Health Claim Rule for Supplements

Introduction to Health Claims for Supplements

The dietary supplement industry has experienced significant growth over the years, with more people turning to supplements to maintain or improve their health. As the industry expands, so does the complexity of regulations surrounding health claims made by supplement manufacturers. In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are the primary agencies responsible for overseeing the marketing and labeling of dietary supplements. Understanding the health claim rule for supplements is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers to ensure compliance with regulations and to make informed decisions.
Understanding Health Claims

Health claims are statements made on the label or in the marketing materials of a dietary supplement that suggest a relationship between the supplement and reducing the risk of a disease or health-related condition. There are several types of claims that can be made, including health claims, nutrient content claims, and structure/function claims. Health claims are the most strictly regulated and require significant scientific evidence to support the claim.
Types of Claims

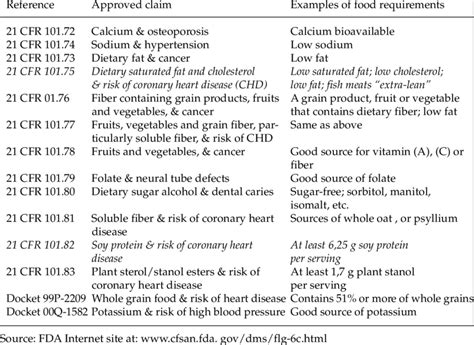
- Health Claims: These claims describe a relationship between a dietary supplement ingredient and the reduced risk of a disease or health-related condition. For example, “Calcium may reduce the risk of osteoporosis.” - Nutrient Content Claims: These claims describe the level of a nutrient in a dietary supplement. For example, “Good source of vitamin C.” - Structure/Function Claims: These claims describe the effect of a dietary supplement on the structure or function of the body. For example, “Supports healthy bones.”
Regulations Surrounding Health Claims

The FDA is responsible for ensuring that health claims made on dietary supplement labels are truthful and not misleading. The agency requires that health claims be supported by significant scientific agreement among experts in the field. This standard is higher than what is required for structure/function claims, which do not need FDA approval before they are made.
📝 Note: Manufacturers must have competent and reliable scientific evidence to support any health-related claim made about their product.
Guidelines for Making Health Claims

To make a health claim, a manufacturer must follow specific guidelines: - Submit a health claim petition to the FDA with sufficient scientific evidence to support the claim. - Ensure that the claim is specific and does not imply a benefit that is not supported by the evidence. - Use qualified health claims when there is emerging evidence for a relationship between a dietary supplement ingredient and a disease, but the evidence is not yet conclusive.
Consequences of Non-Compliance

Failure to comply with the regulations surrounding health claims can result in serious consequences, including: - Warning letters from the FDA or FTC. - Product recalls or seizures. - Fines or penalties for violating federal regulations. - Damage to a company’s reputation and loss of consumer trust.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with health claim regulations is crucial for the dietary supplement industry. It helps ensure that consumers are not misled by false or unsubstantiated claims, thereby protecting public health. Manufacturers must stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and ensure that any claims made about their products are supported by robust scientific evidence.
Future of Health Claims for Supplements

As the dietary supplement industry continues to evolve, regulations surrounding health claims are likely to become even more stringent. The use of new and emerging technologies, such as genomics and metabolomics, may provide new avenues for understanding the effects of dietary supplements on health and for making health claims. However, these advancements will also require manufacturers to be vigilant in ensuring that any claims made are supported by the best available scientific evidence.
What is the primary agency responsible for overseeing health claims made by dietary supplement manufacturers in the United States?

+
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) are the primary agencies responsible for overseeing the marketing and labeling of dietary supplements, including health claims.
What type of claim requires significant scientific agreement among experts in the field?
+
Health claims require significant scientific agreement among experts in the field to be approved by the FDA.
What are the consequences for a manufacturer that does not comply with health claim regulations?

+
Consequences can include warning letters, product recalls or seizures, fines or penalties, and damage to a company's reputation and loss of consumer trust.
In summary, understanding and complying with the health claim rule for supplements is essential for manufacturers to avoid regulatory issues and for consumers to make informed decisions about their health. As the industry and regulations evolve, staying updated on the latest requirements and ensuring that claims are supported by robust scientific evidence will be critical for success and public health protection.
Related Terms:
- fda approved health claims
- dietary supplement disclaimer
- certified health claims pdf
- nutrient content claims
- authorized health claims
- nutrient content claim form



