5 Ways Marines Get Paid

Introduction to Marine Compensation

Marines, like all members of the US Armed Forces, receive a comprehensive compensation package that includes more than just their basic pay. The compensation for Marines is designed to reflect their service, sacrifices, and the unique challenges they face. Understanding the different components of a Marine’s pay can help clarify the overall value of their compensation package. This article will explore the primary ways Marines get paid, highlighting the various elements that contribute to their total compensation.
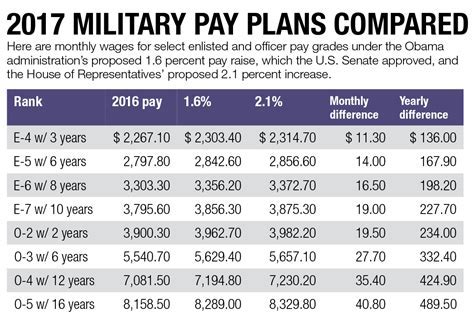
Basic Pay
Basic Pay is the fundamental component of a Marine’s compensation. It is the monthly salary paid to Marines based on their rank and time in service. Basic Pay increases with promotions in rank and years of service, providing a steady increase in income as a Marine advances in their career. The amount of Basic Pay is determined by the Department of Defense and is adjusted annually to reflect cost-of-living increases.
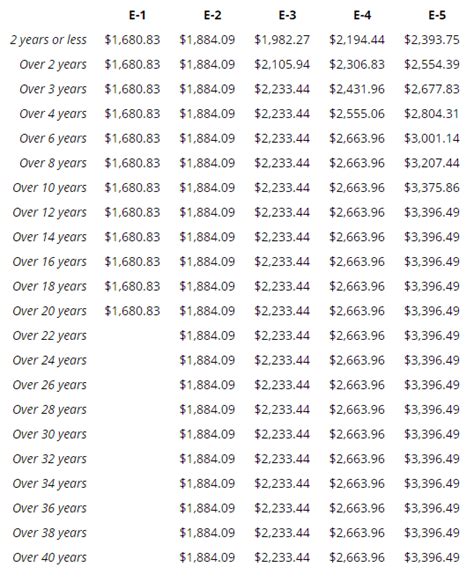
Allowances
Allowances are another critical component of a Marine’s pay. These are monies provided to help offset the costs of specific expenses that Marines may incur due to their service. Key allowances include: - Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): Paid to Marines who do not live in government-provided housing, BAH helps cover the cost of rent or mortgage, utilities, and maintenance. - Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): Intended to offset the cost of food, BAS is paid to all Marines, regardless of whether they live on or off base. - Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): Paid in areas with a high cost of living, COLA helps Marines keep up with local price increases for goods and services.
Special and Incentive Pay

Special and incentive pays are additional forms of compensation that recognize specific skills, duties, or circumstances. Examples include: - Hazardous Duty Pay: Paid for duties that involve unusual danger, such as parachuting or handling explosives. - Special Duty Pay: For assignments that require unusual effort or dedication, like serving in a special operations unit. - Enlistment Bonuses: One-time payments made to new recruits for enlisting in specific Military Occupational Specialties (MOS) that are in high demand. - Retention Bonuses: Paid to Marines who reenlist in critical MOS, encouraging them to continue their service.
Bonuses and Incentives

Bonuses and incentives are used to attract and retain talent in specific areas. They can be particularly lucrative for Marines in high-demand fields or those undertaking special assignments. These include: - Sign-on Bonuses: For new Marines entering specific fields, these bonuses provide an upfront payment for committing to serve. - Reenlistment Bonuses: As mentioned, these are incentives for Marines to extend their service, especially in specialties where the military faces retention challenges. - Officer Commissioning Bonuses: Some programs, like the Officer Candidate School (OCS), may offer bonuses for individuals commissioning as officers in certain fields.
Benefits and Privileges

Beyond monetary compensation, Marines receive a range of benefits and privileges that significantly enhance their quality of life and the value of their service. These include: - Healthcare: Comprehensive medical, dental, and pharmacy coverage for Marines and their families through TRICARE. - Education Assistance: Programs like the GI Bill and Tuition Assistance help Marines pursue higher education or vocational training. - On-Base Facilities: Access to gyms, pools, commissaries, and exchanges, which offer discounted prices on groceries and goods. - Travel Benefits: Space-available flights and lodging discounts can make travel more affordable for Marines and their families.
📝 Note: The specifics of Marine compensation, including pay scales, allowances, and benefits, can change over time due to legislative actions, budget decisions, and policy updates. Always consult the most current resources for the latest information.
In summary, the compensation for Marines is multifaceted, including Basic Pay, allowances, special and incentive pays, bonuses, and a range of benefits and privileges. Each component is designed to recognize the unique aspects of Marine service, from the dangers and difficulties of certain duties to the personal sacrifices made by Marines and their families. Understanding these elements can provide a clearer picture of the total value of serving in the Marine Corps.
How often do Marines receive pay raises?
+
Marines, like all military personnel, receive pay raises as part of annual budget approvals. These raises are typically cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) aimed at keeping pace with inflation.
Do all Marines receive the same allowances?
+
No, allowances can vary based on the Marine’s rank, dependency status, duty location, and whether they are married or have dependents. For example, Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) rates differ by location to reflect local housing costs.
Can Marines use their education benefits at any school?

+
While the GI Bill and other education benefits offer a wide range of educational opportunities, not all schools participate in these programs. Marines should check with the school they’re interested in to confirm it is a participating institution.
Related Terms:
- Private first class pay grade
- PFC pay every 2 weeks
- Private pay Army
- Private First Class Army
- USMC Sgt Pay
- Lance Corporal Marines



