Naval Enlisted Rank Structure Explained
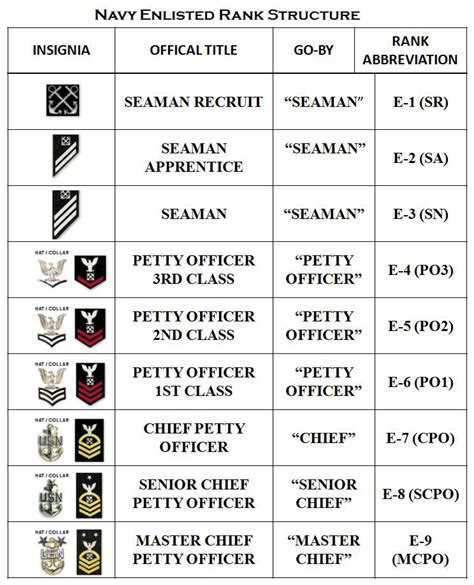
Introduction to Naval Enlisted Rank Structure

The naval enlisted rank structure is a hierarchical system that defines the roles, responsibilities, and pay grades of enlisted personnel in the navy. It is designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize the skills, experience, and leadership abilities of individual sailors. In this article, we will explore the different ranks in the naval enlisted rank structure, their corresponding pay grades, and the responsibilities associated with each rank.
Enlisted Ranks in the Navy
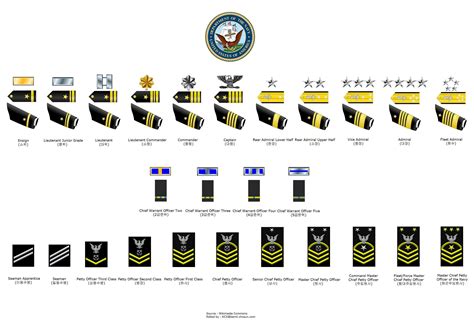
The naval enlisted rank structure consists of nine pay grades, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements. The ranks are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted. The following are the enlisted ranks in the navy, from lowest to highest: * Seaman Recruit (E-1) * Seaman Apprentice (E-2) * Seaman (E-3) * Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) * Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) * Petty Officer First Class (E-6) * Chief Petty Officer (E-7) * Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8) * Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9)
Junior Enlisted Ranks
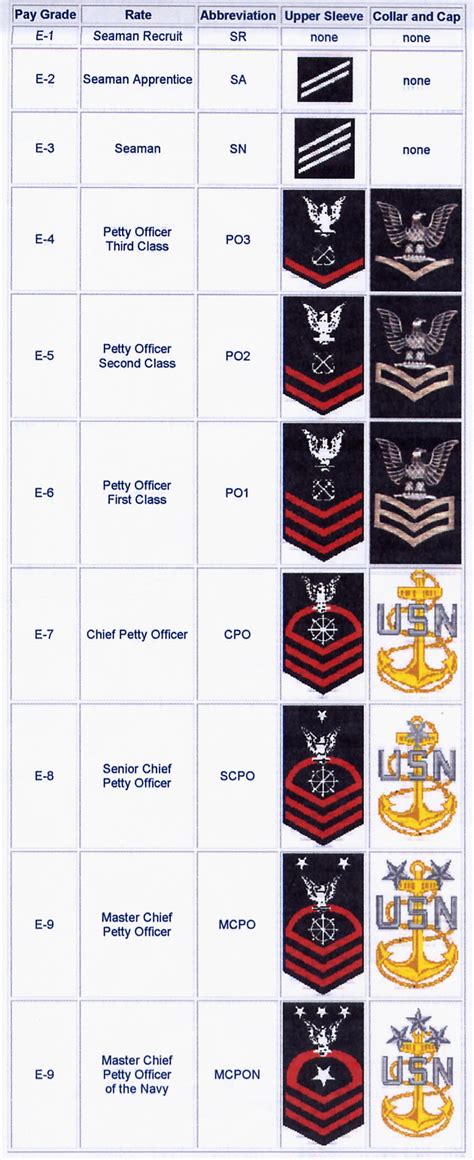
The junior enlisted ranks are the entry-level positions in the navy. These ranks are typically held by new recruits who are still in training or have just completed their initial training. The junior enlisted ranks are: * Seaman Recruit (E-1): This is the lowest rank in the navy, typically held by new recruits who are still in boot camp. * Seaman Apprentice (E-2): This rank is typically held by sailors who have completed their initial training and are assigned to a ship or unit. * Seaman (E-3): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained some experience and have demonstrated their ability to perform their duties effectively.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
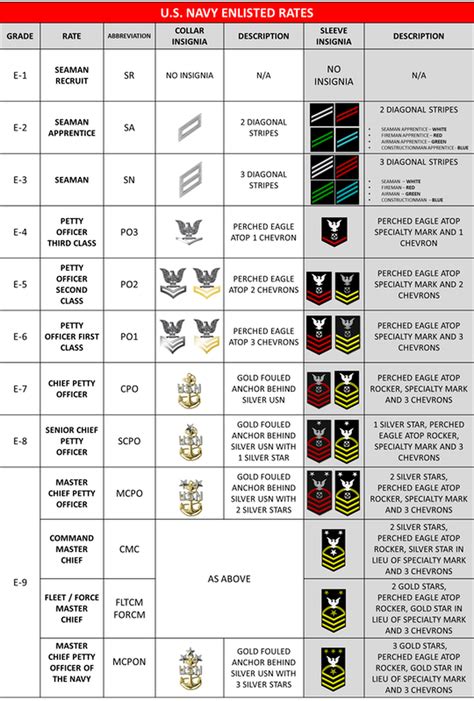
The NCO ranks are the backbone of the navy’s leadership structure. These ranks are typically held by experienced sailors who have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage others. The NCO ranks are: * Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained significant experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead small teams. * Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained even more experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead larger teams. * Petty Officer First Class (E-6): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained a high level of experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage complex teams.
Senior Enlisted Ranks
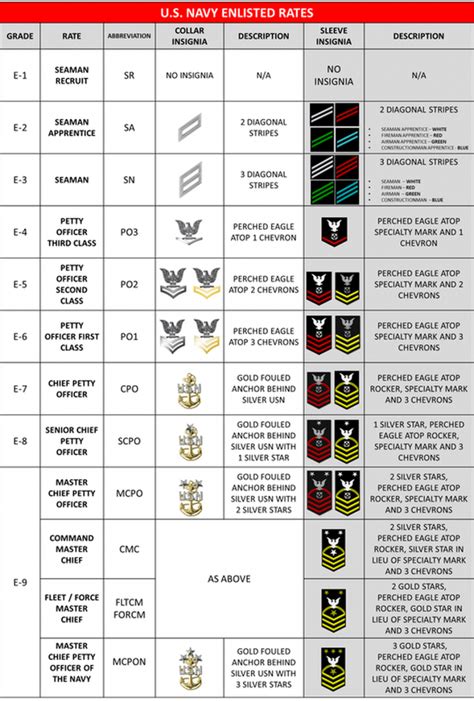
The senior enlisted ranks are the highest ranks in the navy’s enlisted rank structure. These ranks are typically held by highly experienced sailors who have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage at the highest levels. The senior enlisted ranks are: * Chief Petty Officer (E-7): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained a very high level of experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage large teams. * Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): This rank is typically held by sailors who have gained an extremely high level of experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage at the highest levels. * Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): This is the highest rank in the navy’s enlisted rank structure, typically held by sailors who have gained an exceptional level of experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage at the very highest levels.
Responsibilities and Requirements

Each rank in the naval enlisted rank structure has its own set of responsibilities and requirements. Leadership and management skills are essential for advancement, as well as technical expertise and communication skills. The following are some of the key responsibilities and requirements for each rank: * Junior enlisted ranks: Focus on learning and developing their skills, following orders, and performing their duties effectively. * NCO ranks: Focus on leading and managing teams, developing their technical expertise, and communicating effectively with their superiors and subordinates. * Senior enlisted ranks: Focus on leading and managing at the highest levels, developing their strategic thinking and problem-solving skills, and communicating effectively with senior leaders.
Pay Grades and Benefits
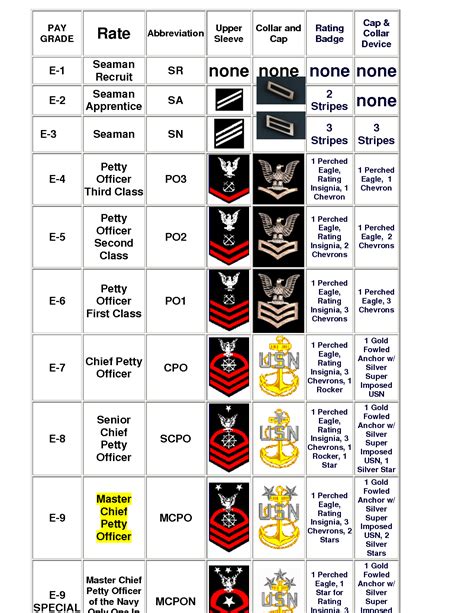
The naval enlisted rank structure is also associated with different pay grades and benefits. The pay grades range from E-1 to E-9, with each rank corresponding to a specific pay grade. The following is a table showing the pay grades and corresponding ranks:
| Pay Grade | Rank |
|---|---|
| E-1 | Seaman Recruit |
| E-2 | Seaman Apprentice |
| E-3 | Seaman |
| E-4 | Petty Officer Third Class |
| E-5 | Petty Officer Second Class |
| E-6 | Petty Officer First Class |
| E-7 | Chief Petty Officer |
| E-8 | Senior Chief Petty Officer |
| E-9 | Master Chief Petty Officer |
In addition to pay, the navy also offers a range of benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance.
📝 Note: The naval enlisted rank structure is subject to change, and the information provided in this article may not reflect the current rank structure or pay grades.
In summary, the naval enlisted rank structure is a hierarchical system that defines the roles, responsibilities, and pay grades of enlisted personnel in the navy. It is designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize the skills, experience, and leadership abilities of individual sailors. By understanding the different ranks, responsibilities, and requirements, sailors can navigate the rank structure and advance in their careers.
What is the lowest rank in the navy?

+
The lowest rank in the navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1), which is typically held by new recruits who are still in boot camp.
What is the highest rank in the navy’s enlisted rank structure?

+
The highest rank in the navy’s enlisted rank structure is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9), which is typically held by sailors who have gained an exceptional level of experience and have demonstrated their ability to lead and manage at the very highest levels.
What are the benefits of advancing in the naval enlisted rank structure?
+
The benefits of advancing in the naval enlisted rank structure include higher pay, greater responsibility, and increased opportunities for leadership and professional development. Additionally, advancing in rank can also lead to increased benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance.
Related Terms:
- navy enlisted rates list
- us navy rank structure chart
- navy military rankings in order
- navy rates and ranks chart
- us navy enlisted rates
- us naval rank chart



