Mental Health in Epidemiology

Introduction to Mental Health in Epidemiology
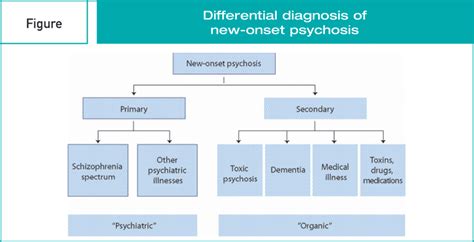
The field of epidemiology has traditionally focused on the study of physical diseases, with mental health often being overlooked. However, in recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of mental health in epidemiology. Mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide, and have a significant impact on individuals, families, and communities. Epidemiology plays a crucial role in understanding the distribution, determinants, and consequences of mental health disorders, and in developing effective strategies for prevention and control.
Defining Mental Health in Epidemiology
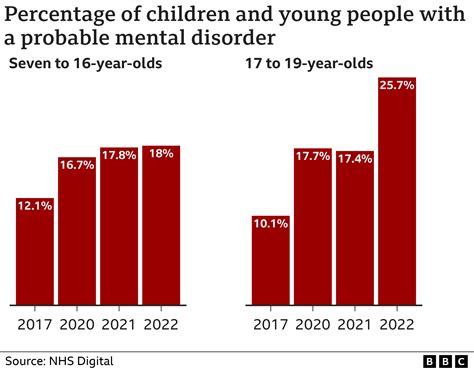
Mental health in epidemiology refers to the study of the distribution and determinants of mental health disorders in populations. It involves the use of epidemiological principles and methods to investigate the causes, consequences, and control of mental health disorders. Mental health disorders can be defined as conditions that affect an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, and can include a range of conditions such as depression, anxiety, psychosis, and substance use disorders. Epidemiologists use a variety of methods, including surveys, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to investigate the epidemiology of mental health disorders.
Importance of Mental Health in Epidemiology
The study of mental health in epidemiology is important for several reasons. Firstly, mental health disorders are a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide, and have a significant impact on individuals, families, and communities. Secondly, mental health disorders are often comorbid with other health conditions, such as chronic diseases, and can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. Finally, the study of mental health in epidemiology can inform the development of effective strategies for prevention and control, and can help to reduce the burden of mental health disorders on individuals and society.
Methods Used in Mental Health Epidemiology
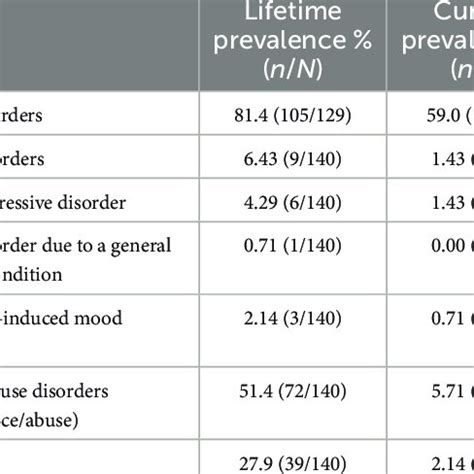
Epidemiologists use a variety of methods to study mental health disorders, including: * Surveys: Surveys are used to collect data on the prevalence and distribution of mental health disorders in populations. * Cohort studies: Cohort studies involve following a group of individuals over time to investigate the causes and consequences of mental health disorders. * Case-control studies: Case-control studies involve comparing individuals with mental health disorders to those without, to investigate the determinants of mental health disorders. * Ecological studies: Ecological studies involve investigating the relationship between mental health disorders and environmental or social factors, such as poverty or social isolation.
Applications of Mental Health Epidemiology

The study of mental health in epidemiology has a number of applications, including: * Public health policy: The study of mental health in epidemiology can inform the development of public health policy, including policies aimed at preventing and controlling mental health disorders. * Clinical practice: The study of mental health in epidemiology can inform clinical practice, including the diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders. * Research: The study of mental health in epidemiology can inform research, including research aimed at understanding the causes and consequences of mental health disorders.
Challenges in Mental Health Epidemiology

The study of mental health in epidemiology faces a number of challenges, including: * Stigma: Mental health disorders are often stigmatized, which can make it difficult to collect accurate data on their prevalence and distribution. * Lack of resources: The study of mental health in epidemiology often requires significant resources, including funding and personnel. * Complexity: Mental health disorders are complex and multifaceted, which can make it difficult to investigate their causes and consequences.
💡 Note: The study of mental health in epidemiology requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach, including the use of epidemiological principles and methods, as well as input from clinicians, policymakers, and community leaders.
Future Directions in Mental Health Epidemiology

The study of mental health in epidemiology is a rapidly evolving field, and there are a number of future directions that research may take. These include: * The use of new technologies: The use of new technologies, such as mobile phones and social media, to collect data on mental health disorders and to deliver interventions. * The investigation of mental health disparities: The investigation of mental health disparities, including disparities in the prevalence and treatment of mental health disorders. * The development of new interventions: The development of new interventions, including pharmacological and psychological interventions, to prevent and treat mental health disorders.
| Mental Health Disorder | Prevalence | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | 300 million worldwide | Disability, mortality, economic burden |
| Anxiety | 260 million worldwide | Disability, mortality, economic burden |
| Psychosis | 20 million worldwide | Disability, mortality, economic burden |
In summary, the study of mental health in epidemiology is a complex and multifaceted field that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach. By using epidemiological principles and methods, researchers can investigate the causes and consequences of mental health disorders, and inform the development of effective strategies for prevention and control. The field of mental health epidemiology is rapidly evolving, and there are a number of future directions that research may take, including the use of new technologies, the investigation of mental health disparities, and the development of new interventions.
What is mental health epidemiology?

+
Mental health epidemiology is the study of the distribution and determinants of mental health disorders in populations.
Why is mental health epidemiology important?

+
Mental health epidemiology is important because mental health disorders are a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide, and have a significant impact on individuals, families, and communities.
What methods are used in mental health epidemiology?

+
Epidemiologists use a variety of methods, including surveys, cohort studies, case-control studies, and ecological studies, to investigate the epidemiology of mental health disorders.
Related Terms:
- types of onset in psychology
- mental health disorders by age
- early onset mental illness
- lifetime prevalence of mental illness
- onset of mental health disorders
- epidemiology of mental health disorders



