5 Ways Enlist

Introduction to Enlisting

Enlisting in the military can be a life-changing decision that offers a wide range of benefits, including education assistance, career opportunities, and personal growth. For those considering this path, it’s essential to understand the various ways to enlist and the requirements for each. In this article, we will explore five ways to enlist in the military, highlighting the unique aspects of each and providing guidance for individuals looking to start their military career.
1. Active Duty Enlistment
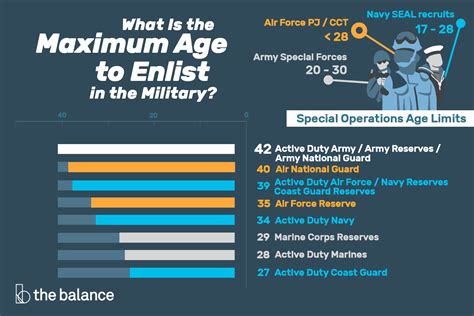
Active duty enlistment is the most common way to join the military. It involves serving full-time in the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, or Coast Guard. To enlist on active duty, individuals must meet specific eligibility requirements, including: * Being a U.S. citizen or permanent resident * Being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions) * Meeting physical and medical standards * Scoring well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test * Having a high school diploma or equivalent Active duty service members typically serve for a set period, usually 3-6 years, and may be stationed anywhere in the world.
2. Reserve Enlistment
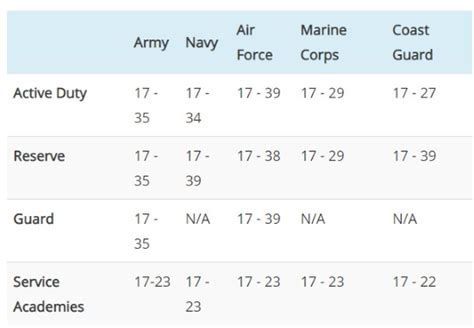
Reserve enlistment allows individuals to serve part-time in the military while maintaining a civilian career. The Reserve components include the Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, Air National Guard, Air Force Reserve, Marine Corps Reserve, and Coast Guard Reserve. To enlist in the Reserve, individuals must: * Meet the same eligibility requirements as active duty enlistees * Be willing to attend drills one weekend per month and annual training for two weeks * Be available for deployment in times of war or national emergency Reserve service members can serve for a set period, usually 3-6 years, and may be eligible for education assistance and other benefits.
3. National Guard Enlistment

The National Guard is a unique component of the military that serves both state and federal roles. To enlist in the National Guard, individuals must: * Meet the same eligibility requirements as active duty enlistees * Be willing to attend drills one weekend per month and annual training for two weeks * Be available for deployment in times of war or national emergency * Be willing to serve in a dual role, supporting both state and federal missions National Guard service members can serve for a set period, usually 3-6 years, and may be eligible for education assistance and other benefits.
4. Officer Candidate School (OCS) Enlistment

Officer Candidate School (OCS) is a program for individuals who want to become officers in the military. To enlist through OCS, individuals must: * Hold a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution * Meet the same eligibility requirements as active duty enlistees * Pass the ASVAB test and a physical fitness test * Complete OCS training, which typically lasts 12-14 weeks OCS enlistment is a competitive process, and selection is based on factors such as education, leadership experience, and physical fitness.
5. Delayed Entry Program (DEP) Enlistment

The Delayed Entry Program (DEP) allows individuals to enlist in the military and delay their entry for up to one year. To enlist through DEP, individuals must: * Meet the same eligibility requirements as active duty enlistees * Be willing to attend basic training and other required training * Be available to ship out to basic training within one year of enlisting DEP enlistment is a great option for individuals who want to enlist but need time to complete education or other obligations before starting their military service.
📝 Note: It's essential to research and understand the enlistment process, including the requirements and benefits of each option, before making a decision.
In summary, there are various ways to enlist in the military, each with its unique requirements and benefits. Whether you’re looking to serve full-time on active duty, part-time in the Reserve, or as an officer, there’s a path that can help you achieve your goals. By understanding the different enlistment options and their requirements, individuals can make informed decisions about their military career.
What are the basic eligibility requirements for enlisting in the military?
+
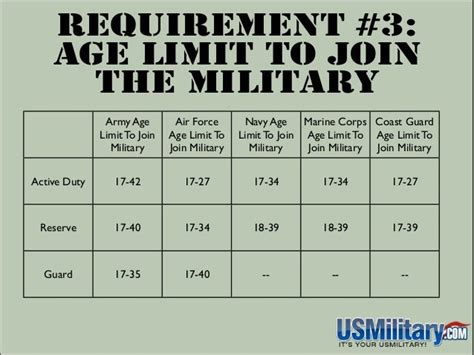
The basic eligibility requirements for enlisting in the military include being a U.S. citizen or permanent resident, being between the ages of 17 and 35, meeting physical and medical standards, scoring well on the ASVAB test, and having a high school diploma or equivalent.
What is the difference between active duty and Reserve enlistment?

+
Active duty enlistment involves serving full-time in the military, while Reserve enlistment involves serving part-time. Reserve service members typically attend drills one weekend per month and annual training for two weeks, and may be deployed in times of war or national emergency.
How do I enlist in the Officer Candidate School (OCS) program?

+
To enlist in the OCS program, you must hold a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution, meet the same eligibility requirements as active duty enlistees, pass the ASVAB test and a physical fitness test, and complete OCS training, which typically lasts 12-14 weeks.
By considering these options and understanding the requirements and benefits of each, individuals can make informed decisions about their military career and find the path that best suits their goals and aspirations. Ultimately, enlisting in the military can be a rewarding and challenging experience that offers a wide range of opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Related Terms:
- us army maximum enlistment age
- military maximum age to join
- army enlistment cut off age
- us army age limit 2024
- army enlistment age cutoff
- maximum age to join army



