5 Jobs Strengthening Health Systems

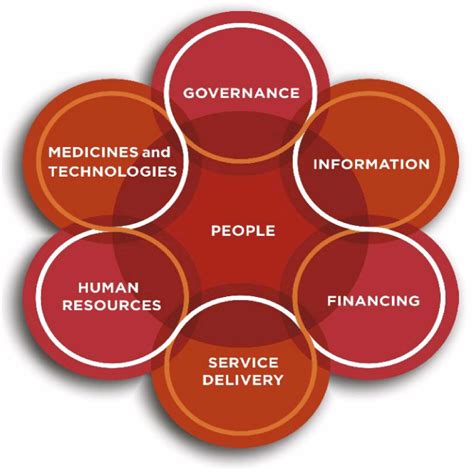
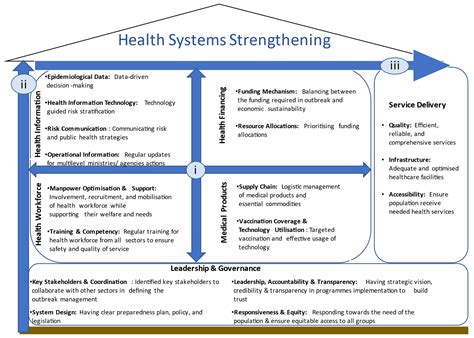
Introduction to Health Systems Strengthening

The global health landscape is constantly evolving, with new challenges and opportunities emerging every day. One of the key factors in ensuring that healthcare is accessible, affordable, and effective is the presence of strong health systems. Health systems strengthening refers to the process of improving the performance of health systems, enabling them to provide high-quality services, and ultimately, better health outcomes. There are several jobs that play a critical role in strengthening health systems, and in this article, we will explore five of them.
Job 1: Health Systems Manager

A health systems manager is responsible for overseeing the planning, implementation, and evaluation of health programs and services. Their primary goal is to ensure that health systems are efficient, effective, and responsive to the needs of the population. Some of the key responsibilities of a health systems manager include: * Developing and implementing health policies and strategies * Managing health budgets and resources * Coordinating with healthcare providers, organizations, and stakeholders * Monitoring and evaluating health system performance * Identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes
Job 2: Public Health Specialist

A public health specialist focuses on preventing disease and promoting health at the population level. They work to identify health risks, develop interventions, and implement programs to address these risks. Some of the key responsibilities of a public health specialist include: * Conducting research and analysis to identify health trends and risks * Developing and implementing public health programs and interventions * Collaborating with healthcare providers, organizations, and stakeholders * Evaluating the effectiveness of public health programs * Developing policies and guidelines to promote public health
Job 3: Health Informatics Specialist
A health informatics specialist uses information technology to improve the delivery of healthcare services. They design, implement, and evaluate health information systems, ensuring that they are efficient, effective, and secure. Some of the key responsibilities of a health informatics specialist include: * Designing and implementing health information systems * Developing and maintaining electronic health records * Analyzing health data to inform decision-making * Ensuring the security and confidentiality of health information * Providing training and support to healthcare providers on health information systems
Job 4: Health Economist

A health economist analyzes the economic aspects of health and healthcare, providing insights that inform decision-making and policy development. They examine the costs and benefits of healthcare interventions, programs, and policies, and identify opportunities to improve efficiency and effectiveness. Some of the key responsibilities of a health economist include: * Conducting economic analysis of healthcare interventions and programs * Developing economic models to predict health outcomes and costs * Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of healthcare programs and policies * Providing advice on resource allocation and prioritization * Collaborating with healthcare providers, organizations, and stakeholders to inform decision-making
Job 5: Global Health Professional
A global health professional works to improve health outcomes in low- and middle-income countries, addressing global health challenges such as infectious diseases, maternal and child health, and non-communicable diseases. They collaborate with international organizations, governments, and local stakeholders to develop and implement health programs and policies. Some of the key responsibilities of a global health professional include: * Developing and implementing global health programs and policies * Collaborating with international organizations, governments, and local stakeholders * Conducting research and analysis to inform global health decision-making * Providing technical assistance and capacity-building to local health systems * Advocating for global health issues and promoting awareness and action
🌎 Note: These jobs often require a combination of education, training, and experience in fields such as public health, health administration, economics, and international development.
In addition to these jobs, there are many other careers that contribute to strengthening health systems, including healthcare providers, policymakers, researchers, and community health workers. By working together, these professionals can help ensure that health systems are strong, resilient, and responsive to the needs of the population.
To further illustrate the importance of these jobs, consider the following table, which highlights some of the key challenges and opportunities in health systems strengthening:
| Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| Weak health infrastructure | Investing in health infrastructure development |
| Limited access to healthcare | Implementing community-based health programs |
| Shortage of healthcare workers | Providing training and capacity-building for healthcare workers |
| Inadequate health information systems | Developing and implementing health information systems |

As we reflect on the importance of these jobs, it becomes clear that strengthening health systems is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires the collaboration and expertise of many different professionals. By working together, we can build stronger, more resilient health systems that provide high-quality care to all individuals, regardless of their background or circumstances. The key takeaways from this discussion include the importance of health systems management, public health, health informatics, health economics, and global health in strengthening health systems. These fields, along with others, are crucial to ensuring that health systems are effective, efficient, and equitable.
Related Terms:
- health care system strengthening jobs
- health systems strengthening unemployment
- health system management degree jobs
- health systems strengthening unjobs
- unjobs in health care systems
- health system strengthening strategies