GI Bill Covers College Tuition
Introduction to the GI Bill
The GI Bill is a vital educational benefit provided to veterans, service members, and their families. It has been a cornerstone of American veterans’ benefits since its inception in 1944, aiming to assist those who have served in the military to cover the costs associated with pursuing higher education. The primary goal of the GI Bill is to help individuals achieve their educational and career goals, thereby enhancing their quality of life and contributing positively to society. Education is a key component of the transition from military to civilian life, and the GI Bill plays a pivotal role in this process.
Types of GI Bill Benefits

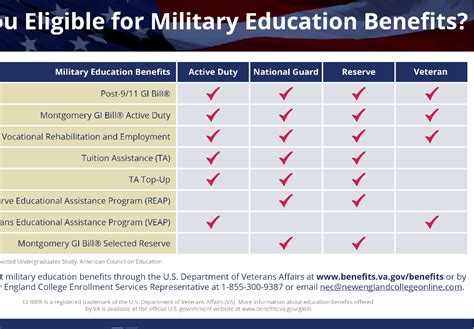
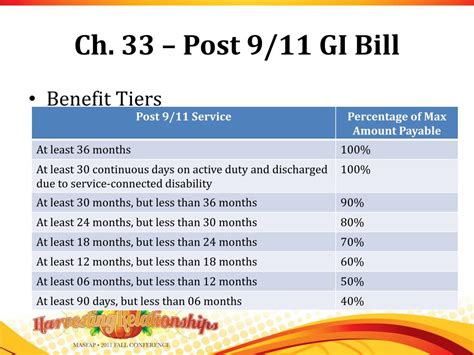
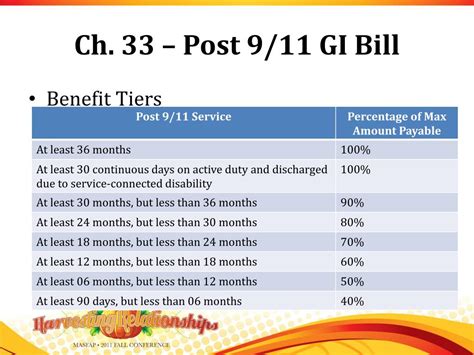
There are several types of GI Bill benefits available, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and benefits. The most common include: - Post-9⁄11 GI Bill (Chapter 33): This is the most comprehensive education benefit package, covering up to 100% of tuition and fees for public in-state schools, and providing a monthly housing stipend and an annual books and supplies stipend. - Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD, Chapter 30): This benefit provides up to 36 months of education benefits, which can be used for degree and certificate programs, flight training, apprenticeships, on-the-job training, and correspondence courses. - Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR, Chapter 1606): Designed for members of the Selected Reserve, this benefit can be used to pursue higher education or vocational training. - Dependent Education Assistance Program (DEA, Chapter 35): This program offers education assistance to spouses and children of veterans who are permanently and totally disabled due to their service, or who died as a result of their service.
Eligibility for GI Bill Benefits

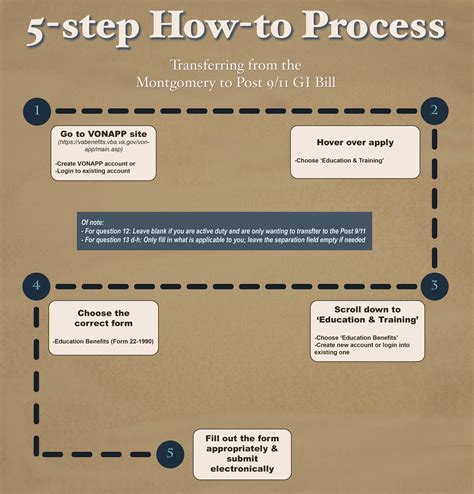
Eligibility for the GI Bill varies depending on the specific benefit. Generally, active-duty service members, veterans, and selected reserve members may be eligible. Additionally, dependents of service members who are eligible for Transfer of Entitlement can also receive benefits under the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill. The requirements include serving a certain amount of time in the military, being honorably discharged, or being a dependent of a service member who has transferred their benefits. It is essential to review the specific eligibility criteria for each type of GI Bill benefit, as they can differ significantly.
Applying for GI Bill Benefits
The application process for GI Bill benefits typically begins with submitting an application through the VA’s website or by visiting a regional office. Applicants will need to provide documentation, such as their DD Form 214 (discharge paperwork) and transcript from previous schools attended, if applicable. The VA will review the application and determine eligibility. Once approved, the veteran or their dependent can use the benefit to cover tuition and fees at an approved educational institution.
Coverage and Payments

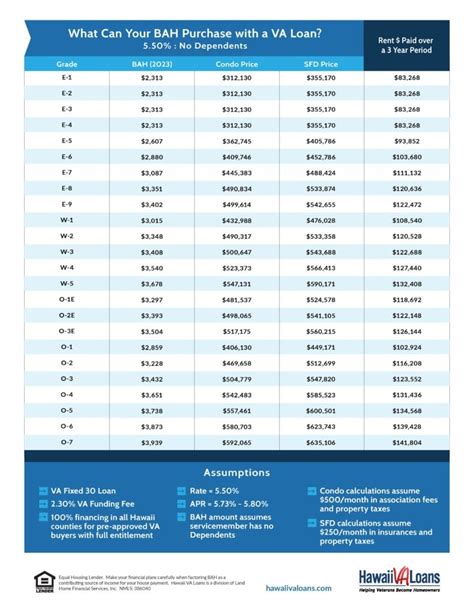
The GI Bill covers a significant portion of college tuition and fees, though the exact amount can vary based on the type of benefit, the institution, and the program of study. For the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, for example, the VA pays tuition and fees directly to the school, up to the in-state tuition and fees rate for public schools. For private or foreign schools, the VA will pay up to $26,042.81 for the 2022-2023 academic year. Additionally, students may receive a monthly housing allowance and an annual stipend for books and supplies. It’s crucial for beneficiaries to understand how their benefits are calculated and what expenses are covered versus those that are not.
Maximizing GI Bill Benefits
To maximize the benefits received from the GI Bill, individuals should: - Choose the right school: Ensure the institution is approved for GI Bill benefits and offers in-state tuition rates, if applicable. - Plan courses carefully: Only take courses that are required for the degree or certification program to avoid wasting benefits on unnecessary classes. - Use additional resources: Many states offer additional education benefits for veterans, and there are also numerous scholarships available. - Stay informed: Keep up-to-date with any changes in GI Bill benefits or eligibility criteria.
📚 Note: Beneficiaries should regularly check the VA's official website for the most current information regarding GI Bill benefits, as policies and benefit amounts can change.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the comprehensive nature of the GI Bill, challenges exist, including navigating the sometimes complex application and benefits process, ensuring timely payments, and dealing with any issues that arise during the course of study. Furthermore, the GI Bill does not cover all educational expenses (such as room and board for all students, or equipment and supplies for certain programs), and not all institutions or programs are eligible for GI Bill funding. Seeking guidance from a veterans’ service organization or the educational institution’s veterans’ office can be invaluable in addressing these challenges.
Conclusion Summary
In summary, the GI Bill is a powerful tool for veterans and their families to achieve their educational goals, covering a significant portion of college tuition and associated fees. With various types of benefits available, each tailored to different service backgrounds and educational pursuits, understanding the specifics of eligibility, application, and coverage is essential for maximizing these benefits. As veterans transition to civilian life, leveraging the GI Bill effectively can play a pivotal role in their successful reintegration and future success.
What types of education and training does the GI Bill cover?

+
The GI Bill covers a wide range of educational programs, including college degrees, vocational training, apprenticeships, on-the-job training, flight training, and correspondence courses, provided they are offered by an approved institution.
Can I use the GI Bill for online courses or distance learning?

+
Yes, the GI Bill can be used for online courses or distance learning programs, as long as the institution and program are approved for GI Bill benefits. However, the housing allowance under the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill may be affected for solely online students.
How long do I have to use my GI Bill benefits?

+
The timeframe for using GI Bill benefits varies depending on the type of benefit. Generally, benefits must be used within a certain number of years following separation from service, typically 10 to 15 years, depending on the specific GI Bill program.
Related Terms:
- current gi bill benefits
- gi bill paying for college
- full gi bill benefits
- gi bill rates 2025
- requirements to use gi bill
- gi bill tuition calculator