Payer Types for Health Claims

Introduction to Payer Types

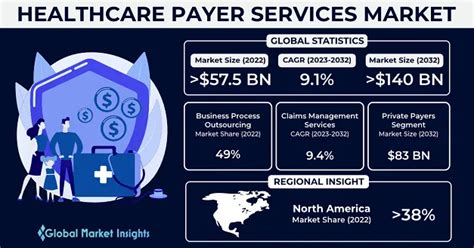
In the healthcare industry, understanding the different types of payers is crucial for managing health claims effectively. Payers are entities that reimburse healthcare providers for the services they render to patients. The complexity of the healthcare system is partly due to the variety of payer types, each with its own set of rules, reimbursement rates, and requirements for claims submission. This complexity necessitates a thorough understanding of the payer landscape for healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients alike.
Types of Payers

There are several types of payers in the healthcare system, including: - Government Payers: These include programs like Medicare and Medicaid in the United States. Medicare primarily covers individuals 65 and older, certain younger people with disabilities, and people with End-Stage Renal Disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant). Medicaid, on the other hand, provides health coverage to millions of Americans, including eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities. - Private Payers: This category encompasses a wide range of health insurance companies and plans. Private payers can be further divided into group health plans (offered by employers to their employees) and individual plans (purchased directly by individuals). Private insurance plans vary significantly in terms of coverage, deductibles, co-payments, and out-of-pocket maximums. - Self-Pay or Uninsured Patients: These are individuals who do not have any form of health insurance. They are responsible for paying their medical bills out-of-pocket. Due to the high costs of healthcare services, being uninsured can lead to significant financial burdens, including medical debt. - Worker’s Compensation: This is a state-mandated insurance program that provides benefits to employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses. Worker’s compensation covers medical expenses and partial replacement of lost wages for workers during the period of their disability.
Claims Processing for Different Payer Types

The process of submitting and managing health claims varies significantly among different payer types. Understanding these differences is essential for efficient claims processing and reimbursement. Here are key aspects of claims processing for each payer type: - Government Payers: Claims for Medicare and Medicaid must be submitted electronically, following specific guidelines and coding requirements. These programs have their own claim forms and billing procedures. - Private Payers: Each private insurance company may have its own set of rules and procedures for claims submission. Some require electronic submission, while others may still accept paper claims. The coding and billing requirements can also vary. - Self-Pay Patients: For patients without insurance, healthcare providers often require payment upfront or at the time of service. There may be options for payment plans or financial assistance for those who cannot afford to pay immediately. - Worker’s Compensation: Claims under worker’s compensation are processed through the employer or the employer’s insurance carrier. The process involves reporting the injury, filing a claim, and undergoing a review to determine eligibility for benefits.
Challenges in Managing Health Claims
Managing health claims across different payer types poses several challenges, including: - Complexity of Billing and Coding: The use of specific codes (such as ICD-10 and CPT) for diagnoses and procedures can be complex, and incorrect coding can lead to denied claims. - Variability in Reimbursement Rates: Different payers reimburse healthcare services at different rates, affecting the financial stability of healthcare providers. - Timeliness of Reimbursement: Delays in reimbursement can impact the cash flow of healthcare providers, making it challenging to operate efficiently. - Patient Satisfaction and Financial Burden: The financial aspect of healthcare can significantly affect patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans. High out-of-pocket costs can lead to financial burdens on patients.
Strategies for Effective Claims Management
To navigate the complexities of health claims management, healthcare providers and organizations can employ several strategies: - Invest in Comprehensive Billing Software: Utilizing advanced billing and coding software can help streamline the claims process, reduce errors, and improve reimbursement rates. - Develop Strong Relationships with Payers: Building strong, communicative relationships with payers can facilitate smoother claims processing and faster resolution of disputes. - Provide Patient Financial Counseling: Offering financial counseling and transparency about costs and billing procedures can improve patient satisfaction and reduce bad debt. - Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes: Regularly updating knowledge on changes in healthcare regulations, coding requirements, and payer policies is crucial for efficient claims management.
💡 Note: Healthcare providers should also consider outsourcing their billing operations to specialized companies if they lack the expertise or resources to manage claims effectively in-house.
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, understanding and adapting to the different payer types and their requirements is vital for successful claims management. By leveraging technology, fostering strong payer relationships, and prioritizing patient financial education, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of the system more effectively, ensuring better outcomes for both the patients and the providers.
What are the main types of payers in the healthcare system?
+
The main types include Government Payers (like Medicare and Medicaid), Private Payers (including group and individual health plans), Self-Pay or uninsured patients, and Worker’s Compensation.
How does claims processing differ among payer types?

+
Claims processing varies significantly among payer types, with differences in submission methods (electronic vs. paper), coding requirements, and billing procedures. Each payer type has its own set of rules and guidelines that must be followed for successful reimbursement.
What strategies can healthcare providers use for effective claims management?

+
Healthcare providers can invest in comprehensive billing software, develop strong relationships with payers, provide patient financial counseling, and stay updated on regulatory changes to improve claims management efficiency and reduce reimbursement issues.
To summarize, the landscape of payer types in healthcare is diverse and complex, with each type presenting unique challenges and requirements for claims management. By understanding these differences and employing effective strategies, healthcare providers can optimize their billing and reimbursement processes, ultimately enhancing patient care and financial stability.
Related Terms:
- Medical claims
- Types of claims in healthcare
- Medical claims examples
- Medical claims vs hospital claims
- Medical claim form
- healthcare payers problems