5 Ways Army Navy Ranks Compare
Introduction to Army and Navy Ranks
The military is a complex and hierarchical institution, with various branches, each having its own set of ranks and insignia. Two of the most prominent branches are the Army and the Navy. While both branches have their own unique ranking systems, there are some similarities and differences between them. In this article, we will explore the comparison between Army and Navy ranks, highlighting the similarities and differences between the two.
Similarities Between Army and Navy Ranks

Both the Army and Navy have a hierarchical ranking system, with enlisted personnel, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and commissioned officers. The ranks are divided into several categories, including: * Enlisted personnel: These are the entry-level ranks, which include privates, seamen, and airmen. * Non-commissioned officers (NCOs): These are the mid-level ranks, which include corporals, sergeants, and petty officers. * Commissioned officers: These are the high-level ranks, which include lieutenants, captains, and admirals. Both branches also have a system of promotion, where personnel can advance through the ranks based on their performance, experience, and education.
Differences Between Army and Navy Ranks
Despite the similarities, there are also some significant differences between Army and Navy ranks. One of the main differences is the terminology used to describe the ranks. For example: * The Army uses terms such as “private”, “sergeant”, and “lieutenant”, while the Navy uses terms such as “seaman”, “petty officer”, and “ensign”. * The Army has a more complex ranking system, with more ranks and sub-ranks, while the Navy has a more streamlined system. * The Navy also has a unique ranking system for its officers, with a focus on specialized roles such as aviation, engineering, and medicine.
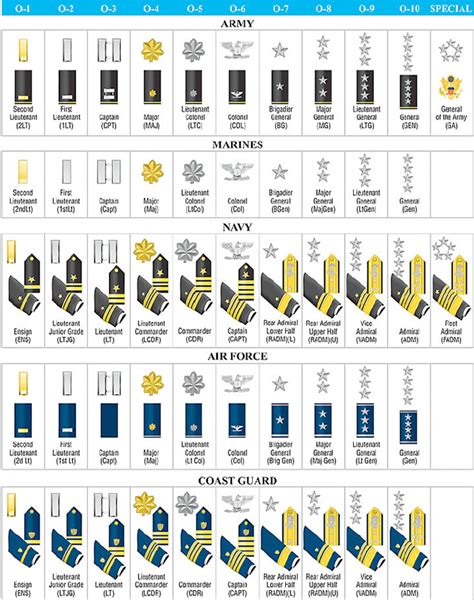
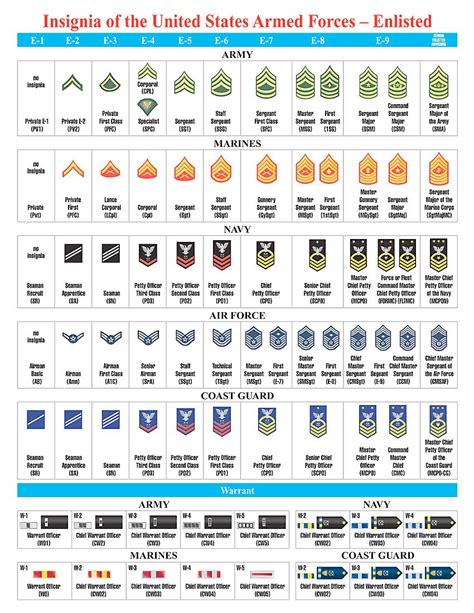
Comparison of Army and Navy Ranks

Here is a comparison of the Army and Navy ranks, from lowest to highest:
| Army Rank | Navy Rank |
|---|---|
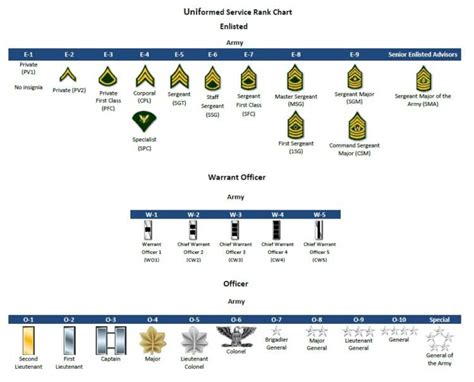
| Private (PVT) | Seaman Recruit (SR) |
| Private First Class (PFC) | Seaman Apprentice (SA) |
| Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) | Petty Officer Third Class (PO3) |
| Sergeant (SGT) | Petty Officer Second Class (PO2) |
| Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Petty Officer First Class (PO1) |
| Sergeant First Class (SFC) | Chief Petty Officer (CPO) |
| Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) | Senior Chief Petty Officer (SCPO) |
| Sergeant Major (SGM) | Master Chief Petty Officer (MCPO) |
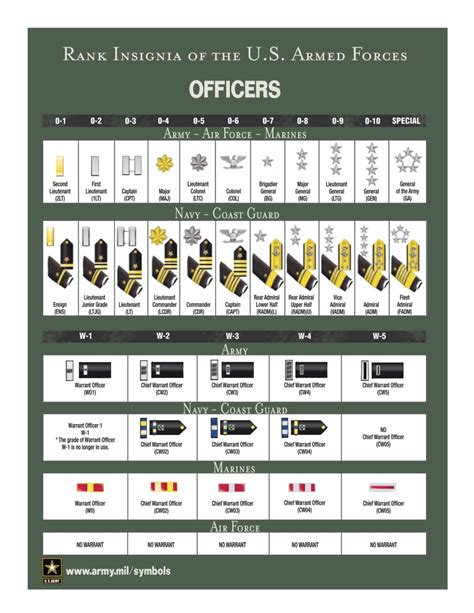
| Second Lieutenant (2LT) | Ensign (ENS) |
| First Lieutenant (1LT) | Lieutenant Junior Grade (LTJG) |
| Captain (CPT) | Lieutenant (LT) |
| Major (MAJ) | Lieutenant Commander (LCDR) |
| Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) | Commander (CDR) |
| Colonel (COL) | Captain (CAPT) |
| Brigadier General (BG) | Rear Admiral Lower Half (RDML) |
| Major General (MG) | Rear Admiral Upper Half (RADM) |
| Lieutenant General (LTG) | Vice Admiral (VA) |
| General (GEN) | Admiral (ADM) |
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, while the Army and Navy have their own unique ranking systems, there are also some similarities between the two. Understanding the differences and similarities between the ranks can help individuals navigate the military hierarchy and make informed decisions about their careers. Some key takeaways from this comparison include: * The Army and Navy have different terminology and ranking systems, but both have a hierarchical structure with enlisted personnel, NCOs, and commissioned officers. * The Navy has a more streamlined ranking system, with a focus on specialized roles, while the Army has a more complex system with more ranks and sub-ranks. * Both branches have a system of promotion, where personnel can advance through the ranks based on their performance, experience, and education.
👀 Note: This comparison is not exhaustive, and there may be additional ranks or variations not included in this article.
The main idea is to provide a general understanding of the comparison between Army and Navy ranks, highlighting the similarities and differences between the two. By understanding these differences, individuals can make informed decisions about their careers and navigate the military hierarchy with confidence.
What is the main difference between Army and Navy ranks?
+
The main difference between Army and Navy ranks is the terminology used to describe the ranks. The Army uses terms such as “private”, “sergeant”, and “lieutenant”, while the Navy uses terms such as “seaman”, “petty officer”, and “ensign”.
How do Army and Navy ranks compare in terms of promotion?
+
Both the Army and Navy have a system of promotion, where personnel can advance through the ranks based on their performance, experience, and education. However, the Navy has a more streamlined ranking system, with a focus on specialized roles, while the Army has a more complex system with more ranks and sub-ranks.
What are the benefits of understanding the comparison between Army and Navy ranks?

+
Understanding the comparison between Army and Navy ranks can help individuals navigate the military hierarchy and make informed decisions about their careers. It can also provide a general understanding of the military structure and the different roles and responsibilities within each branch.
Related Terms:
- Military ranks comparison
- Italian Army rank
- Military rank in the world
- Hungary army ranks
- British Military rank
- South american military ranks