Radioceutical Definition

Introduction to Radioceuticals
Radioceuticals, also known as radiopharmaceuticals, are compound substances that contain radioactive isotopes. These isotopes are used in medical applications, primarily for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The term “radioceutical” is less commonly used than “radiopharmaceutical,” but both refer to the same class of substances. The radioactive properties of these compounds allow them to be used in a variety of medical imaging techniques and treatments.
History of Radioceuticals
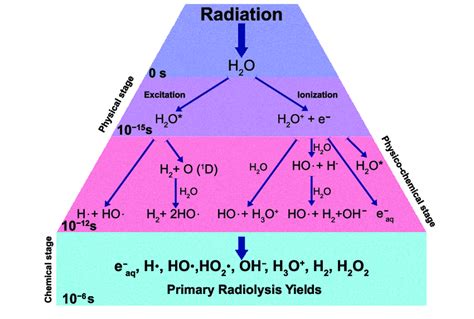
The use of radioactive substances in medicine dates back to the early 20th century, shortly after the discovery of radioactivity by Henri Becquerel in 1896. The first radioceutical application was likely the use of radium for the treatment of cancer in the 1900s. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century, with the development of nuclear reactors and cyclotrons, that a wide range of radioactive isotopes became available for medical use. This led to a significant expansion in the field of nuclear medicine, with radioceuticals playing a central role.
Types of Radioceuticals

There are several types of radioceuticals, each with its own specific medical application. Some of the most common include: - Technetium-99m (Tc-99m): Used in a wide range of diagnostic imaging procedures due to its short half-life and suitable gamma radiation energy. - Iodine-131 (I-131): Often used for the treatment of thyroid cancer and hyperthyroidism due to its ability to selectively target the thyroid gland. - Fluorine-18 (F-18): Incorporated into fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) for use in positron emission tomography (PET) scans, primarily for cancer diagnosis and monitoring. - Samarium-153 (Sm-153): Used for the relief of bone pain associated with osteoblastic metastases.
Production of Radioceuticals

The production of radioceuticals involves several steps, including the creation of the radioactive isotope, its incorporation into a pharmaceutical compound, and quality control measures to ensure the product is safe and effective for medical use. This process can be complex and requires specialized facilities and expertise. Nuclear reactors and cyclotrons are commonly used for the production of radioactive isotopes.
Applications of Radioceuticals
Radioceuticals have a wide range of medical applications, including: - Diagnostic imaging: To visualize specific organs or tissues within the body and diagnose various medical conditions. - Cancer treatment: For the targeted treatment of cancer, reducing the harm to surrounding healthy tissues. - Thyroid disease treatment: For the treatment of thyroid cancer and hyperthyroidism. - Pain management: For the relief of bone pain associated with metastatic cancer.
Benefits and Risks of Radioceuticals

The use of radioceuticals offers several benefits, including the ability to diagnose and treat medical conditions that might be difficult or impossible to manage with other therapies. However, there are also risks associated with radioceutical use, primarily related to radiation exposure. This exposure can increase the risk of secondary cancers and other health problems. Therefore, the use of radioceuticals must be carefully managed to minimize risks while maximizing benefits.
Future of Radioceuticals
The field of radioceuticals is continuously evolving, with ongoing research aimed at developing new and more effective radiopharmaceuticals. Advances in targeted therapy and personalized medicine are expected to play a significant role in the future of radioceutical development. Additionally, improvements in production technologies and regulatory frameworks will be crucial for ensuring the safe and widespread use of radioceuticals in medical practice.
💡 Note: The development and use of radioceuticals are highly regulated due to the potential risks associated with radiation exposure, emphasizing the need for strict safety protocols and regulatory compliance.
In summary, radioceuticals are radioactive substances used in medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Their applications are diverse, ranging from cancer treatment to diagnostic imaging, and they offer significant benefits in the management of various medical conditions. However, their use must be carefully managed to minimize the risks associated with radiation exposure. As research continues to advance, the role of radioceuticals in medicine is likely to expand, offering new and more effective treatments for patients.
What are radioceuticals used for?

+
Radioceuticals are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in medicine, including cancer treatment, diagnostic imaging, and the management of thyroid diseases.
How are radioceuticals produced?

+
Radioceuticals are produced using nuclear reactors and cyclotrons, which create the radioactive isotopes that are then incorporated into pharmaceutical compounds.
What are the benefits and risks of using radioceuticals?
+
The benefits of radioceuticals include their ability to diagnose and treat medical conditions that are difficult to manage with other therapies. However, there are also risks associated with radiation exposure, which can increase the risk of secondary cancers and other health problems.