7 Magnesium Welding Health Hazards

Introduction to Magnesium Welding Health Hazards

Magnesium welding is a process used to join magnesium alloys, which are popular for their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, like any other welding process, magnesium welding poses several health hazards to workers. These hazards can be attributed to the unique properties of magnesium and the welding process itself. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of magnesium welding health hazards, exploring the risks, preventive measures, and best practices for minimizing exposure.
Risks Associated with Magnesium Welding

The primary risks associated with magnesium welding can be categorized into physical hazards, chemical hazards, and biological hazards. Physical hazards include burns from sparks, cuts from sharp metal edges, and eye injuries from UV radiation. Chemical hazards are posed by the inhalation of fumes and particles emitted during the welding process, which can include magnesium oxide, ozone, and nitrogen oxides. Biological hazards, though less common, can arise from the introduction of infectious agents into the workplace.
Chemical Hazards in Magnesium Welding

Chemical hazards are among the most significant concerns in magnesium welding. The welding process releases a variety of harmful substances into the air, including: - Magnesium Oxide: When magnesium burns, it produces a significant amount of magnesium oxide, which can cause respiratory issues when inhaled. - Ozone (O3): Ultraviolet radiation from the welding arc can convert oxygen in the air into ozone, a powerful irritant that can cause respiratory problems and eye irritation. - Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): The high temperatures of the welding process can also convert nitrogen and oxygen in the air into nitrogen oxides, which are harmful to the respiratory system.
Physical Hazards
Physical hazards are also prevalent in magnesium welding and include: - UV Radiation: The welding arc emits intense UV radiation, which can cause eye damage, including cataracts and retinal burns, and skin burns. - Heat and Burns: The welding process generates significant heat, posing a risk of burns from both the arc itself and hot equipment. - Electrical Shock: Improperly grounded equipment or faulty insulation can lead to electrical shock.
Preventive Measures
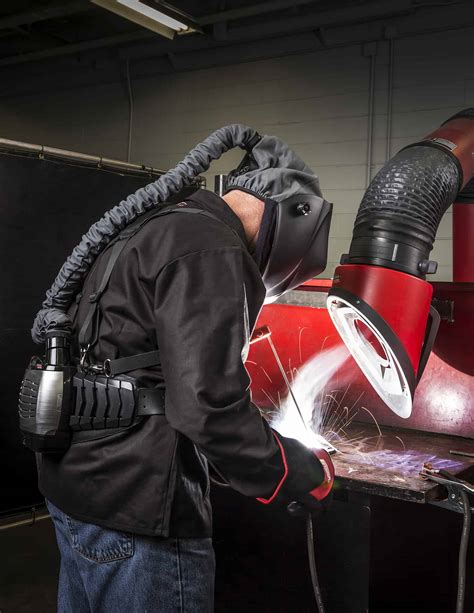

To mitigate the health hazards associated with magnesium welding, several preventive measures can be taken: - Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should always wear appropriate PPE, including welding helmets with shaded lenses to protect against UV radiation, heat-resistant gloves, and respirators to filter out harmful particles and gases. - Ventilation: Good ventilation is crucial to reduce the concentration of harmful substances in the work environment. This can be achieved through natural ventilation, exhaust ventilation systems, or the use of respirators. - Proper Training: Welders should receive comprehensive training on safe welding practices, including how to handle equipment safely, recognize hazards, and respond to emergencies. - Regular Health Checkups: Regular health checkups can help in early detection of any health issues related to magnesium welding.
Best Practices for Minimizing Exposure

Best practices for minimizing exposure to magnesium welding hazards include: - Using Alternative Welding Processes: When possible, using alternative welding processes that produce fewer fumes and less radiation. - Maintaining Equipment: Regular maintenance of welding equipment to ensure it is in good working condition and to prevent leaks or malfunctions. - Following Safety Protocols: Strict adherence to safety protocols, including the use of PPE, proper ventilation, and safe handling of materials.
💡 Note: It is essential for employers to provide a safe working environment and for workers to follow safety guidelines to minimize the risks associated with magnesium welding.
Regulatory Framework
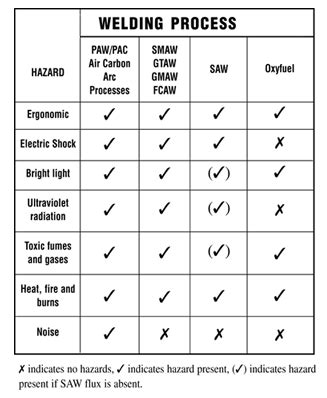
Various regulatory bodies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, set standards and guidelines for safe welding practices. These regulations often include requirements for ventilation, PPE, and worker training. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for ensuring a safe working environment.
Technological Advances

Advances in technology have led to the development of safer welding equipment and methods. For example, improvements in welding helmet design provide better protection against UV radiation, while advancements in respirator technology offer more effective filtration of harmful particles and gases.
Conclusion

In summary, magnesium welding poses several health hazards, including chemical, physical, and biological risks. Understanding these hazards and implementing preventive measures, such as the use of PPE, proper ventilation, and regular health checkups, are critical for minimizing exposure. By following best practices, adhering to regulatory standards, and leveraging technological advances, the risks associated with magnesium welding can be significantly reduced, ensuring a safer working environment for welders.
What are the primary health hazards associated with magnesium welding?

+
The primary health hazards include chemical hazards from inhaling magnesium oxide, ozone, and nitrogen oxides, physical hazards such as UV radiation and heat burns, and potential biological hazards.
How can workers protect themselves from the hazards of magnesium welding?

+
Workers can protect themselves by using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as welding helmets, respirators, and heat-resistant gloves, ensuring good ventilation in the work area, and following safe welding practices and protocols.
What role do regulatory bodies play in ensuring safe magnesium welding practices?

+
Regulatory bodies set standards and guidelines for safe welding practices, including requirements for PPE, ventilation, and worker training. Compliance with these regulations is essential for minimizing the risks associated with magnesium welding.
Related Terms:
- magnesium wire welders
- magnesium welder safety data sheet



