National Guard Ranks List

National Guard Ranks: Understanding the Hierarchy
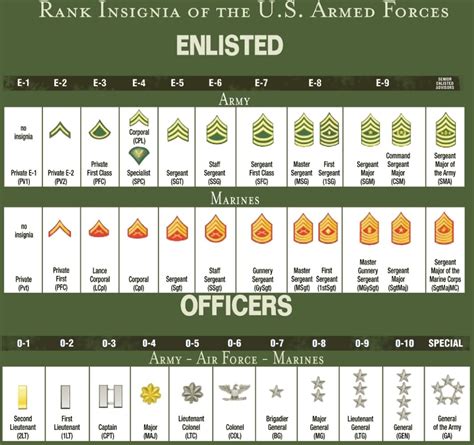
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising both the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. It plays a crucial role in the country’s defense and security, both domestically and overseas. The ranks within the National Guard are similar to those in the regular Army and Air Force, with some minor differences. Understanding these ranks is essential for navigating the organizational structure and chain of command within the National Guard.
Enlisted Ranks

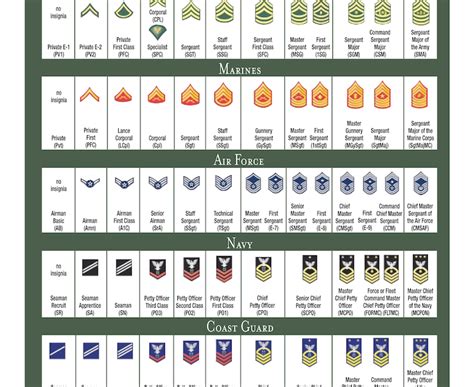
Enlisted ranks in the National Guard are divided into several categories, starting from the lowest to the highest. These ranks are as follows: - Private (PVT): The entry-level rank for new recruits. - Private Second Class (PV2): Typically achieved after completing basic training. - Private First Class (PFC): Requires more experience and responsibility. - Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): Specialist is used in the Army, while Corporal is used in some units for team leaders. - Sergeant (SGT): A non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank that involves leadership and training responsibilities. - Staff Sergeant (SSG): Holds more senior leadership positions. - Sergeant First Class (SFC): Leads squads or sections and is responsible for the welfare, training, and discipline of their team members. - Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): Master Sergeant is a senior NCO rank, while First Sergeant is a senior enlisted advisor at the company level. - Sergeant Major (SGM): One of the highest enlisted ranks, often serving as the senior enlisted advisor to the unit commander. - Command Sergeant Major (CSM): The most senior enlisted rank, responsible for unit morale, welfare, and discipline.
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field and are considered specialists. The ranks are: - Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The entry-level warrant officer rank. - Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): Requires more experience and technical expertise. - Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer rank with advanced technical and leadership skills. - Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): Holds senior technical leadership positions. - Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest warrant officer rank, providing expert guidance and leadership.
Officer Ranks
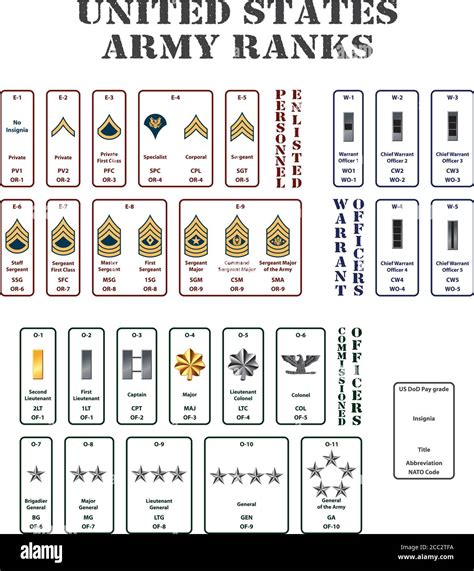
Officer ranks in the National Guard start from the lowest to the highest as follows: - Second Lieutenant (2LT): The entry-level commissioned officer rank. - First Lieutenant (1LT): Typically involves leading platoons. - Captain (CPT): Leads companies or acts as a staff officer at the battalion level. - Major (MAJ): Holds senior staff positions or commands battalions. - Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): Often commands battalions or serves in senior staff roles. - Colonel (COL): A senior officer rank, often serving as brigade commanders or in high-level staff positions. - Brigadier General (BG): The first general officer rank, often serving as assistant division commanders. - Major General (MG): Commands divisions or serves in senior staff positions. - Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general, typically serving in high-level command or staff positions. - General (GEN): The highest rank, usually reserved for the Chief of the National Guard Bureau or other significant positions.
Rank Insignia and Promotion
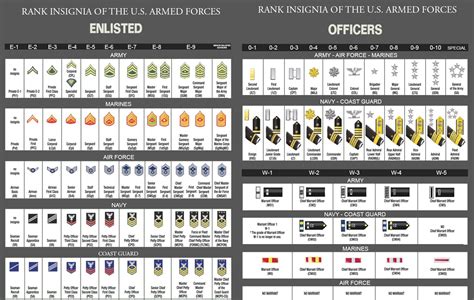
Each rank has its unique insignia, which are worn on the uniform to denote the soldier’s rank. Promotion through the ranks is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, time in grade, performance evaluations, and completion of specific training and education requirements.
👮 Note: The specific requirements for promotion can vary between the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard, and may also depend on the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) or Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC) of the individual.
Comparison with Regular Army and Air Force Ranks

The ranks in the National Guard are largely comparable to those in the regular Army and Air Force, with minor differences in insignia or responsibilities due to the unique nature of the National Guard’s mission and structure. Members of the National Guard can be called to active duty in times of war or national emergency, at which point they are integrated into the regular military structure.
Table of Ranks

| Enlisted Ranks | Warrant Officer Ranks | Officer Ranks |
|---|---|---|
| Private (PVT) - Sergeant Major (SGM) | Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) - Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) | Second Lieutenant (2LT) - General (GEN) |
| Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - Command Sergeant Major (CSM) | Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) - Lieutenant General (LTG) |

In summary, the National Guard ranks reflect a structured hierarchy similar to the regular armed forces, with each rank denoting a specific level of responsibility, expertise, and leadership. Understanding these ranks is crucial for both members of the National Guard and the general public, as it provides insight into the organization and operation of this vital component of the U.S. military.
As we reflect on the structure and ranks within the National Guard, it’s clear that each rank, from Private to General, plays a vital role in the defense and security of the nation. Whether serving part-time or being called to active duty, the men and women of the National Guard embody the values of service, duty, and patriotism.
What is the primary role of the National Guard?

+
The National Guard plays a dual role, supporting both state and federal authorities. It can be called upon for domestic emergencies and disasters, as well as for overseas deployments in support of national defense.
How do promotions work in the National Guard?
+
Promotions in the National Guard are based on a combination of factors including time in service, performance evaluations, completion of specific training and education requirements, and vacancies in the higher rank.
Can National Guard members be deployed overseas?

+
Yes, National Guard members can be deployed overseas in support of national defense operations. When deployed, they are integrated into the regular military structure and operate under the same chain of command as active duty personnel.
Related Terms:
- Military ranks in order
- Sergeant rank
- Military rank in the world
- U S military ranks
- Military rank 2024
- Military rank 1960



