USAID Integrated Health Care Solutions
Introduction to USAID Integrated Health Care Solutions
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has been at the forefront of providing integrated health care solutions to countries around the world. With a focus on improving the health and well-being of vulnerable populations, USAID has developed a comprehensive approach to health care that addresses the complex needs of individuals and communities. This approach is built on the principles of integration, equity, and sustainability, and is guided by a deep understanding of the social, economic, and cultural factors that influence health outcomes.
Key Components of USAID Integrated Health Care Solutions

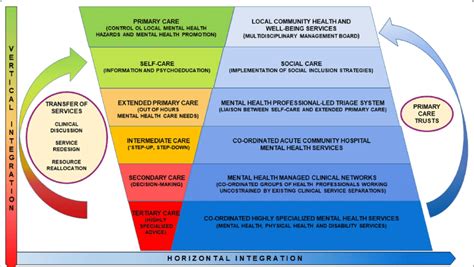
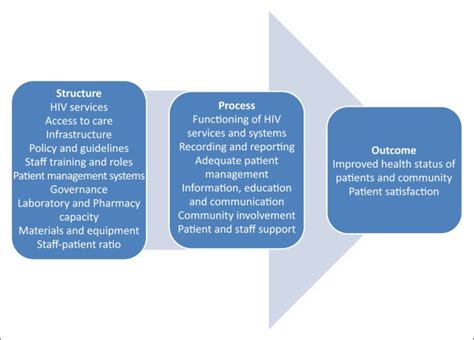
USAID’s integrated health care solutions are designed to address the full range of health needs, from prevention and treatment to care and support. The key components of this approach include: * Health systems strengthening: USAID works with countries to strengthen their health systems, including the development of health policies, laws, and regulations, as well as the training of health care providers and the establishment of health information systems. * Service delivery: USAID supports the delivery of high-quality health services, including maternal and child health, family planning, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria prevention and treatment. * Community engagement: USAID engages with communities to promote health awareness, education, and behavior change, and to support the development of community-based health care programs. * Partnerships and collaboration: USAID partners with governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector to leverage resources, expertise, and knowledge to achieve common health goals.
Benefits of USAID Integrated Health Care Solutions

The benefits of USAID’s integrated health care solutions are numerous and far-reaching. Some of the key benefits include: * Improved health outcomes: By addressing the full range of health needs, USAID’s integrated health care solutions have been shown to improve health outcomes, including reduced morbidity and mortality rates. * Increased access to health care: USAID’s approach has increased access to health care for vulnerable populations, including women, children, and marginalized communities. * Enhanced efficiency and effectiveness: By streamlining health services and promoting coordination and collaboration, USAID’s integrated health care solutions have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of health care delivery. * Sustainability: USAID’s focus on building the capacity of local health systems and promoting community engagement has helped to ensure the sustainability of health care programs and services.
Success Stories

USAID’s integrated health care solutions have been successful in a number of countries around the world. For example: * In Rwanda, USAID’s support for the development of a comprehensive health care system has helped to reduce child mortality rates by 75% and maternal mortality rates by 60%. * In Ethiopia, USAID’s partnership with the government and civil society organizations has helped to increase access to health care for millions of people, particularly in rural areas. * In Haiti, USAID’s integrated health care solutions have helped to improve health outcomes and reduce mortality rates, despite the challenges posed by the country’s fragile health system and frequent natural disasters.
💡 Note: These success stories demonstrate the potential of USAID's integrated health care solutions to improve health outcomes and reduce health disparities in a variety of contexts.
Challenges and Opportunities

Despite the successes of USAID’s integrated health care solutions, there are still a number of challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed. Some of the key challenges include: * Funding: USAID’s health programs are dependent on funding, which can be unpredictable and subject to change. * Capacity building: Building the capacity of local health systems and promoting community engagement requires significant time and resources. * Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainability of health care programs and services is an ongoing challenge, particularly in countries with fragile health systems. On the other hand, there are also a number of opportunities for USAID’s integrated health care solutions, including: * Innovation: The use of new technologies, such as digital health and telemedicine, offers opportunities to improve health care delivery and access. * Partnerships: Partnering with governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can help to leverage resources, expertise, and knowledge to achieve common health goals. * Global health security: USAID’s integrated health care solutions can help to promote global health security by reducing the risk of infectious disease outbreaks and improving health systems’ ability to respond to emergencies.
Future Directions

As USAID continues to evolve and adapt to changing global health needs, there are a number of future directions that the agency is likely to pursue. Some of these directions include: * Increased focus on health systems strengthening: USAID is likely to continue to prioritize health systems strengthening, including the development of health policies, laws, and regulations, as well as the training of health care providers and the establishment of health information systems. * Greater emphasis on community engagement: USAID is likely to place greater emphasis on community engagement, including the promotion of health awareness, education, and behavior change, and the support of community-based health care programs. * More attention to global health security: USAID is likely to pay more attention to global health security, including the reduction of infectious disease outbreaks and the improvement of health systems’ ability to respond to emergencies.
| Country | Health Indicator | Baseline | Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rwanda | Child mortality rate | 125 per 1,000 live births | 50 per 1,000 live births |
| Ethiopia | Access to health care | 40% | 70% |
| Haiti | Maternal mortality rate | 350 per 100,000 live births | 200 per 100,000 live births |

In summary, USAID’s integrated health care solutions have been successful in improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities in a variety of contexts. However, there are still a number of challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed, including funding, capacity building, and sustainability. As the agency continues to evolve and adapt to changing global health needs, it is likely to prioritize health systems strengthening, community engagement, and global health security.
What is the main goal of USAID’s integrated health care solutions?

+
The main goal of USAID’s integrated health care solutions is to improve health outcomes and reduce health disparities in vulnerable populations.
How does USAID’s approach to health care differ from other organizations?

+
USAID’s approach to health care is distinct in its focus on integration, equity, and sustainability, and its emphasis on building the capacity of local health systems and promoting community engagement.
What are some of the key challenges facing USAID’s integrated health care solutions?
+
Some of the key challenges facing USAID’s integrated health care solutions include funding, capacity building, and sustainability, as well as the need to adapt to changing global health needs and priorities.
Related Terms:
- Haiti healthcare
- Healthcare access in Haiti
- Haiti public health issues
- Haiti health system structure
- Haiti Ministry of Health
- usaid pillar bureau



