Contract Army Option 4 Explained

Introduction to Contract Army Options

The concept of a contract army has gained significant attention in recent years, especially with the rise of private military companies (PMCs) and the increasing complexity of modern warfare. Among the various options available, Contract Army Option 4 is a unique and intriguing approach that has sparked debate among military strategists and policymakers. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of Contract Army Option 4, exploring its key components, advantages, and challenges.
What is Contract Army Option 4?
Contract Army Option 4 refers to a specific model of outsourcing military services, where a private company is contracted to provide a comprehensive range of military capabilities, including combat troops, logistics, and support services. This option is distinct from other contract army models, which may focus on specific services such as security guarding or training. Under Option 4, the private company is responsible for recruiting, training, and deploying military personnel, as well as providing equipment and supplies.
Key Components of Contract Army Option 4

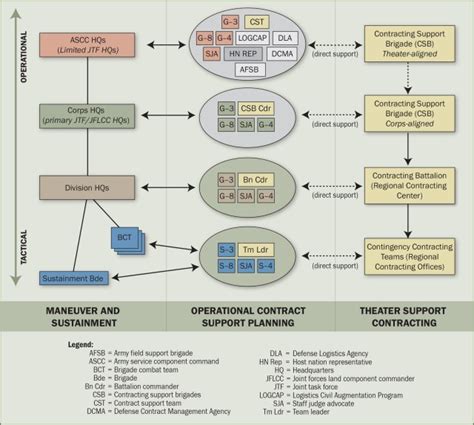
The key components of Contract Army Option 4 include: * Private Military Company (PMC): A private company that provides military services, including combat troops, logistics, and support services. * Contractual Agreement: A binding contract between the government and the PMC, outlining the terms and conditions of the agreement, including the scope of work, payment terms, and performance metrics. * Comprehensive Services: The PMC provides a comprehensive range of military capabilities, including combat troops, logistics, and support services. * Equipment and Supplies: The PMC is responsible for providing equipment and supplies, including weapons, ammunition, and vehicles.
Advantages of Contract Army Option 4

The advantages of Contract Army Option 4 include: * Cost Savings: Outsourcing military services to a private company can result in significant cost savings, as the government does not have to bear the costs of recruiting, training, and deploying military personnel. * Flexibility: Contract Army Option 4 allows for greater flexibility in responding to changing military requirements, as the private company can quickly scale up or down to meet emerging needs. * Access to Specialized Skills: Private companies may have access to specialized skills and expertise that are not readily available within the military, such as advanced technologies or linguistic capabilities. * Reduced Risk: By outsourcing military services, the government can reduce its risk exposure, as the private company assumes responsibility for the safety and security of its personnel.
Challenges of Contract Army Option 4

Despite the advantages, Contract Army Option 4 also poses several challenges, including: * Accountability: Ensuring accountability and oversight of private military companies can be challenging, particularly in complex and dynamic operational environments. * Regulatory Framework: The lack of a clear regulatory framework governing the use of private military companies can create uncertainty and ambiguity. * Public Perception: The use of private military companies can be controversial, and may be perceived as mercenaries or profiteers. * Integration: Integrating private military companies into existing military structures and systems can be challenging, requiring significant coordination and planning.
💡 Note: The use of private military companies is subject to various laws and regulations, including the Montreux Document and the International Code of Conduct for Private Security Service Providers.
Real-World Examples of Contract Army Option 4

There are several real-world examples of Contract Army Option 4, including: * Blackwater USA: A private military company that provided security services in Iraq and Afghanistan. * DynCorp International: A private military company that provided logistics and support services in Iraq and Afghanistan. * Academi: A private military company that provided training and advisory services in Iraq and Afghanistan.
| Company | Services Provided | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Blackwater USA | Security Services | Iraq and Afghanistan |
| DynCorp International | Logistics and Support Services | Iraq and Afghanistan |
| Academi | Training and Advisory Services | Iraq and Afghanistan |

In summary, Contract Army Option 4 is a unique approach to outsourcing military services, where a private company provides a comprehensive range of military capabilities. While this option offers several advantages, including cost savings and flexibility, it also poses significant challenges, including accountability and regulatory framework. As the use of private military companies continues to evolve, it is essential to carefully consider the implications and potential consequences of Contract Army Option 4.
What is the main difference between Contract Army Option 4 and other contract army models?

+
The main difference between Contract Army Option 4 and other contract army models is the comprehensive range of military capabilities provided by the private company, including combat troops, logistics, and support services.
What are the advantages of using Contract Army Option 4?

+
The advantages of using Contract Army Option 4 include cost savings, flexibility, access to specialized skills, and reduced risk.
What are the challenges of using Contract Army Option 4?
+
The challenges of using Contract Army Option 4 include accountability, regulatory framework, public perception, and integration.
Related Terms:
- army re enlistment options
- option 4 mos contract linked
- reenlistment options army
- national guard 4 year contract
- us army enlistment options
- army enlistment contract online