Energy Poverty Impacts Health
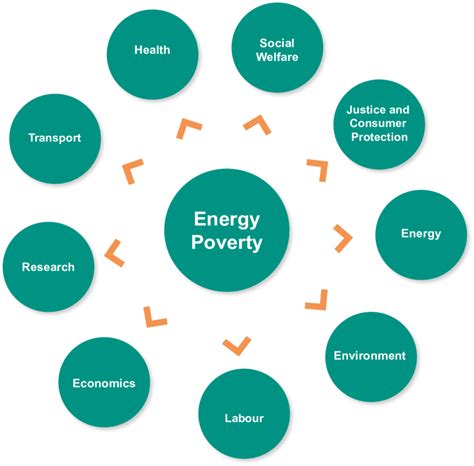
Introduction to Energy Poverty

Energy poverty, also known as fuel poverty, refers to a situation where individuals or households cannot afford to purchase the energy they need to maintain a satisfactory quality of life. This condition is often associated with low-income households that spend a disproportionate amount of their income on energy bills, leaving them with limited financial resources for other essential expenses such as food, healthcare, and education. Energy poverty can have severe implications on the health and well-being of affected individuals, making it a critical issue that requires immediate attention and action.
Health Impacts of Energy Poverty

The health impacts of energy poverty are far-reaching and devastating. When households cannot afford to heat their homes adequately, they are more likely to experience respiratory problems, such as bronchitis and asthma, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and the elderly. Moreover, energy poverty can lead to malnutrition and related health issues, as households may have to choose between paying energy bills and buying food. The stress and anxiety caused by energy poverty can also have significant mental health implications, including depression, anxiety disorders, and even suicidal tendencies.
Causes of Energy Poverty

Energy poverty is often the result of a combination of factors, including low income, high energy prices, and inefficient housing. In many cases, households may be living in poorly insulated homes with outdated heating systems, which can lead to high energy consumption and exorbitant energy bills. Additionally, lack of access to affordable energy sources, such as renewable energy, can exacerbate energy poverty, particularly in rural or remote areas.
Addressing Energy Poverty
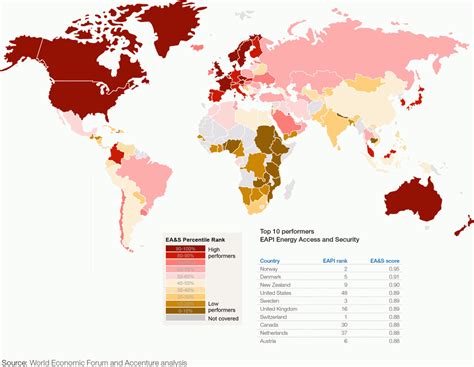
To address energy poverty, governments, organizations, and individuals must work together to implement effective solutions. Some possible strategies include: * Improving energy efficiency in homes through insulation, double glazing, and modern heating systems * Providing financial assistance to low-income households to help them pay energy bills * Investing in renewable energy sources to reduce energy costs and increase energy access * Implementing policies and regulations to protect vulnerable populations from energy poverty
🔍 Note: Governments and organizations can also provide education and training programs to help households reduce their energy consumption and manage their energy bills more effectively.
Case Studies and Examples

Several countries have implemented successful programs to address energy poverty. For example, the UK’s Winter Fuel Payment scheme provides financial assistance to low-income households to help them pay energy bills during the winter months. Similarly, the US’s Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) provides funding to help low-income households pay energy bills and improve energy efficiency in their homes.
| Country | Program | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UK | Winter Fuel Payment | Financial assistance to low-income households to pay energy bills during winter |
| US | LIHEAP | Funding to help low-income households pay energy bills and improve energy efficiency |

Future Directions and Recommendations

To effectively address energy poverty, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive and multifaceted approach that involves governments, organizations, and individuals. Some recommendations include: * Conducting thorough assessments of energy poverty levels and impacts * Developing targeted policies and programs to address energy poverty * Investing in energy efficiency and renewable energy sources * Providing education and training programs to help households reduce energy consumption and manage energy bills
As we move forward, it is crucial to prioritize the health and well-being of individuals and households affected by energy poverty. By working together and implementing effective solutions, we can reduce the impacts of energy poverty and create a more equitable and sustainable energy future for all.
In summary, energy poverty has severe implications for the health and well-being of affected individuals, and it is essential to address this issue through a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. By implementing effective solutions, providing financial assistance, and investing in energy efficiency and renewable energy sources, we can reduce the impacts of energy poverty and create a more equitable and sustainable energy future.
What is energy poverty?

+
Energy poverty, also known as fuel poverty, refers to a situation where individuals or households cannot afford to purchase the energy they need to maintain a satisfactory quality of life.
What are the health impacts of energy poverty?

+
The health impacts of energy poverty are far-reaching and devastating, including respiratory problems, malnutrition, and related health issues, as well as significant mental health implications.
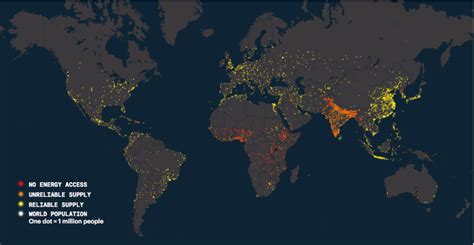
How can energy poverty be addressed?
+
Energy poverty can be addressed through a comprehensive and multifaceted approach, including improving energy efficiency, providing financial assistance, investing in renewable energy sources, and implementing policies and regulations to protect vulnerable populations.
Related Terms:
- Fuel poverty systematic review
- energy poverty in the world
- what is energy poverty definition
- energy poverty around the world
- examples of energy poverty
- energy poverty theory



