Military Pay After Taxes
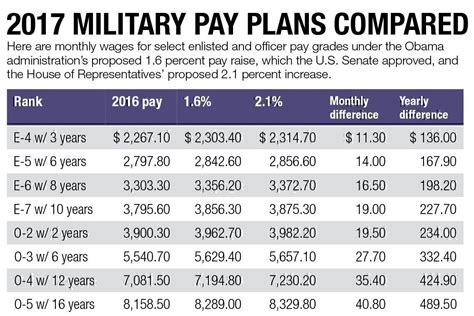
Understanding Military Pay After Taxes
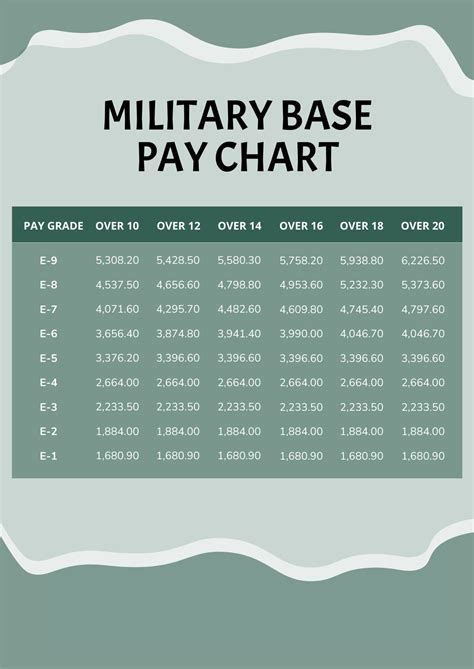
The military pay system can be complex, especially when it comes to understanding how much money you’ll take home after taxes. Gross pay, which is the total amount of money you earn before taxes and deductions, is an important figure to consider. However, it’s the net pay, or take-home pay, that truly matters. In this article, we’ll break down the factors that affect military pay after taxes and provide you with a better understanding of how to calculate your take-home pay.
Military Pay Components

To understand how military pay is taxed, it’s essential to know the different components of military pay. These include: * Basic Pay: This is the base salary for your rank and time in service. * Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This is a monthly allowance to help cover the cost of housing. * Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This is a monthly allowance to help cover the cost of food. * Special Pay: This includes bonuses, hazard pay, and other special pays. * Overtime Pay: This is paid for work performed beyond regular hours.
Taxation of Military Pay
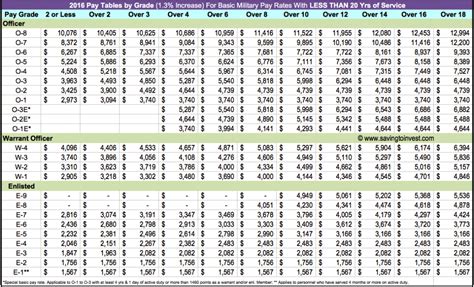
Military pay is subject to federal income tax, but some components are tax-free. For example, BAH and BAS are not subject to federal income tax. However, Basic Pay and Special Pay are taxable. The amount of taxes withheld from your pay will depend on your tax filing status, number of dependents, and other factors.
Calculating Military Pay After Taxes
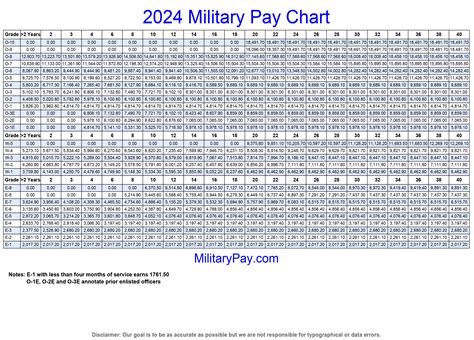
To calculate your military pay after taxes, you’ll need to consider the following factors: * Gross Pay: Your total pay before taxes and deductions. * Taxable Pay: The amount of your pay that is subject to federal income tax. * Tax Withholding: The amount of taxes withheld from your pay. * Deductions: Other deductions, such as health insurance premiums and retirement contributions.
Here’s an example of how to calculate military pay after taxes:
| Component | Amount |
|---|---|
| Basic Pay | 4,000</td> </tr> <tr> <td>BAH</td> <td>1,500 |
| BAS | 300</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Special Pay</td> <td>500 |
| Gross Pay | 6,300</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Taxable Pay</td> <td>4,500 |
| Tax Withholding | 800</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Net Pay</td> <td>5,500 |

💸 Note: This is a simplified example and actual calculations may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Factors That Affect Military Pay After Taxes
Several factors can affect your military pay after taxes, including: * Tax Filing Status: Your tax filing status, such as single or married, can impact your tax withholding. * Number of Dependents: The number of dependents you claim can affect your tax withholding. * State of Residence: Some states do not tax military pay, while others do. * Other Income: If you have other sources of income, such as a spouse’s income or investments, it can impact your tax withholding.
Minimizing Taxes on Military Pay
There are several ways to minimize taxes on military pay, including: * Maximizing Tax-Free Benefits: Take advantage of tax-free benefits, such as BAH and BAS. * Claiming Dependents: Claiming dependents can reduce your tax withholding. * Contributing to Retirement Accounts: Contributing to retirement accounts, such as the Thrift Savings Plan, can reduce your taxable income. * Consulting a Tax Professional: Consulting a tax professional can help you navigate the complex tax laws and ensure you’re taking advantage of all eligible deductions and credits.
In summary, understanding military pay after taxes requires considering multiple factors, including taxable pay, tax withholding, and deductions. By maximizing tax-free benefits, claiming dependents, and contributing to retirement accounts, you can minimize taxes on your military pay. It’s essential to consult a tax professional to ensure you’re taking advantage of all eligible deductions and credits.
What is the difference between gross pay and net pay?
+
Gross pay is the total amount of money you earn before taxes and deductions, while net pay is the amount of money you take home after taxes and deductions.
Are all components of military pay taxable?
+
No, some components of military pay, such as BAH and BAS, are not taxable.
How can I minimize taxes on my military pay?

+
You can minimize taxes on your military pay by maximizing tax-free benefits, claiming dependents, contributing to retirement accounts, and consulting a tax professional.
Related Terms:
- Military pay calculator after taxes
- Military pay Calculator monthly
- Military pay 2025
- Military Pay chart
- Military dependent pay chart
- National Guard pay calculator



