Gatekeeper Role in Health Insurance

Introduction to Gatekeeper Role in Health Insurance
The gatekeeper role in health insurance refers to a system where a primary care physician (PCP) acts as an intermediary between the patient and specialist care. This role is designed to improve the quality of care and reduce healthcare costs by ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care for their conditions. The gatekeeper model has been widely adopted in many countries, including the United States, as a way to manage healthcare resources and enhance patient outcomes.
Key Components of the Gatekeeper Role

The gatekeeper role involves several key components, including: * Primary care physician (PCP) selection: Patients select a PCP from a network of participating providers. * Referral requirements: Patients must obtain a referral from their PCP to see a specialist. * Care coordination: The PCP coordinates care with specialists and other healthcare providers. * Continuity of care: The PCP provides ongoing care and monitoring for patients.
Benefits of the Gatekeeper Role
The gatekeeper role offers several benefits, including: * Improved quality of care: PCPs can ensure that patients receive evidence-based care and follow established treatment guidelines. * Reduced healthcare costs: By coordinating care and reducing unnecessary referrals, the gatekeeper model can help reduce healthcare costs. * Enhanced patient satisfaction: Patients who have a consistent relationship with their PCP tend to be more satisfied with their care. * Better health outcomes: The gatekeeper model can lead to better health outcomes by ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Challenges and Limitations of the Gatekeeper Role
Despite its benefits, the gatekeeper role also presents several challenges and limitations, including: * Restrictive access to specialist care: Patients may experience delays or difficulties in accessing specialist care, particularly if their PCP is not readily available. * Increased administrative burden: The gatekeeper model can create additional administrative tasks for PCPs, such as managing referrals and coordinating care. * Patient dissatisfaction: Some patients may feel that the gatekeeper model restricts their access to care or creates unnecessary barriers to specialist treatment.
Examples of Gatekeeper Models
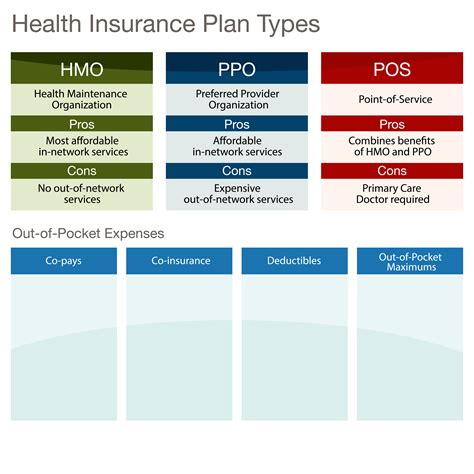
There are several examples of gatekeeper models in use, including: * Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs are a type of health insurance plan that requires patients to select a PCP and obtain referrals for specialist care. * Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs are a type of health insurance plan that allows patients to see any healthcare provider, but may require a referral from a PCP for specialist care. * Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): ACOs are a type of healthcare organization that brings together providers to coordinate care and improve patient outcomes.
| Gatekeeper Model | Description |
|---|---|
| HMO | Requires patients to select a PCP and obtain referrals for specialist care |
| PPO | Allows patients to see any healthcare provider, but may require a referral from a PCP for specialist care |
| ACO | Brings together providers to coordinate care and improve patient outcomes |

💡 Note: The gatekeeper role is not without its challenges, and healthcare organizations must carefully balance the need for cost control with the need for patient access to care.
Future Directions for the Gatekeeper Role

The gatekeeper role is likely to continue evolving in response to changes in the healthcare landscape. Some potential future directions for the gatekeeper role include: * Increased use of technology: Electronic health records and telemedicine may enhance the gatekeeper model by improving communication and coordination between providers. * Greater emphasis on patient-centered care: The gatekeeper model may need to adapt to prioritize patient-centered care and shared decision-making. * More flexible referral requirements: Some healthcare organizations may adopt more flexible referral requirements to improve patient access to care.
As the healthcare system continues to evolve, the gatekeeper role will likely play an important part in shaping the delivery of care. By understanding the benefits and challenges of the gatekeeper model, healthcare organizations can work to create a more efficient and effective system that prioritizes patient needs.
The main points to take away from this discussion are that the gatekeeper role is a critical component of health insurance, designed to improve the quality of care and reduce healthcare costs. While it presents several benefits, including improved quality of care and reduced healthcare costs, it also has its challenges and limitations, such as restrictive access to specialist care and increased administrative burden. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the gatekeeper role will likely adapt to prioritize patient-centered care, technology, and flexibility.
What is the gatekeeper role in health insurance?
+
The gatekeeper role refers to a system where a primary care physician (PCP) acts as an intermediary between the patient and specialist care.
What are the benefits of the gatekeeper role?

+
The benefits of the gatekeeper role include improved quality of care, reduced healthcare costs, enhanced patient satisfaction, and better health outcomes.
What are the challenges and limitations of the gatekeeper role?

+
The challenges and limitations of the gatekeeper role include restrictive access to specialist care, increased administrative burden, and patient dissatisfaction.
Related Terms:
- gatekeeper model
- what is a gatekeeper system
- gatekeeper insurance meaning
- gatekeeper examples
- gatekeeper model insurance plans
- role of gatekeeper