5 WW2 Japanese Aircraft

Introduction to Japanese Aircraft of WW2

The Japanese aircraft of World War 2 played a significant role in the war, with some models becoming legendary for their performance, maneuverability, and impact on the conflict. Japan’s military aviation was characterized by innovative designs, often focusing on long-range capabilities, speed, and agility. This blog post will delve into five of the most notable Japanese aircraft of WW2, exploring their characteristics, roles, and the impact they had on the war.
Mitsubishi A6M Zero

The Mitsubishi A6M Zero, commonly known as the Zero, is arguably the most famous Japanese aircraft of WW2. Introduced in 1940, it was designed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and quickly gained a reputation for its exceptional maneuverability and long-range capabilities. The Zero was significantly lighter than its contemporaries, thanks to its minimalist design and lack of armor, which allowed it to achieve remarkable speeds and ranges. Its debut in China in 1940 and later in the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 made it a household name, symbolizing Japanese air power.
Nakajima Ki-43 Hayabusa

The Nakajima Ki-43 Hayabusa, or “Peregrine Falcon,” was another notable fighter aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Army. First deployed in 1941, the Ki-43 was known for its outstanding maneuverability and climb rate, making it a formidable opponent in dogfighting scenarios. Although it was eventually outclassed by Allied fighters, the Ki-43 remained in service throughout the war, with its pilots relying on their flying skills to counter the superior firepower and armor of enemy aircraft.
Mitsubishi G4M

The Mitsubishi G4M, also known as the “Betty” by the Allies, was a twin-engine bomber used by the Imperial Japanese Navy. Introduced in 1940, the G4M was notable for its range and payload capacity, which allowed it to conduct long-range missions, including the bombing of cities and naval bases. However, its lack of defensive armor and self-sealing fuel tanks made it vulnerable to enemy fire, leading to significant losses, especially in the later stages of the war.
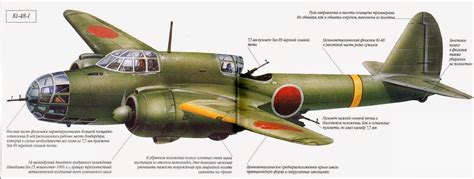
Kawasaki Ki-48

The Kawasaki Ki-48 was a twin-engine light bomber used by the Imperial Japanese Army. Developed in the late 1930s, it was designed to replace earlier bombers with a more modern design, offering better performance and armament. Although it saw extensive service in China and Southeast Asia, the Ki-48’s lack of defensive capabilities and limited payload made it less effective against well-defended targets.
Nakajima B5N

The Nakajima B5N, known to the Allies as the “Kate,” was a single-engine carrier-based torpedo bomber and reconnaissance aircraft. It played a crucial role in the early stages of the Pacific War, particularly during the attack on Pearl Harbor, where its torpedo capabilities were used to devastating effect against anchored Allied ships. Despite being largely obsolete by the mid-war period, the B5N remained in service, albeit in reduced numbers and roles.
🚀 Note: Understanding the development and deployment of these aircraft provides valuable insights into Japan's military strategy and the evolution of air warfare during WW2.
In summary, these five aircraft - the Mitsubishi A6M Zero, Nakajima Ki-43 Hayabusa, Mitsubishi G4M, Kawasaki Ki-48, and Nakajima B5N - represent some of the most significant contributions of Japanese aviation to the Second World War. Each model brought unique capabilities to the battlefield, influencing the outcome of numerous engagements and campaigns. Their designs and operational histories offer a fascinating glimpse into the technological and tactical developments of the era.
What made the Mitsubishi A6M Zero so successful?
+
The Zero’s success can be attributed to its exceptional maneuverability, long-range capabilities, and lightweight design, which gave it a significant advantage over contemporaries.
What was the role of the Nakajima B5N in the attack on Pearl Harbor?

+
The Nakajima B5N played a crucial role as a torpedo bomber during the attack on Pearl Harbor, using its torpedo capabilities to attack anchored Allied ships.
How did the Mitsubishi G4M’s design impact its operational effectiveness?

+
The Mitsubishi G4M’s lack of defensive armor and self-sealing fuel tanks made it vulnerable to enemy fire, leading to significant losses, despite its range and payload capacity advantages.
Related Terms:
- best japanese ww2 planes
- best japanese fighter of ww2
- best japanese fighter planes ww2
- best japanese aircraft carrier ww2
- ww2 japanese fighter planes
- ww2 japanese jet fighter



