7 Marine Ranks

Introduction to Marine Ranks
The Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces, and its rank structure is designed to define the roles and responsibilities of its personnel. Understanding the different Marine ranks is essential for both Marines and civilians who want to learn more about the Corps. In this article, we will delve into the seven primary Marine ranks, exploring their responsibilities, requirements, and distinctions.
Enlisted Ranks

The enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Marine Corps, comprising the majority of its personnel. These ranks are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and staff non-commissioned officers (SNCOs).
Junior Enlisted Ranks
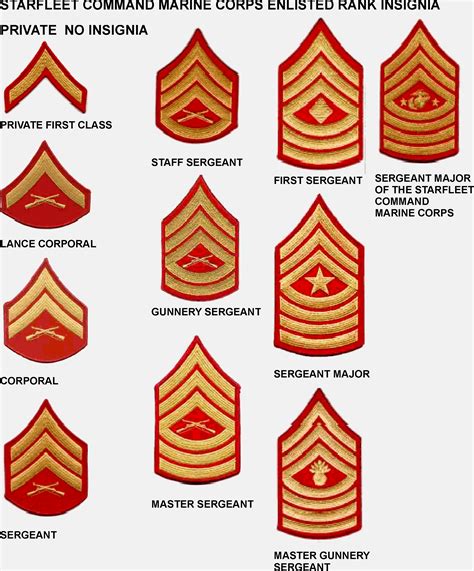

The junior enlisted ranks are the entry-level positions in the Marine Corps. These ranks include: * Private (Pvt): The lowest rank in the Marine Corps, typically held by new recruits. * Private First Class (PFC): A higher rank than Private, often assigned to Marines who have completed basic training. * Lance Corporal (LCpl): A non-commissioned officer rank, typically held by Marines who have gained some experience and demonstrated leadership potential.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks

NCOs are experienced Marines who have demonstrated leadership skills and a strong understanding of the Corps’ values and traditions. The NCO ranks include: * Corporal (Cpl): A higher rank than Lance Corporal, often assigned to Marines who have shown exceptional leadership and technical expertise. * Sergeant (Sgt): A senior NCO rank, typically held by Marines who have significant experience and have demonstrated a high level of competence.
Staff Non-Commissioned Officer (SNCO) Ranks

SNCOs are senior enlisted Marines who have achieved a high level of expertise and leadership. The SNCO ranks include: * Staff Sergeant (SSgt): A senior rank that requires significant experience and technical expertise. * Gunnery Sergeant (GySgt): A high-ranking SNCO position, typically held by Marines who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills. * Master Sergeant (MSgt) and First Sergeant (1stSgt): The highest SNCO ranks, which require extensive experience, technical expertise, and strong leadership skills.
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant Officers are technical experts who have gained specialized knowledge and skills in a particular field. These ranks include: * Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The entry-level Warrant Officer rank, typically held by Marines who have completed a Warrant Officer training program. * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CWO2) to Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CWO5): Higher Warrant Officer ranks, which require increasing levels of technical expertise and leadership experience.
Officer Ranks

Officer ranks are divided into three categories: company-grade officers, field-grade officers, and general officers.
Company-Grade Officer Ranks

Company-grade officers are junior officers who have recently commissioned into the Marine Corps. These ranks include: * Second Lieutenant (2ndLt): The lowest officer rank, typically held by new officers. * First Lieutenant (1stLt): A higher rank than Second Lieutenant, often assigned to officers who have gained some experience. * Captain (Capt): A senior company-grade officer rank, typically held by officers who have demonstrated leadership potential and technical expertise.
Table of Marine Ranks

| Rank | Abbreviation | Pay Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Private | Pvt | E-1 |
| Private First Class | PFC | E-2 |
| Lance Corporal | LCpl | E-3 |
| Corporal | Cpl | E-4 |
| Sergeant | Sgt | E-5 |
| Staff Sergeant | SSgt | E-6 |
| Gunnery Sergeant | GySgt | E-7 |
| Master Sergeant | MSgt | E-8 |
| First Sergeant | 1stSgt | E-8 |
| Warrant Officer 1 | WO1 | W-1 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 | CWO2 | W-2 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 3 | CWO3 | W-3 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 4 | CWO4 | W-4 |
| Chief Warrant Officer 5 | CWO5 | W-5 |
| Second Lieutenant | 2ndLt | O-1 |
| First Lieutenant | 1stLt | O-2 |
| Captain | Capt | O-3 |

💡 Note: The rank structure and pay grades may be subject to change, and it's essential to check with the Marine Corps for the most up-to-date information.
In summary, the Marine Corps has a complex rank structure, with seven primary ranks and several sub-ranks. Understanding these ranks is crucial for both Marines and civilians who want to learn more about the Corps. By recognizing the different ranks and their responsibilities, individuals can appreciate the hierarchy and organization of the Marine Corps.
What is the highest rank in the Marine Corps?

+
The highest rank in the Marine Corps is General (Gen), which is a four-star general officer rank.
How do Marines advance in rank?

+
Marines can advance in rank through a combination of time-in-service, performance evaluations, and completion of professional military education courses.
What is the difference between a Warrant Officer and a Commissioned Officer?

+
A Warrant Officer is a technical expert who has gained specialized knowledge and skills in a particular field, while a Commissioned Officer is a leader who has completed a commissioning program and has been appointed to a position of authority.
Related Terms:
- Marine ranks One Piece
- Rank in the Marine Corps
- Marine ranks on uniforms
- Marine Sergeant ranks
- U S Army rank
- Marine shoulder ranks



