5 Ways Sickle Cell Impacts Public Health
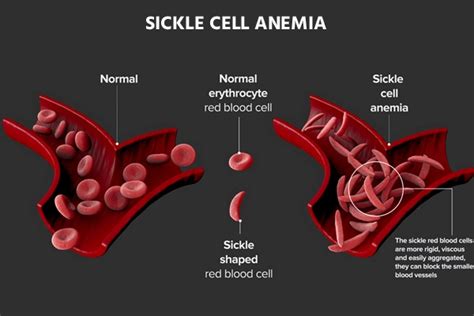
Introduction to Sickle Cell Disease

Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders that affect the hemoglobin in red blood cells. It is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, which codes for the beta-globin subunit of hemoglobin. This mutation leads to the production of abnormal hemoglobin, known as sickle hemoglobin or hemoglobin S. Sickle cell disease is a significant public health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions, where malaria is common. In this post, we will explore the impact of sickle cell disease on public health, highlighting five key areas of concern.
1. Increased Risk of Infections
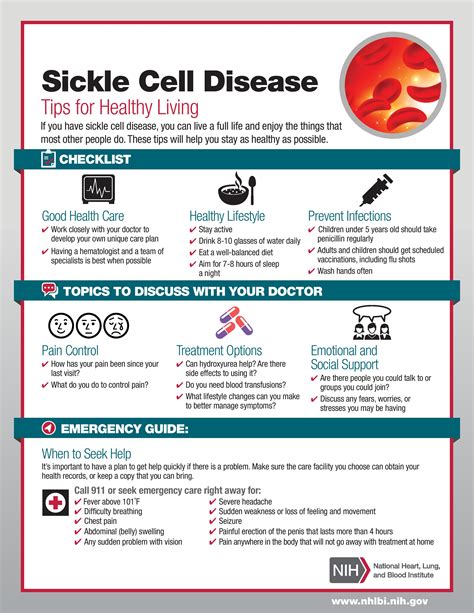
Individuals with sickle cell disease are more susceptible to infections, particularly those caused by encapsulated bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. This increased risk is due to the dysfunction of the spleen, which is responsible for filtering the blood and removing pathogens. In people with SCD, the spleen is often damaged or non-functional, making them more vulnerable to infections. This can lead to a range of complications, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
2. Economic Burden
Sickle cell disease imposes a significant economic burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems. The cost of medical care, including hospitalizations, medications, and other treatments, can be substantial. Additionally, individuals with SCD may experience reduced productivity and lost income due to frequent hospitalizations and sick leave. A study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine estimated that the annual cost of SCD in the United States is approximately $1.1 billion.
3. Psychosocial Impact
Sickle cell disease can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting their physical, emotional, and social well-being. The chronic nature of the disease, combined with the risk of sudden and severe pain episodes, can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress. Furthermore, the stigma associated with SCD can result in social isolation and discrimination, exacerbating the psychosocial burden. It is essential to address these issues through comprehensive care, including counseling, support groups, and patient education.
4. Healthcare Access and Utilization
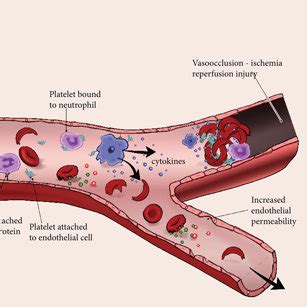
Access to quality healthcare is critical for individuals with sickle cell disease. However, disparities in healthcare access and utilization persist, particularly in low-income and minority communities. Barriers to care include lack of health insurance, limited access to specialist care, and cultural and linguistic barriers. To address these disparities, healthcare systems must prioritize culturally competent care, patient education, and community outreach.
5. Genetic Counseling and Testing
Genetic counseling and testing are essential components of sickle cell disease management. Genetic counseling can help individuals understand their risk of passing the disease to their offspring and inform reproductive decisions. Genetic testing, such as newborn screening, can identify individuals with SCD early in life, enabling prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications. The following table highlights the importance of genetic counseling and testing in SCD management:
| Genetic Testing | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Newborn screening | Early diagnosis and treatment, reduced risk of complications |
| Carrier testing | Identification of carriers, informed reproductive decisions |
| Prenatal testing | Detection of affected fetuses, informed reproductive decisions |
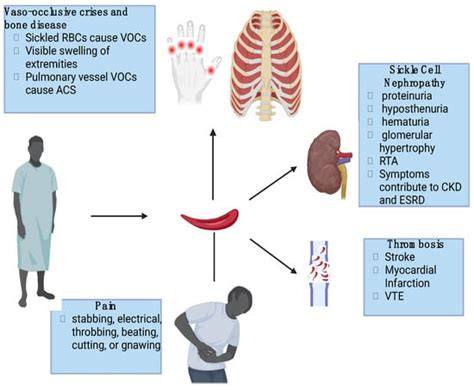
💡 Note: Genetic counseling and testing should be provided in a culturally sensitive and non-directive manner, respecting the individual's autonomy and decision-making capacity.
In summary, sickle cell disease has a significant impact on public health, affecting not only individuals with the disease but also their families and communities. The five areas of concern highlighted in this post – increased risk of infections, economic burden, psychosocial impact, healthcare access and utilization, and genetic counseling and testing – underscore the need for comprehensive and coordinated care. By addressing these challenges and promoting awareness, education, and research, we can improve the health and well-being of individuals with sickle cell disease and reduce the burden on public health.
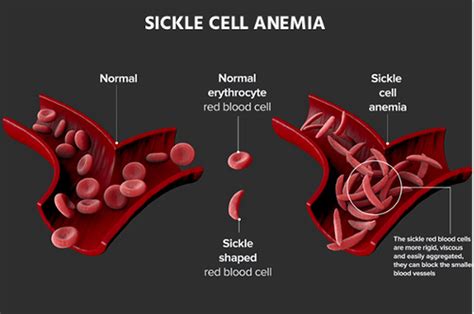
What is sickle cell disease?
+
Sickle cell disease is a group of blood disorders that affect the hemoglobin in red blood cells, causing them to become misshapen and break down.
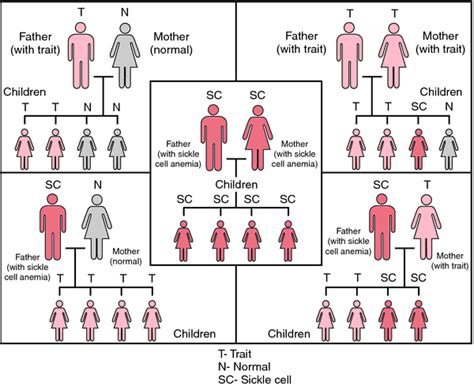
How is sickle cell disease inherited?

+
Sickle cell disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated HBB gene (one from each parent) to express the disease.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
+
The symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary in severity and may include anemia, pain episodes, increased risk of infections, and delayed growth and development.



