5 Ways Lumped Model
Introduction to Lumped Models

Lumped models are a type of mathematical model used to describe the behavior of complex systems. These models are called “lumped” because they simplify the system by grouping together similar components or parameters, rather than modeling each individual component separately. This approach can be useful for understanding and analyzing systems that are too complex to model in detail. In this post, we will explore five ways that lumped models are used in different fields.
What are Lumped Models?
Lumped models are a type of simplified model that represents a complex system as a single, aggregate unit. This approach is often used when the system is too complex to model in detail, or when the detailed behavior of individual components is not important for understanding the overall system behavior. Lumped models can be used to model a wide range of systems, from electrical circuits to biological systems.
5 Ways Lumped Models are Used
Here are five ways that lumped models are used in different fields: * Electrical Engineering: Lumped models are used to simplify the analysis of complex electrical circuits. By representing the circuit as a single, aggregate unit, engineers can quickly and easily analyze the behavior of the circuit without having to model each individual component. * Biological Systems: Lumped models are used to understand the behavior of complex biological systems, such as the human body. By representing the body as a single, aggregate unit, researchers can model the behavior of the system and understand how different components interact. * Chemical Engineering: Lumped models are used to simplify the analysis of complex chemical systems. By representing the system as a single, aggregate unit, engineers can quickly and easily analyze the behavior of the system without having to model each individual component. * Thermal Systems: Lumped models are used to understand the behavior of complex thermal systems, such as heating and cooling systems. By representing the system as a single, aggregate unit, engineers can model the behavior of the system and understand how different components interact. * Mechanical Systems: Lumped models are used to simplify the analysis of complex mechanical systems, such as engines and gearboxes. By representing the system as a single, aggregate unit, engineers can quickly and easily analyze the behavior of the system without having to model each individual component.
Advantages of Lumped Models
Lumped models have several advantages, including: * Simpllicity: Lumped models are often simpler and easier to understand than detailed models. * Speed: Lumped models can be analyzed quickly and easily, without the need for complex simulations. * Cost: Lumped models can be less expensive to develop and analyze than detailed models. * Flexibility: Lumped models can be used to analyze a wide range of systems, from electrical circuits to biological systems.
Limitations of Lumped Models

While lumped models have several advantages, they also have some limitations. These include: * Lack of detail: Lumped models simplify the system by grouping together similar components or parameters, which can result in a lack of detail. * Assumptions: Lumped models often rely on assumptions about the behavior of the system, which can be inaccurate. * Limited accuracy: Lumped models can be less accurate than detailed models, especially for complex systems.
📝 Note: Lumped models should be used with caution, as they can be less accurate than detailed models. However, they can be a useful tool for understanding and analyzing complex systems.
Example of a Lumped Model
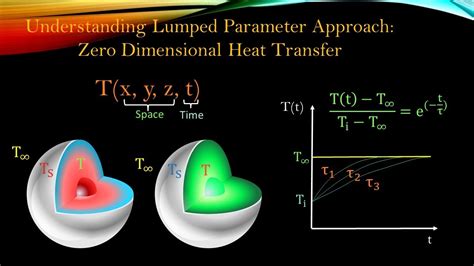
A simple example of a lumped model is a thermal model of a building. In this model, the building is represented as a single, aggregate unit, with a single temperature and heat transfer coefficient. This model can be used to analyze the thermal behavior of the building, without the need for a detailed model of each individual component.
| Component | Lumped Model |
|---|---|
| Walls | Single heat transfer coefficient |
| Windows | Single heat transfer coefficient |
| Roof | Single heat transfer coefficient |
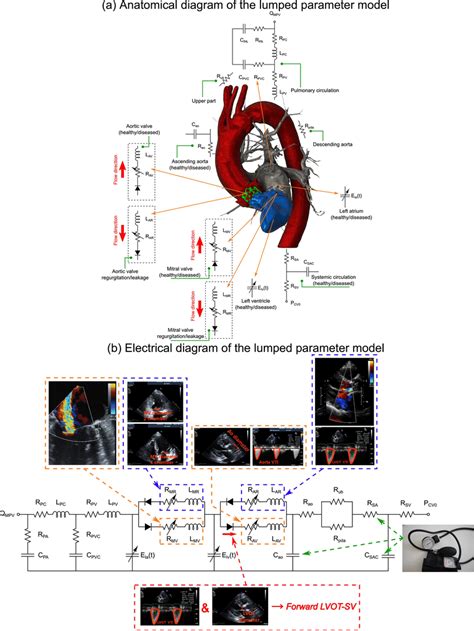
In this example, the lumped model simplifies the thermal behavior of the building by representing each component (walls, windows, roof) as a single, aggregate unit. This model can be used to analyze the thermal behavior of the building, without the need for a detailed model of each individual component.
In final thoughts, lumped models are a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing complex systems. By simplifying the system and representing it as a single, aggregate unit, engineers and researchers can quickly and easily analyze the behavior of the system, without the need for complex simulations. While lumped models have some limitations, they can be a useful tool for a wide range of applications, from electrical engineering to biological systems.
What is a lumped model?
+
A lumped model is a type of mathematical model that represents a complex system as a single, aggregate unit.
What are the advantages of lumped models?
+
The advantages of lumped models include simplicity, speed, cost, and flexibility.
What are the limitations of lumped models?
+
The limitations of lumped models include a lack of detail, assumptions, and limited accuracy.
Related Terms:
- lumped parameter model healthcare
- Lumped capacity model
- Lumped mass meaning
- Lumped elements
- Lumped system Theory
- Lumped system analysis



