Military
National Guard Pay By Rank
Understanding National Guard Pay by Rank

The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. Its members are citizen-soldiers and airmen who serve part-time, typically one weekend per month and two weeks per year, while also having civilian careers. The pay for National Guard members is based on their rank and the time they serve. In this article, we will delve into the details of National Guard pay by rank, exploring how it is structured, the factors that influence it, and what members can expect in terms of compensation.
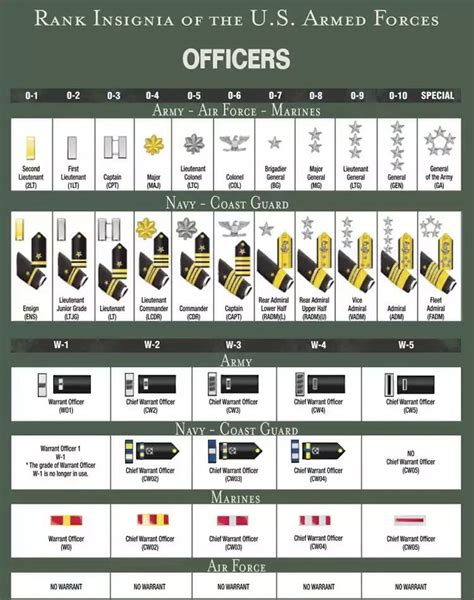
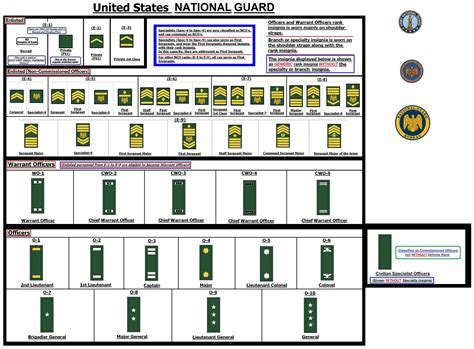
Rank Structure in the National Guard

The rank structure in the National Guard mirrors that of the active-duty Army and Air Force, with enlisted ranks, warrant officer ranks, and officer ranks. Understanding the rank structure is essential to grasp how pay is determined. Here is a brief overview of the ranks: - Enlisted Ranks: These range from Private (E-1) to Sergeant Major of the Army (E-9) in the Army National Guard and from Airman Basic (E-1) to Chief Master Sergeant (E-9) in the Air National Guard. - Warrant Officer Ranks: These ranks are for technical experts and range from Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) to Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5). - Officer Ranks: These range from Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10) in both the Army and Air National Guard.
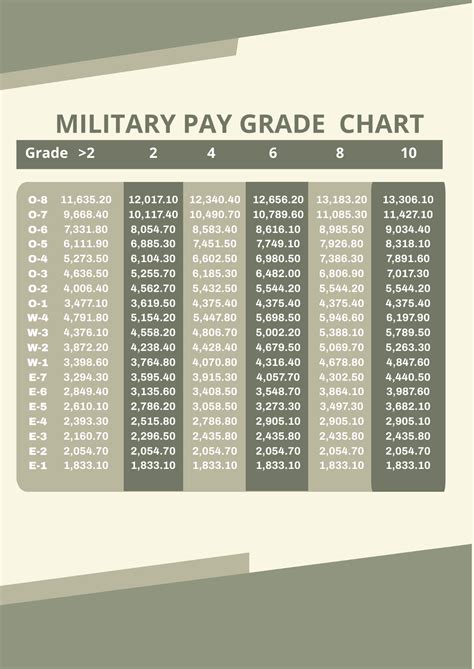
Pay Scales

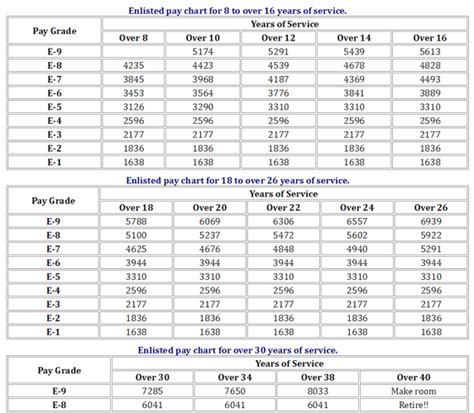
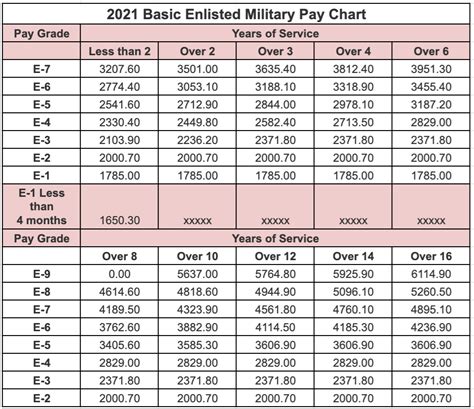
The pay scales for the National Guard are based on the federal government’s pay tables, which are adjusted annually. The pay for drill weekends (one weekend per month) is calculated based on the member’s rank and the number of drills attended. For annual training (two weeks per year) and any additional active-duty time, members are paid based on their rank and time served, similar to active-duty personnel.
Factors Influencing Pay
Several factors can influence a National Guard member’s pay: - Rank: The higher the rank, the higher the pay. - Time in Service: Generally, the longer a member has served, the higher their pay grade within their rank. - Time Served: The amount of time a member serves on active duty or participates in drills affects their pay. - Special Duties: Some special duties or assignments may come with special pay or allowances. - Education and Certifications: Higher levels of education or specific certifications can sometimes lead to higher pay grades or special pays.
Examples of National Guard Pay

To give a clearer picture, here are some examples of monthly drill pay (for one weekend of drills per month) for different ranks in the National Guard, based on the 2022 pay tables: - Private (E-1): Approximately 200 per month for drills. - Staff Sergeant (E-6): Approximately 450 per month for drills. - Second Lieutenant (O-1): Approximately 400 per month for drills. - Captain (O-3): Approximately 700 per month for drills.
Benefits Beyond Pay

While pay is an important consideration, National Guard members also receive a range of benefits, including: - Education Assistance: The National Guard offers education assistance, such as the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Army National Guard’s State Tuition Reimbursement (STR) program. - Health and Dental Care: Members and their families may be eligible for TRICARE, the military’s health care program. - Retirement Benefits: National Guard members can qualify for retirement benefits after 20 years of service, with the ability to retire and receive pay at the age of 60. - Career Advancement Opportunities: Service in the National Guard can provide valuable skills and experience, enhancing civilian career prospects.
📝 Note: Pay figures and benefits can change, so it's essential for current or prospective National Guard members to consult the latest information from official sources.
Calculating Your Pay
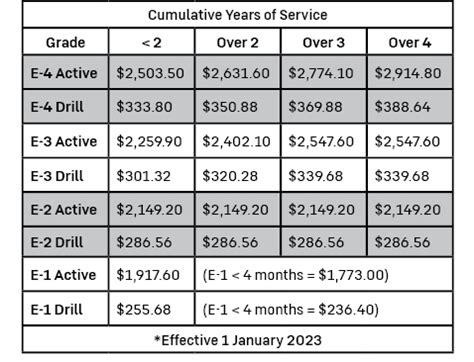
To calculate your pay, you’ll need to consider the number of drills you attend, any periods of active duty, your rank, and your time in service. The National Guard and the Department of Defense provide pay calculators and tables that can help you estimate your pay more accurately.
Conclusion Summary
In summary, National Guard pay is determined by rank, time in service, and the amount of time served on active duty or in drills. Members receive a range of benefits beyond their pay, including education assistance, health and dental care, retirement benefits, and opportunities for career advancement. Understanding how pay is structured and what benefits are available can help individuals make informed decisions about their service in the National Guard.
How often do National Guard members get paid?

+
National Guard members typically receive pay for drills once a month and for any periods of active duty according to the standard military pay schedule.
Do National Guard members receive benefits in addition to pay?
+
Yes, National Guard members are eligible for a variety of benefits, including education assistance, health and dental care, retirement benefits, and opportunities for career advancement.
How does rank affect pay in the National Guard?
+
The higher the rank, the higher the pay. Rank is one of the primary factors in determining pay for National Guard members, along with time in service and the type of duty performed.
Related Terms:
- national guard pay scale 2024
- national guard base pay chart
- national guard pay website
- 2025 military drill pay chart
- national guard full time pay
- military pay charts 2025



