Population Health Defined

Introduction to Population Health

Population health refers to the interdisciplinary approach that focuses on improving the health and well-being of a specific population. This concept goes beyond the traditional healthcare delivery system, which often focuses on treating individual patients. Population health involves analyzing and addressing the various factors that affect the health of a group of people, including social determinants, environmental factors, and healthcare systems. The goal of population health is to prevent illnesses, promote healthy behaviors, and improve health outcomes for the entire population.
Key Components of Population Health
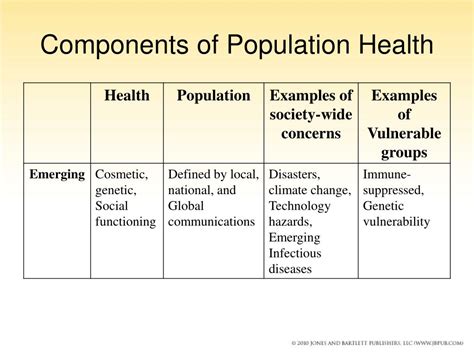
The key components of population health include: * Health outcomes: This refers to the results of healthcare interventions, such as reduced mortality rates, improved quality of life, and reduced disease burden. * Health disparities: This involves identifying and addressing the differences in health outcomes between different populations, such as racial and ethnic minorities, rural communities, and low-income populations. * Social determinants: This includes factors such as education, housing, employment, and access to healthcare, which can affect the health and well-being of a population. * Healthcare systems: This refers to the organizations and structures that provide healthcare services, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers. * Prevention and promotion: This involves interventions aimed at preventing illnesses and promoting healthy behaviors, such as vaccination programs, health education, and disease screening.
Population Health Strategies
Effective population health strategies involve a multi-faceted approach that includes: * Data analysis: This involves collecting and analyzing data on health outcomes, health disparities, and social determinants to identify areas for improvement. * Community engagement: This involves working with community leaders, organizations, and residents to develop and implement health improvement initiatives. * Healthcare system redesign: This involves reorganizing healthcare systems to focus on prevention, promotion, and population health management. * Policy development: This involves creating and implementing policies that support population health, such as laws and regulations that promote healthy behaviors and access to healthcare. * Collaboration and partnership: This involves working with various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, community organizations, and government agencies, to develop and implement population health initiatives.
Benefits of Population Health

The benefits of population health include: * Improved health outcomes: By focusing on prevention and promotion, population health initiatives can improve health outcomes and reduce the burden of disease. * Reduced healthcare costs: By preventing illnesses and promoting healthy behaviors, population health initiatives can reduce healthcare costs and improve the efficiency of healthcare systems. * Increased access to healthcare: Population health initiatives can improve access to healthcare, particularly for underserved populations. * Enhanced community engagement: Population health initiatives can foster community engagement and empowerment, leading to a greater sense of ownership and responsibility for health improvement.
Challenges in Implementing Population Health
Despite the benefits of population health, there are several challenges to implementing population health initiatives, including: * Limited resources: Implementing population health initiatives can require significant resources, including funding, personnel, and infrastructure. * Complexity of social determinants: Addressing social determinants can be complex and require a deep understanding of the underlying factors that affect health outcomes. * Limited data and analytics: Collecting and analyzing data on health outcomes and social determinants can be challenging, particularly in resource-constrained settings. * Resistance to change: Implementing population health initiatives can require significant changes to healthcare systems and community norms, which can be met with resistance from stakeholders.
🚨 Note: Effective population health initiatives require a deep understanding of the complex factors that affect health outcomes and a willingness to collaborate and partner with various stakeholders.
Population Health in Practice
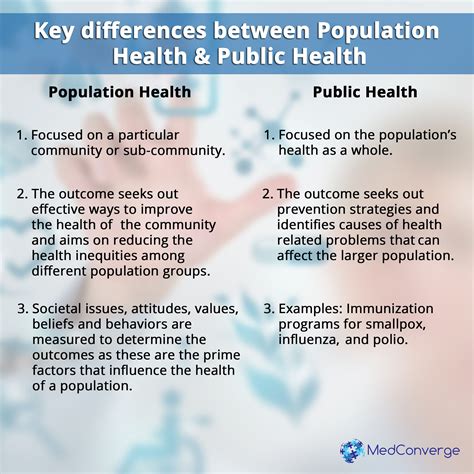
Population health initiatives are being implemented in various settings, including: * Community health centers: These centers provide primary care services and often serve as a hub for population health initiatives. * Hospitals and health systems: These organizations are increasingly focusing on population health management and are implementing initiatives to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. * Government agencies: Government agencies are playing a critical role in promoting population health, particularly through policy development and funding for population health initiatives. * Non-profit organizations: Non-profit organizations are often at the forefront of population health initiatives, particularly in areas such as health education and community engagement.
| Population Health Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination programs | Programs aimed at increasing vaccination rates and preventing infectious diseases |
| Health education programs | Programs aimed at promoting healthy behaviors and improving health literacy |
| Disease screening programs | Programs aimed at early detection and treatment of diseases, such as cancer and diabetes |

In summary, population health is a critical approach to improving the health and well-being of populations. By focusing on prevention, promotion, and population health management, we can improve health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance community engagement. While there are challenges to implementing population health initiatives, the benefits are clear, and it is essential that we continue to work towards improving the health and well-being of populations.
What is population health?
+
Population health refers to the interdisciplinary approach that focuses on improving the health and well-being of a specific population.
What are the key components of population health?

+
The key components of population health include health outcomes, health disparities, social determinants, healthcare systems, and prevention and promotion.
What are the benefits of population health?
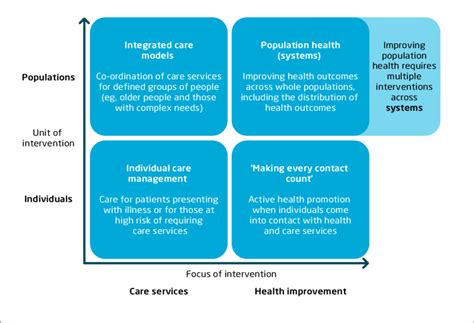
+
The benefits of population health include improved health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, increased access to healthcare, and enhanced community engagement.
Related Terms:
- population health explained
- 10 components of population health
- individual vs population health
- why is population health important
- four pillars of population health



