5 Radiolucent Facts

Introduction to Radiolucent Materials
Radiolucent materials are substances that allow the passage of radiation, such as X-rays, with little to no absorption. These materials are crucial in medical and industrial applications, where the ability to transmit radiation is essential for imaging and inspection purposes. In this article, we will delve into five key facts about radiolucent materials, exploring their properties, applications, and importance in various fields.
Fact 1: Definition and Properties

Radiolucent materials are characterized by their low density and low atomic number, which enable them to transmit radiation with minimal attenuation. Density and atomic number are critical factors in determining a material’s radiolucency. Materials with low density and atomic number, such as plastics, wood, and air, are generally more radiolucent than those with high density and atomic number, like metals and lead. Understanding the properties of radiolucent materials is essential for selecting the appropriate materials for specific applications.
Fact 2: Medical Applications
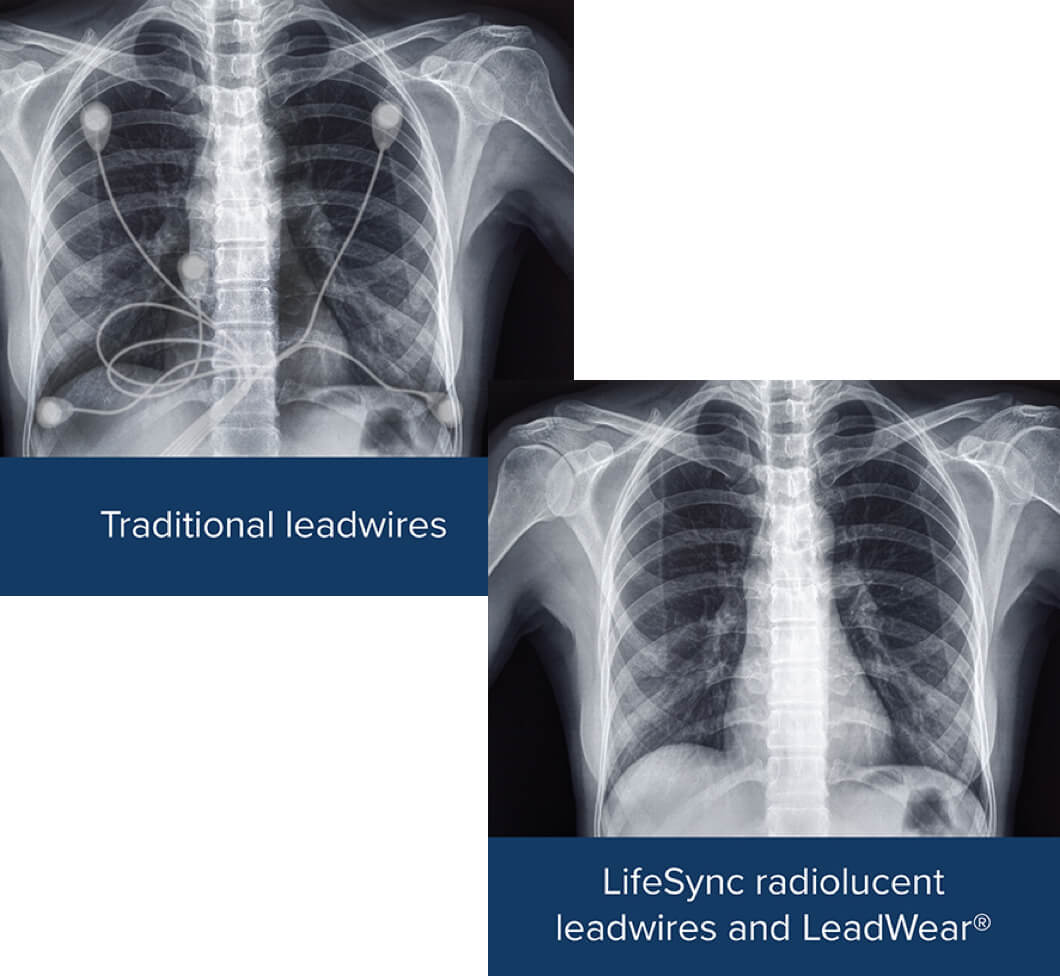
Radiolucent materials play a vital role in medical imaging, particularly in X-ray and computed tomography (CT) scans. In medical applications, radiolucent materials are used to: * Reduce radiation exposure to patients * Improve image quality by minimizing artifacts * Enable the use of lower radiation doses * Facilitate the visualization of internal structures and organs Examples of radiolucent materials used in medical applications include acrylic, polyethylene, and polycarbonate.
Fact 3: Industrial Applications

Radiolucent materials are also used in various industrial applications, including: * Non-destructive testing (NDT): Radiolucent materials are used to inspect the internal structure of components and detect defects or flaws. * Quality control: Radiolucent materials are used to verify the integrity of products and ensure they meet specifications. * Research and development: Radiolucent materials are used to study the properties of materials and develop new technologies. * Security screening: Radiolucent materials are used to inspect luggage, cargo, and personnel for hidden threats.
Fact 4: Comparison of Radiolucent Materials

The following table compares the properties of common radiolucent materials:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Atomic Number | Radiolucency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic | 1.18 | 6 | High |
| Polyethylene | 0.95 | 6 | High |
| Polycarbonate | 1.20 | 6 | High |
| Wood | 0.5-0.8 | 6 | High |
| Air | 0.0012 | 7 | Very High |

This comparison highlights the varying degrees of radiolucency among different materials, which is essential for selecting the most suitable material for a specific application.
Fact 5: Future Developments and Challenges

The development of new radiolucent materials with improved properties is an ongoing area of research. Nanomaterials and composite materials are being explored for their potential to enhance radiolucency while maintaining mechanical strength and durability. However, challenges such as cost, toxicity, and scalability must be addressed before these new materials can be widely adopted.
💡 Note: The development of radiolucent materials with enhanced properties requires a deep understanding of the underlying physics and chemistry, as well as collaboration between materials scientists, engineers, and industry experts.
In summary, radiolucent materials play a vital role in various applications, from medical imaging to industrial inspection. Understanding the properties and characteristics of these materials is essential for selecting the most suitable material for a specific use case. As research and development continue to advance, we can expect to see new and innovative radiolucent materials with improved properties, enabling further advancements in medical and industrial applications.
What is the primary characteristic of radiolucent materials?
+
Radiolucent materials are characterized by their low density and low atomic number, which enable them to transmit radiation with minimal attenuation.
What are some common applications of radiolucent materials in medicine?

+
Radiolucent materials are used in medical imaging, particularly in X-ray and CT scans, to reduce radiation exposure, improve image quality, and enable the visualization of internal structures and organs.
What are some challenges associated with developing new radiolucent materials?

+
Challenges associated with developing new radiolucent materials include cost, toxicity, and scalability, which must be addressed before these materials can be widely adopted.
Related Terms:
- simple healthcare definition of radiolucent
- simple healthcare definition of radiolucent
- Radiopaque vs radiolucent
- Radiolucent examples
- Radiolucent meaning x ray
- Radiodense



