Reservoir Health Example
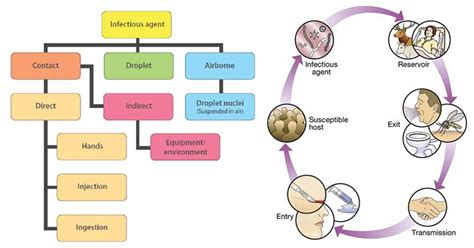
Introduction to Reservoir Health
Reservoir health is a critical aspect of maintaining optimal water quality and ensuring the longevity of reservoirs. A reservoir is a man-made or natural lake that stores water for various purposes, including drinking water supply, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation. The health of a reservoir is influenced by several factors, including water level fluctuations, inflow and outflow rates, water quality parameters, and sedimentation rates. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of reservoir health, exploring its importance, factors that affect it, and strategies for maintaining optimal reservoir health.
Importance of Reservoir Health
Maintaining good reservoir health is essential for ensuring a reliable water supply, supporting aquatic ecosystems, and preventing waterborne diseases. A healthy reservoir provides numerous benefits, including: * Improved water quality: Reduced levels of pollutants, sediments, and nutrients, making the water safer for human consumption and aquatic life. * Increased water storage capacity: Minimized sedimentation and optimal water levels enable the reservoir to store more water, reducing the risk of water shortages during droughts. * Enhanced biodiversity: A healthy reservoir supports a diverse range of aquatic plants and animals, maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. * Reduced maintenance costs: Regular maintenance and monitoring of reservoir health can help prevent costly repairs and prolong the lifespan of the reservoir.
Factors Affecting Reservoir Health

Several factors can impact reservoir health, including: * Water level fluctuations: Changes in water levels can cause erosion, sedimentation, and altered water quality. * Inflow and outflow rates: Excessive inflow or outflow can lead to increased sedimentation, nutrient loading, and altered water quality. * Water quality parameters: High levels of pollutants, nutrients, or sediments can degrade water quality and harm aquatic life. * Sedimentation rates: Excessive sedimentation can reduce water storage capacity, increase maintenance costs, and alter the reservoir’s ecosystem.
Strategies for Maintaining Optimal Reservoir Health
To maintain optimal reservoir health, the following strategies can be employed: * Regular monitoring: Continuous monitoring of water quality, sedimentation rates, and water levels helps identify potential issues before they become major problems. * Sediment management: Implementing sediment management techniques, such as dredging or sediment traps, can help reduce sedimentation rates and maintain water storage capacity. * Water quality management: Implementing best management practices, such as reducing nutrient inputs or using aquatic plants to absorb excess nutrients, can help maintain good water quality. * Habitat restoration: Restoring natural habitats and ecosystems within the reservoir can help maintain biodiversity and support aquatic life.
| Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular monitoring | Early detection of potential issues, reduced maintenance costs |
| Sediment management | Reduced sedimentation rates, maintained water storage capacity |
| Water quality management | Improved water quality, reduced risk of waterborne diseases |
| Habitat restoration | Enhanced biodiversity, maintained ecosystem balance |
💡 Note: Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial for maintaining optimal reservoir health. By implementing these strategies, reservoir managers can help ensure a reliable water supply, support aquatic ecosystems, and prevent waterborne diseases.
As we conclude our discussion on reservoir health, it is essential to remember that maintaining optimal reservoir health requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. By understanding the factors that affect reservoir health and implementing effective strategies, we can ensure the long-term sustainability of our water resources.
What is reservoir health, and why is it important?
+
Reservoir health refers to the condition of a reservoir in terms of its water quality, sedimentation rates, and ecosystem balance. Maintaining good reservoir health is essential for ensuring a reliable water supply, supporting aquatic ecosystems, and preventing waterborne diseases.
What are the primary factors that affect reservoir health?
+
The primary factors that affect reservoir health include water level fluctuations, inflow and outflow rates, water quality parameters, and sedimentation rates. These factors can impact the reservoir’s ecosystem, water quality, and storage capacity.
How can reservoir health be maintained and improved?
+
Reservoir health can be maintained and improved through regular monitoring, sediment management, water quality management, and habitat restoration. These strategies help identify potential issues, reduce sedimentation rates, improve water quality, and support aquatic life.
Related Terms:
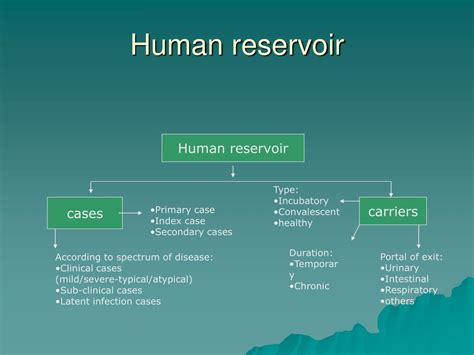
- Human reservoir
- Infectious disease
- Chain of infection
- Source of infection
- difference between reservoir and carrier
- types of reservoirs examples



