Gujarat Health Statistics
Introduction to Gujarat Health Statistics
Gujarat, a state located in the western part of India, has been making significant strides in the healthcare sector. The state’s health statistics provide valuable insights into the health status of its population, healthcare infrastructure, and the effectiveness of various health programs. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of Gujarat’s health statistics, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of the state’s healthcare system.
Demographic and Health Indicators

Gujarat’s health statistics are influenced by its demographic characteristics. The state has a population of over 60 million people, with a sex ratio of 919 females per 1,000 males. The population growth rate is 1.2%, which is lower than the national average. The state’s demographic and health indicators are as follows: * Crude Birth Rate (CBR): 20.5 per 1,000 population * Crude Death Rate (CDR): 6.1 per 1,000 population * Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): 30 per 1,000 live births * Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR): 70 per 100,000 live births * Life Expectancy at Birth: 69.5 years for males and 72.5 years for females
Healthcare Infrastructure

Gujarat has a well-developed healthcare infrastructure, with a mix of public and private healthcare providers. The state has: * Hospitals: 442 government hospitals and 1,444 private hospitals * Health Centers: 1,344 primary health centers, 312 community health centers, and 25 sub-district hospitals * Medical Colleges: 24 government medical colleges and 12 private medical colleges * Nursing Colleges: 144 nursing colleges
👨⚕️ Note: The healthcare infrastructure in Gujarat is constantly evolving, with new facilities being added and existing ones being upgraded.
Diseases and Health Conditions
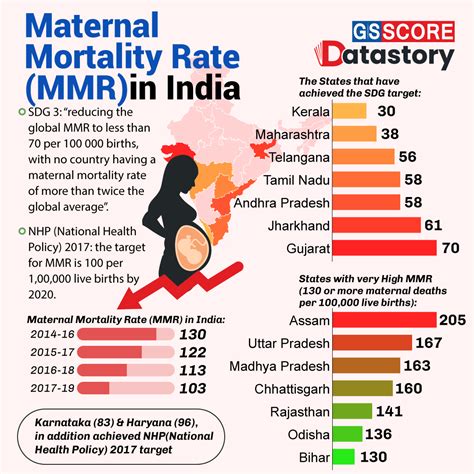
Gujarat’s health statistics reveal a high prevalence of certain diseases and health conditions. The top five causes of death in the state are: * Cardiovascular diseases: 24.1% * Cancer: 12.1% * Respiratory diseases: 10.3% * Accidents and injuries: 8.5% * Diabetes: 6.2%
Maternal and Child Health

Maternal and child health is a critical aspect of Gujarat’s health statistics. The state has made significant progress in reducing maternal and infant mortality rates. However, there is still room for improvement. Key indicators include: * Institutional delivery rate: 94.1% * Antenatal care coverage: 85.1% * Postnatal care coverage: 74.1% * Exclusive breastfeeding rate: 55.1%
Challenges and Opportunities
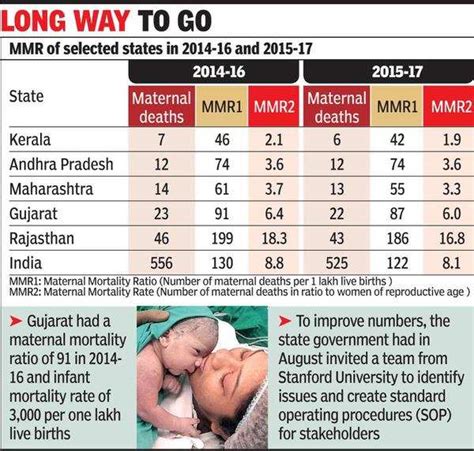
Despite the progress made, Gujarat’s health statistics highlight several challenges and opportunities for improvement. These include: * Rural-urban disparities: Healthcare access and quality vary significantly between rural and urban areas. * Shortage of healthcare professionals: Gujarat faces a shortage of doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals, particularly in rural areas. * Non-communicable diseases: The state needs to focus on preventing and managing non-communicable diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and diabetes. * Mental health: Mental health is a growing concern in Gujarat, and the state needs to strengthen its mental health services.
Way Forward
To improve Gujarat’s health statistics, the state government and healthcare stakeholders must work together to address the challenges and opportunities highlighted above. Key strategies include: * Strengthening healthcare infrastructure: Upgrading existing healthcare facilities and adding new ones, particularly in rural areas. * Increasing healthcare workforce: Recruiting and retaining healthcare professionals, especially in rural areas. * Promoting preventive care: Encouraging healthy behaviors and providing preventive care services to reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases. * Enhancing mental health services: Strengthening mental health services and promoting mental well-being across the state.
💡 Note: The way forward for Gujarat's health statistics requires a collaborative effort from the government, healthcare providers, and the community.
In summary, Gujarat’s health statistics provide a comprehensive overview of the state’s health status, healthcare infrastructure, and the effectiveness of various health programs. While there are challenges to be addressed, the state has made significant progress in improving healthcare outcomes. By working together and implementing strategic interventions, Gujarat can continue to improve its health statistics and provide better healthcare services to its population.
What is the current status of Gujarat’s healthcare infrastructure?

+
Gujarat has a well-developed healthcare infrastructure, with a mix of public and private healthcare providers, including 442 government hospitals and 1,444 private hospitals.
What are the top causes of death in Gujarat?
+
The top five causes of death in Gujarat are cardiovascular diseases, cancer, respiratory diseases, accidents and injuries, and diabetes.
What is the institutional delivery rate in Gujarat?

+
The institutional delivery rate in Gujarat is 94.1%, indicating a high percentage of births taking place in healthcare facilities.
Related Terms:
- gujarat health statistics
- NFHS 5 Gujarat fact sheet
- nfhs 5 gujarat pdf
- MMR of Gujarat 2024
- Most common disease in Gujarat
- MMR in Gujarat 2023



