5 Facts P38 Lightning

Introduction to the P-38 Lightning

The P-38 Lightning was a revolutionary fighter aircraft used by the United States during World War II. Its unique design and capabilities made it one of the most recognizable and feared planes of its time. Here are five key facts about the P-38 Lightning that highlight its significance in aviation history.
Design and Development

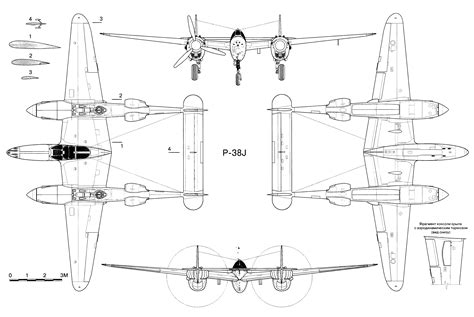
The P-38 was designed by Clarence “Kelly” Johnson, a renowned engineer at Lockheed. It was the first fighter to use a twin-engine and twin-boom design, which provided exceptional stability, maneuverability, and firepower. The aircraft’s development began in 1937, and it first flew in 1939. The innovative design featured a central nacelle that housed the cockpit and armament, with two booms extending back to the tail, each containing an engine.
Operational History

The P-38 Lightning saw extensive service in various theaters of World War II, including the European, Mediterranean, and Pacific theaters. It was used for fighter, attack, and reconnaissance missions. The P-38 was particularly effective in the Pacific, where its long range and heavy firepower made it an ideal platform for intercepting Japanese bombers and fighters. The aircraft’s operational ceiling was over 40,000 feet, allowing it to engage enemy planes at high altitudes.
Specifications and Performance

The P-38 Lightning had a top speed of over 400 mph and a range of approximately 3,000 miles. It was powered by two Allison V-1710 engines, each producing 1,600 horsepower. The aircraft was heavily armed, with a combination of machine guns and a 20mm cannon. The P-38’s exceptional performance and firepower made it a formidable opponent in dogfighting and ground attack missions.
Tactical Advantages

The P-38 Lightning offered several tactical advantages over its contemporaries. Its twin-engine design provided redundancy in case one engine was damaged, allowing the pilot to return to base safely. The aircraft’s long range enabled it to escort bombers deep into enemy territory and engage enemy fighters at extended distances. Additionally, the P-38’s heavy firepower made it an effective ground attack platform, capable of delivering significant damage to enemy installations and troop concentrations.
Legacy and Impact

The P-38 Lightning played a significant role in the Allied victory in World War II. Its unique design and capabilities influenced the development of future fighter aircraft. The P-38’s twin-boom design was later adopted in other aircraft, such as the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star. The aircraft’s legacy extends beyond its military service, as it has become an iconic symbol of American aviation and a popular subject among model builders and enthusiasts.
💡 Note: The P-38 Lightning's development and operational history are a testament to the innovative spirit and engineering prowess of the Lockheed team, led by Clarence "Kelly" Johnson.
In summary, the P-38 Lightning was a groundbreaking fighter aircraft that played a crucial role in World War II. Its unique design, exceptional performance, and heavy firepower made it a formidable opponent in the skies, and its legacy continues to inspire aviation enthusiasts and historians today.
What was the primary role of the P-38 Lightning in World War II?
+
The primary role of the P-38 Lightning was as a fighter aircraft, although it was also used for attack and reconnaissance missions.
What was the top speed of the P-38 Lightning?
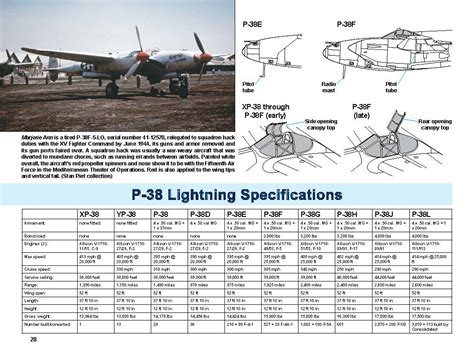
+
The top speed of the P-38 Lightning was over 400 mph.
What was the unique feature of the P-38 Lightning’s design?

+
The P-38 Lightning had a twin-boom design, with two engines and a central nacelle that housed the cockpit and armament.
Related Terms:
- P 47 Thunderbolt
- p 51 mustang
- P38 Lightning
- F4U Corsair
- p 36 hawk
- P38 pistol



