Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
Introduction to Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
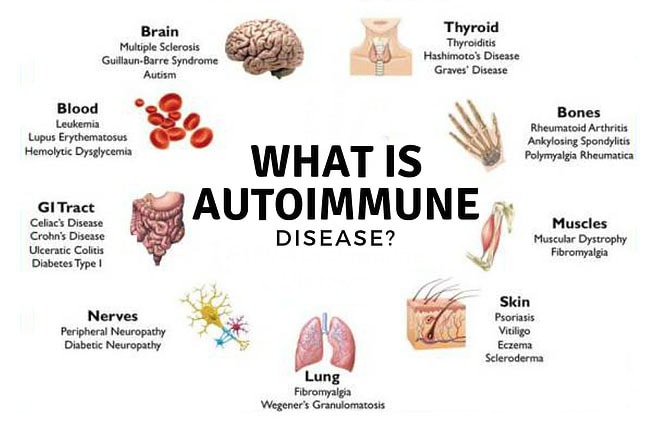
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, tissues, and organs. These diseases can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, muscles, and other organs. There are over 80 known autoimmune diseases, with some of the most common being rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. However, a significant concern in the medical field is the disparities in healthcare that individuals with autoimmune diseases face, particularly among different racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups.
Prevalence of Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
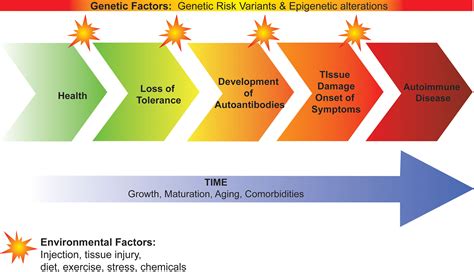
Research has shown that autoimmune diseases disproportionately affect certain populations, including women, minorities, and individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds. For example, lupus is more prevalent among African American women than among white women. Similarly, rheumatoid arthritis is more common among Native American and Alaskan Native populations than among other racial groups. These disparities are often attributed to a combination of factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and access to healthcare.
Factors Contributing to Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
Several factors contribute to the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare. Some of the key factors include: * Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic mutations can increase an individual’s risk of developing an autoimmune disease. These mutations may be more prevalent in specific racial or ethnic groups. * Environmental exposures: Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, has been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune diseases. * Access to healthcare: Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face barriers in accessing healthcare, including lack of health insurance, high copays, and limited access to specialists. * Socioeconomic status: Lower socioeconomic status can lead to increased stress, poor nutrition, and limited access to healthcare, all of which can exacerbate autoimmune disease symptoms.
Impact of Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
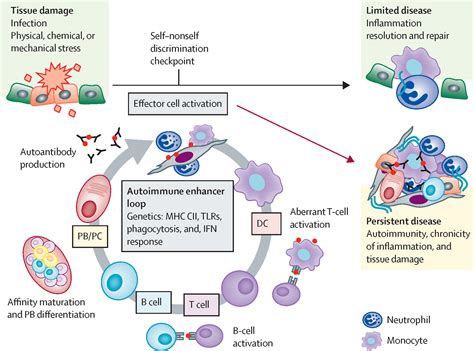
The disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare can have significant consequences, including: * Poor health outcomes: Delayed diagnosis and inadequate treatment can lead to poor health outcomes, including increased morbidity and mortality. * Increased healthcare costs: The cost of treating autoimmune diseases can be high, particularly if diagnosis is delayed or treatment is inadequate. * Reduced quality of life: Autoimmune diseases can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, including their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in daily activities.
Addressing Autoimmune Disease Health Disparities
To address the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare, several strategies can be employed, including: * Increasing awareness: Educating healthcare providers and the general public about autoimmune diseases and the disparities in healthcare can help to increase awareness and promote early diagnosis and treatment. * Improving access to healthcare: Expanding access to healthcare, including increasing the number of healthcare providers and reducing costs, can help to reduce disparities in healthcare. * Developing targeted interventions: Developing interventions that are tailored to specific populations, such as culturally sensitive education programs, can help to reduce disparities in healthcare.
| Disease | Prevalence | Disparities |
|---|---|---|
| Lupus | 1 in 1,000 | African American women are 3 times more likely to develop lupus than white women |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | 1 in 100 | Native American and Alaskan Native populations are 2 times more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis than other racial groups |
| Multiple Sclerosis | 1 in 1,000 | African American individuals are more likely to experience severe symptoms and disability than white individuals |
💡 Note: These statistics highlight the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare and the need for targeted interventions to address these disparities.
Future Directions
To reduce the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare, future research should focus on developing targeted interventions, improving access to healthcare, and increasing awareness about autoimmune diseases. Additionally, healthcare providers should be trained to recognize and address the unique needs of diverse populations. By working together, we can reduce the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare and improve health outcomes for all individuals.
In summary, autoimmune disease health disparities are a significant concern, with certain populations facing a higher risk of developing autoimmune diseases and experiencing poor health outcomes. By understanding the factors that contribute to these disparities and developing targeted interventions, we can work towards reducing the disparities in autoimmune disease healthcare and improving health outcomes for all individuals. The importance of addressing these disparities cannot be overstated, as it has the potential to improve the lives of millions of people worldwide. Ultimately, it is crucial that we continue to prioritize research and education on autoimmune diseases, ensuring that all individuals have access to the care and support they need to manage their condition effectively.
Related Terms:
- Female autoimmune diseases
- Autoimmune disease by race
- African American autoimmune diseases
- Autoimmune disease news
- X linked autoimmune disease
- Autoimmune disease rates by state



