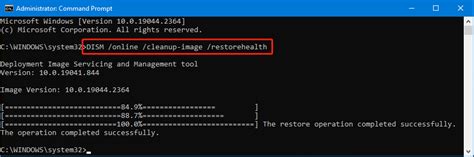
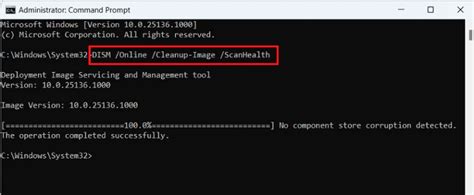
Sometimes, it’s useful to first check for corruption without immediately proceeding to repair. You can use the /ScanHealth option instead of /RestoreHealth:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
This command scans the Windows image for corruption but does not perform any repairs. It’s a good first step to understand the extent of corruption before deciding on the repair strategy.
Embedding Images for Better Understanding

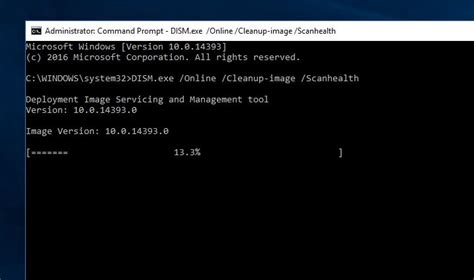
 This image illustrates how the DISM command with the
This image illustrates how the DISM command with the /RestoreHealth option is used in the Command Prompt, providing a visual aid to the steps described.
Table of DISM Commands

| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth | Restores health using Windows Update as the source. |
| Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:wim:X:\Sources\Install.wim | Uses a specified local Windows image as the repair source. |
| Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth | Scans the Windows image for corruption without repairing. |
📝 Note: Always ensure you are running the Command Prompt as an administrator to use DISM commands effectively.
To summarize, the Dism Restore Health feature is a powerful tool in the arsenal of Windows system administrators and users alike, offering multiple ways to restore the health of a Windows system by repairing corrupted system files. By understanding and applying these methods, users can effectively troubleshoot and resolve a wide range of issues that may arise due to system file corruption, ensuring their Windows installation remains stable and functional.
What is the primary function of the DISM tool in Windows?
+
The primary function of the DISM tool is to service and manage Windows images, including checking for corruption and repairing damaged files.
How do I use DISM to scan for corruption without repairing it immediately?

+
To scan for corruption without immediate repair, use the command Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth.
Can I use a local Windows image as the source for repairing corrupted files with DISM?
+
Yes, you can use a local Windows image as the source by specifying its location in the DISM command, for example, Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:wim:X:\Sources\Install.wim /LimitAccess.
Related Terms:
- Pemeriksa Berkas Sistem
- CHKDSK
- Malwarebytes
- Windows
- Windows Update
- Pemulihan Sistem



