5 Ways National Guard Pay Works

Introduction to National Guard Pay
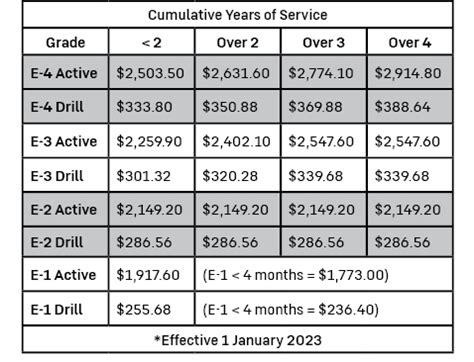
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising both the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. Members of the National Guard are known as citizen-soldiers or citizen-airmen, as they serve part-time, typically one weekend per month and two weeks per year, while also maintaining civilian careers. One of the critical aspects of National Guard service is the compensation members receive for their time and service. Understanding how National Guard pay works is essential for those considering joining or who are already part of the Guard.
Basic Pay Structure
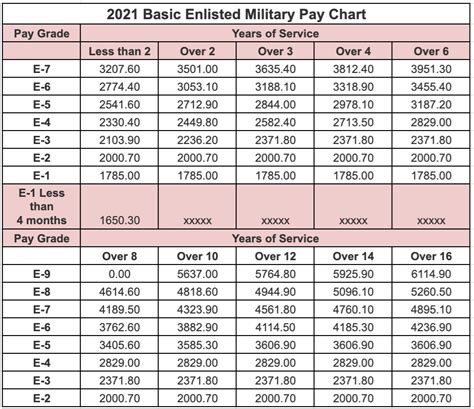
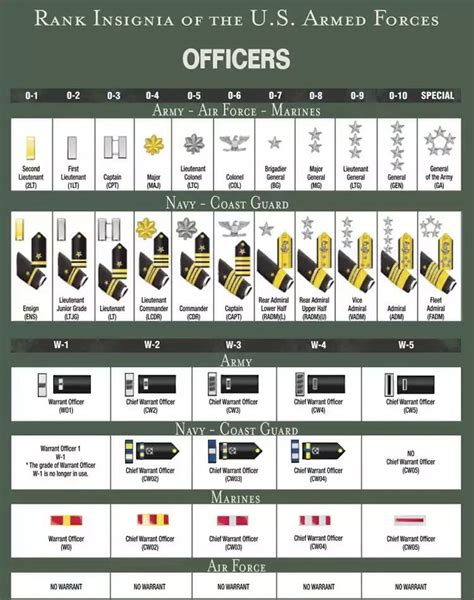
National Guard members are paid based on their rank and the number of years they have served. The pay scale is similar to that of active-duty military personnel, with two primary differences: the amount of time served and the frequency of payment. Guard members are typically paid for their weekend drills and for any additional days they serve, including annual training periods. Basic pay is the fundamental component of compensation and is based on the member’s rank and time in service.
Drill Pay

Drill pay refers to the compensation Guard members receive for attending their monthly drills. These drills are usually held over a weekend and are mandatory for all Guard members. The pay for drills is calculated based on the number of drill periods attended, with each drill period being approximately four hours long. For a typical weekend drill, a Guard member would receive pay for four drill periods. The drill pay chart outlines the specific pay rates based on rank and years of service.
Special Pay and Allowances
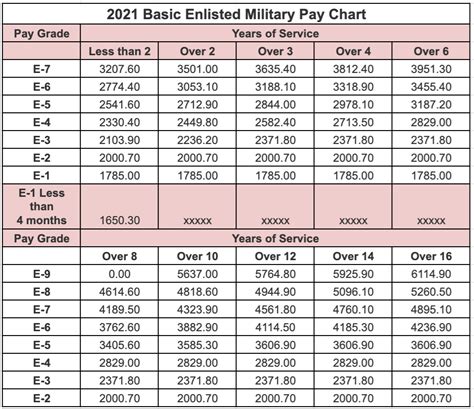
In addition to basic pay and drill pay, National Guard members may be eligible for special pay and allowances. These can include: - Hazardous Duty Pay: For serving in hazardous conditions or performing hazardous duties. - Special Duty Pay: For serving in special duty assignments that require unique skills or are particularly demanding. - Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): For members who do not live in military housing, this allowance helps offset the cost of housing. - Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): Meant to help offset the cost of food for members, though it’s not always provided to Guard members unless they are on active duty orders.
Education Benefits
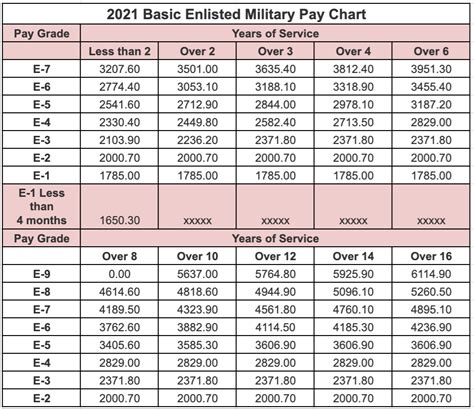
National Guard members are also eligible for significant education benefits, which can be a major incentive for joining. The Montgomery GI Bill - Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill are two programs that provide financial assistance for education expenses. These benefits can help Guard members pursue higher education or vocational training, making their service in the Guard a valuable investment in their future.
Retirement Benefits
After 20 years of qualifying service, National Guard members can retire and receive retirement pay. The retirement pay is calculated based on the member’s rank at retirement and their total years of qualifying service. This benefit is a significant long-term advantage of serving in the National Guard, providing members with a steady income after their service.
👉 Note: To qualify for retirement benefits, Guard members must have served at least 20 years, with a portion of that service being in a qualifying status. It's crucial for members to understand how their service time is counted towards retirement eligibility.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In summary, National Guard pay is multifaceted, incorporating basic pay, drill pay, special pays, allowances, education benefits, and retirement benefits. Each component contributes to the overall compensation package that Guard members receive. Understanding these elements is vital for both current members and those considering joining the National Guard. By offering a combination of immediate financial compensation and long-term benefits, the National Guard provides its members with a unique set of rewards for their service.
How often do National Guard members get paid?

+
National Guard members typically receive pay for their drills, which are held one weekend per month, and for their annual training periods. The exact frequency can depend on the specific service requirements and any additional duty assignments.
What benefits does the National Guard offer besides pay?

+
Besides pay, the National Guard offers a range of benefits including education assistance through the GI Bill, access to base facilities, comprehensive health insurance, and retirement benefits after 20 years of service. These benefits significantly enhance the overall value of serving in the Guard.
Can National Guard members use their education benefits for online courses?

+
Yes, National Guard members can use their education benefits, including the GI Bill, for online courses. Many institutions offer online degree programs that are approved for GI Bill benefits, making it easier for Guard members to pursue their educational goals while serving.
Related Terms:
- National Guard pay per month
- National Guard pay chart
- National guard salary
- National Guard pay calculator
- Full time National Guard pay
- National Guard pay by rank



