Military
US Army Age History

Introduction to the US Army Age History

The United States Army has a rich and diverse history that spans over two centuries. From its humble beginnings to the present day, the US Army has undergone significant transformations, shaped by the events and challenges of each era. One aspect of this history is the evolution of the age requirements for enlistment and service, which have changed over time in response to societal, technological, and military needs.
Early Years: American Revolution to the Civil War

During the American Revolution, the Continental Army, precursor to the US Army, did not have strict age limits for enlistment. Young men and even boys as young as 15 or 16 could join the army, although it was not common. The focus was more on ability and willingness to fight rather than age. As the young nation grew, so did its military. By the time of the Civil War, the age range for soldiers was generally between 18 and 45, though again, these were not hard and fast rules, and exceptions were made based on need and individual circumstances.
World War I and the Interwar Period

With the advent of World War I, the US Army began to formalize its age requirements. The draft, implemented through the Selective Service Act of 1917, required men between the ages of 21 and 30 to register, though later amendments expanded the age range to 18 to 45. The interwar period saw a continuation of these policies, with the US Army maintaining a relatively traditional age structure for its personnel.
World War II and the Post-War Era

During World War II, the US Army lowered its minimum enlistment age to 18, and with the introduction of the draft, men up to the age of 45 were eligible for service. The post-war era saw significant changes in the US Army’s approach to age. The Universal Military Training and Service Act of 1951 lowered the draft age to 18.5, reflecting a broader societal trend towards recognizing the maturity and responsibility of younger adults.
Vietnam War and the End of the Draft
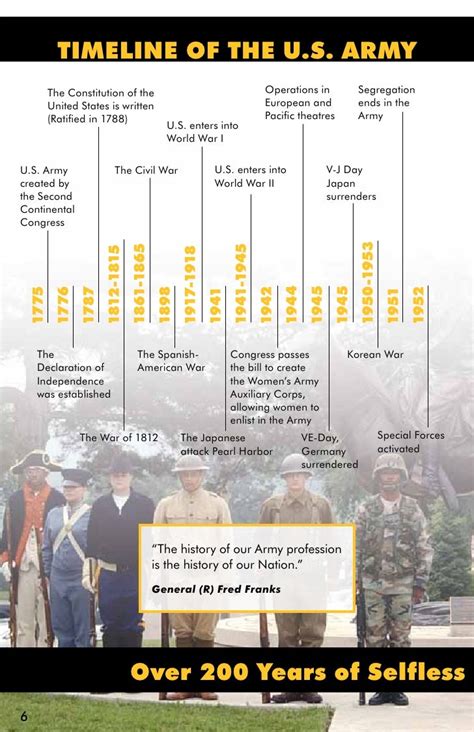
The Vietnam War marked a significant turning point in the US Army’s approach to age and service. The draft continued to play a major role, with men aged 18 to 25 being eligible for conscription. However, towards the end of the Vietnam War, the US moved towards an all-volunteer force, ending the draft in 1973. This shift allowed the army to reconsider its age policies, focusing on attracting and retaining high-quality volunteers across a range of ages.
Modern Era: Age and Service in the US Army

Today, the US Army maintains specific age requirements for enlistment and commissioning. For enlisted personnel, the typical age range is between 17 and 35, though some specialties allow for older enlistees. Officers typically must be between 17 and 32 when they receive their commission, though again, there are exceptions for certain roles and those with prior service. The emphasis on quality over quantity and the recognition of the value of mature, experienced personnel have led to a more flexible approach to age within the army.
Table: Age Requirements for US Army Service

| Service Component | Minimum Age | Maximum Age |
|---|---|---|
| Enlisted Personnel | 17 | 35 (varies by specialty) |
| Officer Candidates | 17 | 32 (varies by commissioning path) |
| Warrant Officer Candidates | 17 | 46 (varies by specialty) |

📝 Note: These ages are general guidelines and can vary based on the specific role, the individual's background, and current army policies.
Conclusion and Reflection

The history of age and service in the US Army reflects broader societal changes, technological advancements, and the evolving nature of warfare. From the flexible age policies of the early years to the more structured requirements of today, the army has sought to balance its needs with the capabilities and potential of its personnel. As the US Army looks to the future, its approach to age will continue to adapt, ensuring that it remains a vibrant, effective, and inclusive institution.
What is the current minimum age for enlistment in the US Army?

+
The current minimum age for enlistment in the US Army is 17, with parental consent required for those under 18.
Are there any exceptions to the maximum age limit for enlistment?

+
Yes, some specialties within the US Army allow for enlistees older than 35, and prior service members may also be eligible for re-enlistment beyond the typical age limits.
How has the US Army’s approach to age changed over time?

+
The US Army’s approach to age has evolved significantly, from relatively flexible policies in the early years to more structured requirements today, reflecting societal changes, technological advancements, and the needs of the military.
Related Terms:
- origin of the us army
- united states army founding date
- when was the military established
- army 250th birthday
- us army facts history
- us army founding date



