Navy Chain of Command Ranks Explained
Introduction to Navy Chain of Command Ranks
The Navy chain of command is a hierarchical structure that defines the line of authority and responsibility within the naval forces. Understanding the different ranks and their roles is essential for effective communication, coordination, and execution of naval operations. In this article, we will delve into the various ranks of the Navy chain of command, exploring their responsibilities, duties, and areas of expertise.
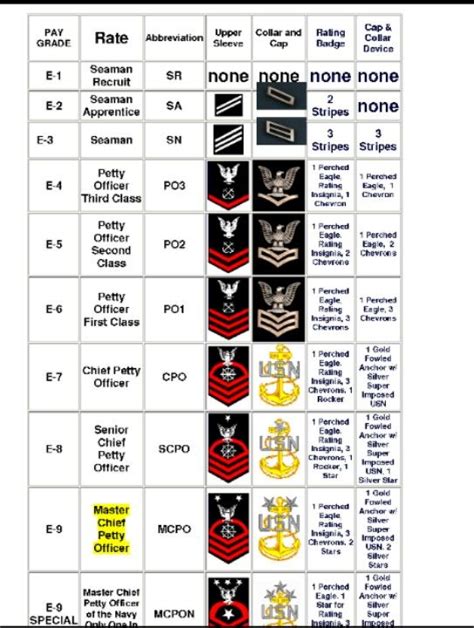
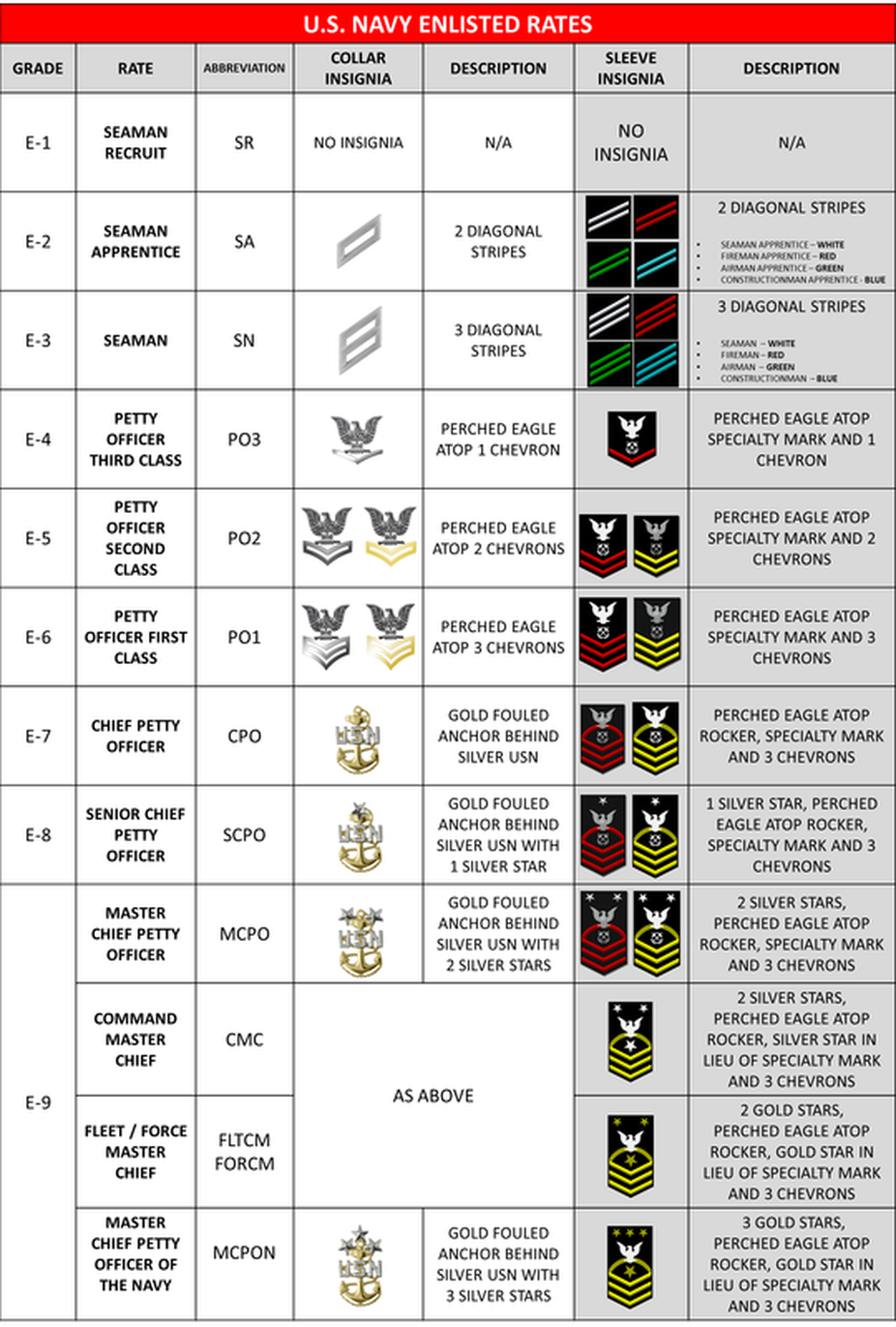
Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Navy, comprising the majority of personnel. These ranks are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted.
- Junior Enlisted Ranks:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The entry-level rank, responsible for basic tasks and training.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): Assists in various tasks, such as maintenance and repairs.
- Seaman (E-3): Performs specific duties, like navigation and communication.
- Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks:
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): Leads a team, provides guidance, and performs specialized tasks.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): Oversees multiple teams, develops training programs, and assumes more significant responsibilities.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): Serves as a senior leader, mentor, and expert in their field.
- Senior Enlisted Ranks:
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): Provides technical expertise, leadership, and guidance to junior personnel.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): Assumes senior leadership roles, develops policies, and advises commanding officers.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): The highest enlisted rank, responsible for advising senior officers, developing strategies, and leading large-scale operations.
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts who have risen through the enlisted ranks and possess specialized knowledge and skills.
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): A technical expert in a specific field, such as aviation or engineering.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): Leads teams, develops training programs, and provides technical guidance.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): Serves as a senior technical expert, advisor, and leader.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): Assumes senior leadership roles, develops policies, and advises commanding officers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): The highest warrant officer rank, responsible for providing strategic guidance, developing doctrine, and leading large-scale operations.
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers are responsible for leading and commanding naval units, ships, and personnel.
- Ensign (O-1): The entry-level commissioned officer rank, responsible for basic leadership and training.
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2): Assists in leadership roles, develops training programs, and performs specific duties.
- Lieutenant (O-3): Leads teams, develops strategies, and assumes more significant responsibilities.
- Lieutenant Commander (O-4): Serves as a senior leader, advisor, and expert in their field.
- Commander (O-5): Assumes senior leadership roles, develops policies, and advises commanding officers.
- Captain (O-6): The highest commissioned officer rank, responsible for commanding ships, units, and leading large-scale operations.
Flag Officer Ranks
Flag officers are senior leaders who have achieved the highest ranks in the Navy.
- Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7): A one-star flag officer, responsible for leading smaller fleets and task forces.
- Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (O-8): A two-star flag officer, responsible for leading larger fleets and task forces.
- Vice Admiral (O-9): A three-star flag officer, responsible for leading major fleets and task forces.
- Admiral (O-10): The highest flag officer rank, responsible for leading the entire Navy and advising the Secretary of the Navy.
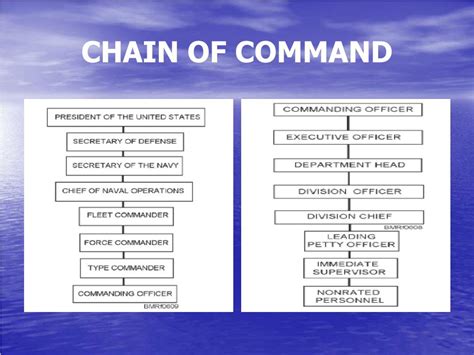
Chain of Command Structure

The Navy chain of command is structured as follows:
| Rank | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Enlisted | Performs specific duties, leads teams |
| Warrant Officer | Provides technical expertise, leads teams |
| Commissioned Officer | Leads units, develops strategies |
| Flag Officer | Leads fleets, task forces, and the Navy |
💡 Note: Understanding the chain of command is crucial for effective communication and coordination within the Navy.
In conclusion, the Navy chain of command is a complex hierarchy that requires a deep understanding of the various ranks, responsibilities, and duties. By recognizing the roles and expertise of each rank, naval personnel can work together seamlessly to achieve their objectives and protect national interests.
What is the highest enlisted rank in the Navy?
+
The highest enlisted rank in the Navy is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
What is the difference between a Warrant Officer and a Commissioned Officer?

+
A Warrant Officer is a technical expert who has risen through the enlisted ranks, while a Commissioned Officer is a leader who has been commissioned to command naval units and personnel.
What is the highest rank in the Navy?
+
The highest rank in the Navy is Admiral (O-10), which is a four-star flag officer rank.
Related Terms:
- time in grade requirements navy
- naval chain of command current
- navy echelons explained
- highest ranking enlisted navy
- navy command structure explained
- navy ranks highest to lowest



